An optimized protocol for analysis of EST sequences - PubMed (original) (raw)
An optimized protocol for analysis of EST sequences
F Liang et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000.
Abstract
The vast body of Expressed Sequence Tag (EST) data in the public databases provide an important resource for comparative and functional genomics studies and an invaluable tool for the annotation of genomic sequences. We have developed a rigorous protocol for reconstructing the sequences of transcribed genes from EST and gene sequence fragments. A key element in developing this protocol has been the evaluation of a number of sequence assembly programs to determine which most faithfully reproduce transcript sequences from EST data. The TIGR Gene Indices constructed using this protocol for human, mouse, rat and a variety of other plant and animal models have demonstrated their utility in a variety of applications and are freely available to the scientific research community.
Figures
Figure 1
DNA sequencing base call error probability. Error probability distribution adapted from Ewing and Green (12) used to simulate systematic base call errors.
Figure 2
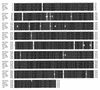
CLUSTAL W (17) alignment of consensus sequence assemblies for the rat cytochrome c oxidase gene produced by Phrap, CAP3, TA-EST and TIGR Assembler.
Figure 3
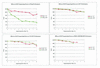
Consensus sequence errors. Plot of A-scores for the best consensus assemblies produced by Phrap, CAP3, TA-EST and TIGR Assembler (TA) using simulated data for various error rates at 5× and 50× sequence coverage.
Figure 4
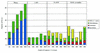
Error source distribution and normalized A-score for assemblies of 73 known genes. Consensus sequence error classification for Phrap, CAP3, TA-EST and TIGR Assembler using EST sequences containing 5% errors at various depths of coverage.
Figure 5
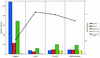
DNA sequencing base call error probability. The total number of errors, classified by type, in the best assembly produced by the four assemblers and the normalized A-score for 73 known genes.
Similar articles
- The TIGR Gene Indices: analysis of gene transcript sequences in highly sampled eukaryotic species.
Quackenbush J, Cho J, Lee D, Liang F, Holt I, Karamycheva S, Parvizi B, Pertea G, Sultana R, White J. Quackenbush J, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jan 1;29(1):159-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.159. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11125077 Free PMC article. - The TIGR Gene Indices: clustering and assembling EST and known genes and integration with eukaryotic genomes.
Lee Y, Tsai J, Sunkara S, Karamycheva S, Pertea G, Sultana R, Antonescu V, Chan A, Cheung F, Quackenbush J. Lee Y, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 1;33(Database issue):D71-4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki064. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15608288 Free PMC article. - The TIGR gene indices: reconstruction and representation of expressed gene sequences.
Quackenbush J, Liang F, Holt I, Pertea G, Upton J. Quackenbush J, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):141-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.141. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 10592205 Free PMC article. - A hitchhiker's guide to expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis.
Nagaraj SH, Gasser RB, Ranganathan S. Nagaraj SH, et al. Brief Bioinform. 2007 Jan;8(1):6-21. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbl015. Epub 2006 May 23. Brief Bioinform. 2007. PMID: 16772268 Review. - Identification and analysis of gene families from the duplicated genome of soybean using EST sequences.
Nelson RT, Shoemaker R. Nelson RT, et al. BMC Genomics. 2006 Aug 9;7:204. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-204. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16899135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Efficient clustering of large EST data sets on parallel computers.
Kalyanaraman A, Aluru S, Kothari S, Brendel V. Kalyanaraman A, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jun 1;31(11):2963-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg379. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12771222 Free PMC article. - Making sense of EST sequences by CLOBBing them.
Parkinson J, Guiliano DB, Blaxter M. Parkinson J, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2002 Oct 25;3:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-3-31. BMC Bioinformatics. 2002. PMID: 12398795 Free PMC article. - PCAP: a whole-genome assembly program.
Huang X, Wang J, Aluru S, Yang SP, Hillier L. Huang X, et al. Genome Res. 2003 Sep;13(9):2164-70. doi: 10.1101/gr.1390403. Genome Res. 2003. PMID: 12952883 Free PMC article. - Widespread A-to-I RNA editing of Alu-containing mRNAs in the human transcriptome.
Athanasiadis A, Rich A, Maas S. Athanasiadis A, et al. PLoS Biol. 2004 Dec;2(12):e391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020391. Epub 2004 Nov 9. PLoS Biol. 2004. PMID: 15534692 Free PMC article.
References
- Adams M.D., Kelley,J.M., Gocayne,J.D., Dubnick,M., Polymeropoulos,M.H., Xiao,H., Merril,C.R., Wu,A., Olde,B., Moreno,R.F. et al. (1991) Science, 252, 1651–1661. - PubMed
- Adams M.D., Kerlavage,A.R., Fleischmann,R.D., Fuldner,R.A., Bult,C.J., Lee,N.H., Kirkness,E.F., Weinstock,K.G., Gocayne,J.D., White,O. et al. (1995) Nature, 377, 3–174. - PubMed
- Hudson T.J., Stein,L.D., Gerety,S.S., Ma,J., Castle,A.B., Silva,J., Slonim,D.K., Baptista,R., Kruglyak,L., Xu,S.H. et al. (1995) Science, 270, 1945–1954. - PubMed
- Schuler G.D., Boguski,M.S., Stewart,E.A., Stein,L.D., Gyapay,G., Rice,K., White,R.E., Rodriguez-Tome,P., Aggarwal,A., Bajorek,E. et al. (1996) Science, 274, 540–546. - PubMed
- Bouck J., Yu,W., Gibbs,R. and Worley,K. (1999) Trends Genet., 15, 159–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials