SarA represses agr operon expression in a purified in vitro Staphylococcus aureus transcription system - PubMed (original) (raw)
SarA represses agr operon expression in a purified in vitro Staphylococcus aureus transcription system
S K Chakrabarti et al. J Bacteriol. 2000 Oct.
Abstract
Mutation and genetic complementation studies suggested that two chromosomal loci, agr and sar, are involved in the upregulation of several exotoxin genes and the downregulation of a number of surface protein genes in a growth phase-dependent manner in Staphylococcus aureus. We purified recombinant T7-tagged SarA from Escherichia coli and determined its effect on transcription from several S. aureus promoters by using purified RNA polymerase reconstituted with either sigma(A) or sigma(B) from S. aureus. Of the seven sigma(A)-dependent promoters that we tested, SarA repressed transcription from agrP2, agrP3, cna, sarP1, and sea promoters and did not affect sec and znt promoters. Furthermore, SarA had no effect on transcription from the sigma(B)-dependent sarP3 promoter. In vitro experimental data presented in this report suggest that SarA expression is autoregulated.
Figures
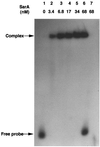
FIG. 1
Binding of SarA to the cna promoter. EMSA was done as described in the text.
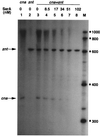
FIG. 2
Effect of SarA protein on transcription from the cna promoter. pMP7-cna and pMP7-zntPR DNA (Table 1) were used as templates for the determination of transcriptional activities from the cna and znt promoters (indicated at the top), respectively. The specific transcripts are indicated by arrows. Lane M, RNA markers (sizes are in nucleotides).
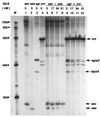
FIG. 3
SarA protein affects transcription of several specific ςA-dependent promoters in a dose-dependent manner. Plasmid DNA containing the specific promoter along with a partial or complete gene adjacent to the promoter, as indicated in Table 1, was used as the template. The different promoter DNAs used in each lane are noted at the top. The specific transcripts are indicated by arrows. Lane M, RNA markers (sizes are in nucleotides).
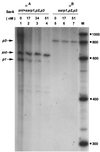
FIG. 4
Effect of SarA on transcription from the sar promoters. pALC561 DNA containing the entire sar operon was used as the template. pMP7-zntPR DNA was used as a control in lanes 1 to 4. RNA polymerase reconstituted with either ςA (lanes 1 to 4) or ςB (lanes 5 to 7) from S. aureus, in the presence of different concentrations of SarA, was used for the transcription reactions. Lane M, RNA markers (sizes are in nucleotides).
Similar articles
- Coordinated regulation by AgrA, SarA, and SarR to control agr expression in Staphylococcus aureus.
Reyes D, Andrey DO, Monod A, Kelley WL, Zhang G, Cheung AL. Reyes D, et al. J Bacteriol. 2011 Nov;193(21):6020-31. doi: 10.1128/JB.05436-11. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21908676 Free PMC article. - Molecular interactions between two global regulators, sar and agr, in Staphylococcus aureus.
Chien Y, Cheung AL. Chien Y, et al. J Biol Chem. 1998 Jan 30;273(5):2645-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.5.2645. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9446568 - Alternative transcription factor sigmaSB of Staphylococcus aureus: characterization and role in transcription of the global regulatory locus sar.
Deora R, Tseng T, Misra TK. Deora R, et al. J Bacteriol. 1997 Oct;179(20):6355-9. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.20.6355-6359.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9335283 Free PMC article. - Identification and characterization of SarH1, a new global regulator of virulence gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus.
Tegmark K, Karlsson A, Arvidson S. Tegmark K, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2000 Jul;37(2):398-409. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02003.x. Mol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10931334 - SarA, a global regulator of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus, binds to a conserved motif essential for sar-dependent gene regulation.
Chien Y, Manna AC, Projan SJ, Cheung AL. Chien Y, et al. J Biol Chem. 1999 Dec 24;274(52):37169-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.52.37169. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10601279
Cited by
- Influence of a functional sigB operon on the global regulators sar and agr in Staphylococcus aureus.
Bischoff M, Entenza JM, Giachino P. Bischoff M, et al. J Bacteriol. 2001 Sep;183(17):5171-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.17.5171-5179.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11489871 Free PMC article. - Transcriptional profiling of XdrA, a new regulator of spa transcription in Staphylococcus aureus.
McCallum N, Hinds J, Ender M, Berger-Bächi B, Stutzmann Meier P. McCallum N, et al. J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):5151-64. doi: 10.1128/JB.00491-10. Epub 2010 Jul 30. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20675497 Free PMC article. - Coordinated regulation by AgrA, SarA, and SarR to control agr expression in Staphylococcus aureus.
Reyes D, Andrey DO, Monod A, Kelley WL, Zhang G, Cheung AL. Reyes D, et al. J Bacteriol. 2011 Nov;193(21):6020-31. doi: 10.1128/JB.05436-11. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21908676 Free PMC article. - Presence and mRNA Expression of the sar Family Genes in Clinical and Non-clinical (Healthy Conjunctiva and Healthy Skin) Isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Cancino-Diaz ME, Gómez-Chávez F, Cancino-Diaz JC. Cancino-Diaz ME, et al. Indian J Microbiol. 2024 Sep;64(3):1301-1309. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01339-x. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Indian J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39282185 - sarA inactivation reduces vancomycin-intermediate and ciprofloxacin resistance expression by Staphylococcus aureus.
Lamichhane-Khadka R, Cantore SA, Riordan JT, Delgado A, Norman AE, Dueñas S, Zaman S, Horan S, Wilkinson BJ, Gustafson JE. Lamichhane-Khadka R, et al. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009 Aug;34(2):136-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.01.018. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009. PMID: 19324528 Free PMC article.
References
- Betley M J, Soltis T M, Couch J L. Molecular biological analysis of staphylococcal toxins. In: Novick R P, editor. Molecular biology of the staphylococci. New York, N.Y: VCH Publishers; 1990. pp. 327–342.
- Blevins J S, Gillaspy A F, Rechtin T M, Hulburt B K, Smeltzer M S. The staphylococcal accessory regulator (sar) represses transcription of the Staphylococcus aureus collagen adhesion gene (cna) in an agr-independent manner. Mol Microbiol. 1999;33:317–326. - PubMed
- Borst D W, Betley M J. Promoter analysis of the staphylococcal enterotoxin A gene. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:1883–1888. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous