The Streptococcus pneumoniae beta-galactosidase is a surface protein - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
The Streptococcus pneumoniae beta-galactosidase is a surface protein
D Zähner et al. J Bacteriol. 2000 Oct.
Abstract
The beta-galactosidase gene of Streptococcus pneumoniae, bgaA, encodes a putative 2,235-amino-acid protein with the two amino acid motifs characteristic of the glycosyl hydrolase family of proteins. In addition, an N-terminal signal sequence and a C-terminal LPXTG motif typical of surface-associated proteins of gram-positive bacteria are present. Trypsin treatment of cells resulted in solubilization of the enzyme, documenting that it is associated with the cell envelope. In order to obtain defined mutants suitable for lacZ reporter experiments, the bgaA gene was disrupted, resulting in a complete absence of endogenous beta-galactosidase activity. The results are consistent with beta-galactosidase being a surface protein that seems not to be involved in lactose metabolism but that may play a role during pathogenesis.
Figures
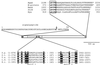
FIG. 1
Schematic representation of the β-galactosidase of_S. pneumoniae_ (S.p.). The amino acid (aa) sequences are given for three important regions: the N-terminal signal peptide (residues 1 to 55; the arrow marks the putative signal peptidase cleavage site); the two conserved motifs of glycosyl hydrolase family 2 (hatched boxes) within the region homologous to other β-galactosidases (stippled box; approximately residues 90 to 600); and 35 C-terminal residues with the cell wall-anchoring LPXTG motif (stippled box at right end). The putative active site is aligned with β-galactosidases of the following organisms: S.t., S. thermophilus (SWISS-PROT P23989); T.e., Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus (SWISS-PROT P77989); L.d., Lactobacillus delbrueckii (SWISS-PROT P33486); and E. coli (GenBank AJ002684). Strictly conserved amino acid residues within the motifs are highlighted. The C-terminal region is compared to those of other proteins containing an LPXTG motif: M-protein, S. pyogenes M protein (PIR S30283); S. pneumoniae proteins NanA (neuraminidase A; SWISS-PROT 59959), StrH (β-_N_-acetylglucosaminidase; SWISS-PROT P49610), and Hya (hyaluronidase; SWISS-PROT Q54873). Dots indicate gaps in the alignment; the asterisk marks the C terminus.
Similar articles
- Unravelling the multiple functions of the architecturally intricate Streptococcus pneumoniae β-galactosidase, BgaA.
Singh AK, Pluvinage B, Higgins MA, Dalia AB, Woodiga SA, Flynn M, Lloyd AR, Weiser JN, Stubbs KA, Boraston AB, King SJ. Singh AK, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2014 Sep 11;10(9):e1004364. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004364. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25210925 Free PMC article. - Characterization of the Streptococcus pneumoniae BgaC protein as a novel surface beta-galactosidase with specific hydrolysis activity for the Galbeta1-3GlcNAc moiety of oligosaccharides.
Jeong JK, Kwon O, Lee YM, Oh DB, Lee JM, Kim S, Kim EH, Le TN, Rhee DK, Kang HA. Jeong JK, et al. J Bacteriol. 2009 May;191(9):3011-23. doi: 10.1128/JB.01601-08. Epub 2009 Mar 6. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19270088 Free PMC article. - A new integrative reporter plasmid for Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Halfmann A, Hakenbeck R, Brückner R. Halfmann A, et al. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 Mar;268(2):217-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00584.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17328748 - Isolation and characterization of three Streptococcus pneumoniae transformation-specific loci by use of a lacZ reporter insertion vector.
Pestova EV, Morrison DA. Pestova EV, et al. J Bacteriol. 1998 May;180(10):2701-10. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.10.2701-2710.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9573156 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Epigenetic Switch Driven by DNA Inversions Dictates Phase Variation in Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Li J, Li JW, Feng Z, Wang J, An H, Liu Y, Wang Y, Wang K, Zhang X, Miao Z, Liang W, Sebra R, Wang G, Wang WC, Zhang JR. Li J, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2016 Jul 18;12(7):e1005762. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005762. eCollection 2016 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27427949 Free PMC article. - Mutational studies on endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase D which hydrolyzes core portion of asparagine-linked complex type oligosaccharides.
Yamamoto S, Muramatsu H, Muramatsu T. Yamamoto S, et al. Glycoconj J. 2005 Feb;22(1-2):35-42. doi: 10.1007/s10719-005-0847-7. Glycoconj J. 2005. PMID: 15864433 - The role of complex carbohydrate catabolism in the pathogenesis of invasive streptococci.
Shelburne SA, Davenport MT, Keith DB, Musser JM. Shelburne SA, et al. Trends Microbiol. 2008 Jul;16(7):318-25. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2008.04.002. Epub 2008 May 27. Trends Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18508271 Free PMC article. Review. - A functional genomics approach to establish the complement of carbohydrate transporters in Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Bidossi A, Mulas L, Decorosi F, Colomba L, Ricci S, Pozzi G, Deutscher J, Viti C, Oggioni MR. Bidossi A, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033320. Epub 2012 Mar 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22428019 Free PMC article. - Vancomycin tolerance induced by erythromycin but not by loss of vncRS, vex3, or pep27 function in Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Robertson GT, Zhao J, Desai BV, Coleman WH, Nicas TI, Gilmour R, Grinius L, Morrison DA, Winkler ME. Robertson GT, et al. J Bacteriol. 2002 Dec;184(24):6987-7000. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.24.6987-7000.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12446649 Free PMC article.
References
- Alloing G, Granadel C, Morrison D A, Claverys J-P. Competence pheromone, oligopeptide permease, and induction of competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1996;21:471–478. - PubMed
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases