Repair of chromosomal abasic sites in vivo involves at least three different repair pathways - PubMed (original) (raw)
Repair of chromosomal abasic sites in vivo involves at least three different repair pathways
M Otterlei et al. EMBO J. 2000.
Abstract
We introduced multiple abasic sites (AP sites) in the chromosome of repair-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli, in vivo, by expressing engineered variants of uracil-DNA glycosylase that remove either thymine or cytosine. After introduction of AP sites, deficiencies in base excision repair (BER) or recombination were associated with strongly enhanced cytotoxicity and elevated mutation frequencies, selected as base substitutions giving rifampicin resistance. In these strains, increased fractions of transversions and untargeted mutations were observed. In a recA mutant, deficient in both recombination and translesion DNA synthesis (TLS), multiple AP sites resulted in rapid cell death. Preferential incorporation of dAMP opposite a chromosomal AP site ('A rule') required UmuC. Furthermore, we observed an 'A rule-like' pattern of spontaneous mutations that was also UmuC dependent. The mutation patterns indicate that UmuC is involved in untargeted mutations as well. In a UmuC-deficient background, a preference for dGMP was observed. Spontaneous mutation spectra were generally strongly dependent upon the repair background. In conclusion, BER, recombination and TLS all contribute to the handling of chromosomal AP sites in E.coli in vivo.
Figures
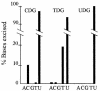
Fig. 1. Specificity of engineered DNA glycosylases. In vitro excision of adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T) and uracil (U) by CDG, TDG and UDG, from double-stranded DNA after incubation for 3 h.
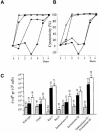
Fig. 2. The cytotoxic effect of TDG expression in wild-type E.coli (filled squares) compared with expression in strains deficient in (A) UmuC (filled diamonds), RuvA (filled stars) and RecA (filled circles), or (B) endonuclease IV (open diamonds), exonuclease III (open stars) or endonuclease IV/exonuclease III (open circles). (C) Mutation frequency (rifR bacteria per 108 ampR bacteria) spontaneously (grey bars) and after induction of AP sites with CDG (black bars) or TDG (white bars). The n values indicate the number of experiments for each column and bars indicate standard deviations.
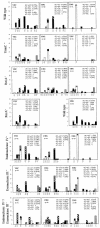
Fig. 3. Mutation spectra in the rpoB gene (RNA polymerase β) within codons 509–574 from rifR colonies, spontaneous (VEC) and after expression of UDG (only wild type), CDG or TDG. Codon positions are given on the X axis, and the number of mutations are given on the Y axis. The n value at the top left corner gives the total number of sequences. The mutations are classified as GC transitions (black bars), AT transitions (white bars), GC transversions (checked bars) and AT transversions (striped bars). The type of transitions and transversions, given as numbers as well as percentages, are specified at the top right corner of the spectra. In the recA mutant, only the spontaneous mutation spectrum was analysed.
Similar articles
- Characterization of DNA strand cleavage by enzymes that act at abasic sites in DNA.
Deutsch WA, Yacoub A. Deutsch WA, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 1999;113:281-8. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-675-4:281. Methods Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10443427 No abstract available. - Escherichia coli uracil- and ethenocytosine-initiated base excision DNA repair: rate-limiting step and patch size distribution.
Sung JS, Mosbaugh DW. Sung JS, et al. Biochemistry. 2003 Apr 29;42(16):4613-25. doi: 10.1021/bi027115v. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12705824 - What structural features determine repair enzyme specificity and mechanism in chemically modified DNA?
Singer B, Hang B. Singer B, et al. Chem Res Toxicol. 1997 Jul;10(7):713-32. doi: 10.1021/tx970011e. Chem Res Toxicol. 1997. PMID: 9250405 Review. - Repair of oxidative DNA damage--an important factor reducing cancer risk. Minireview.
Brozmanová J, Dudás A, Henriques JA. Brozmanová J, et al. Neoplasma. 2001;48(2):85-93. Neoplasma. 2001. PMID: 11478699 Review.
Cited by
- Genetically induced redox stress occurs in a yeast model for Roberts syndrome.
Mfarej MG, Skibbens RV. Mfarej MG, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Feb 4;12(2):jkab426. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab426. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 34897432 Free PMC article. - DNA damage in cancer development: special implications in viral oncogenesis.
Katerji M, Duerksen-Hughes PJ. Katerji M, et al. Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 15;11(8):3956-3979. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34522461 Free PMC article. - New insights into abasic site repair and tolerance.
Thompson PS, Cortez D. Thompson PS, et al. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Jun;90:102866. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102866. Epub 2020 Apr 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32417669 Free PMC article. Review. - Peptides containing the PCNA interacting motif APIM bind to the β-clamp and inhibit bacterial growth and mutagenesis.
Nedal A, Ræder SB, Dalhus B, Helgesen E, Forstrøm RJ, Lindland K, Sumabe BK, Martinsen JH, Kragelund BB, Skarstad K, Bjørås M, Otterlei M. Nedal A, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 4;48(10):5540-5554. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa278. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32347931 Free PMC article. - Identification of a prototypical single-stranded uracil DNA glycosylase from Listeria innocua.
Li J, Yang Y, Guevara J, Wang L, Cao W. Li J, et al. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017 Sep;57:107-115. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Jul 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017. PMID: 28719838 Free PMC article.
References
- Blatny J.M., Brautaset,T., Winther-Larsen,H.C., Karunakaran,P. and Valla,S. (1997) Improved broad-host-range RK2 vectors useful for high and low regulated gene expression levels in gram-negative bacteria. Plasmid, 38, 35–51. - PubMed
- Christensen J.R., LeClerc,J.E., Tata,P.V., Christensen,R.B. and Lawrence,C.W. (1988) UmuC function is not essential for the production of all targeted lacI mutations induced by ultraviolet light. J. Mol. Biol., 203, 635–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources