Signaling networks: the origins of cellular multitasking - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Signaling networks: the origins of cellular multitasking
J D Jordan et al. Cell. 2000.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
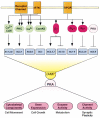
Adenylyl Cyclases as Examples of a Junction The signal receiving capabilities of the various adenylyl cyclase isoforms and the capability of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) to regulate various physiological functions are shown. Receptor channel, ligand gated channel (e.g., NMDA receptor); RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; GPCR, G protein–coupled receptor. Stimulatory signals are shown as arrows and inhibitory signals as plungers. The various cellular components or processes regulated by PKA are shown in the red ovals and the resultant physiological functions are given below.
Figure 2
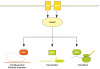
Cdc42, a Member of the Rho Family of GTPases as an Example of a Node Cdc42 may be stimulated both by receptor-tyrosine kinases (RTK) as well as G protein–coupled receptors (GPCR), and in turn regulate different cellular functions by regulating the distinct downstream kinases Pak, S6K (S6-kinase), or the serum response factor (SRF).
Figure 3
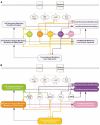
Postulated Postsynaptic Signaling Network in the CA1 Pyramidal Neuron A simplified version of some of the key elements of the network and its interface with the various cellular machinery is shown. The purpose of the two figures is to highlight the interconnections between the key protein kinases within the network and the different cellular machinery. In both figures signal flow from the receptor through signal transducers and second messengers is shown in gray. The black arrows denote connections between the various cellular machinery. Panel (A) highlights the connections between the different kinases and the various cellular machinery. It can be readily seen that each protein kinase in the network can regulate multiple cellular machinery. Panel (B) highlights the view from the cellular machinery perspective to indicate that most cellular machines are regulated by multiple protein kinases. It is predicted that such meshing results in a system in which multiple machinery can be coordinately regulated by the signaling network in a robust manner.
Comment on
- Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases.
Schlessinger J. Schlessinger J. Cell. 2000 Oct 13;103(2):211-25. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00114-8. Cell. 2000. PMID: 11057895 Review. No abstract available. - Ras and Rho GTPases: a family reunion.
Bar-Sagi D, Hall A. Bar-Sagi D, et al. Cell. 2000 Oct 13;103(2):227-38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00115-x. Cell. 2000. PMID: 11057896 Review. No abstract available. - Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases.
Davis RJ. Davis RJ. Cell. 2000 Oct 13;103(2):239-52. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00116-1. Cell. 2000. PMID: 11057897 Review. No abstract available. - TOR, a central controller of cell growth.
Schmelzle T, Hall MN. Schmelzle T, et al. Cell. 2000 Oct 13;103(2):253-62. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00117-3. Cell. 2000. PMID: 11057898 Review. - Signaling takes shape in the immune system.
Dustin ML, Chan AC. Dustin ML, et al. Cell. 2000 Oct 13;103(2):283-94. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00120-3. Cell. 2000. PMID: 11057901 Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Signaling to Rho GTPases.
Kjoller L, Hall A. Kjoller L, et al. Exp Cell Res. 1999 Nov 25;253(1):166-79. doi: 10.1006/excr.1999.4674. Exp Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 10579921 Review. - Neurobiology. Receptors as kissing cousins.
Milligan G. Milligan G. Science. 2000 Apr 7;288(5463):65-7. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5463.65. Science. 2000. PMID: 10766637 No abstract available. - Cellular signaling for activation of Rho GTPase Cdc42.
Sinha S, Yang W. Sinha S, et al. Cell Signal. 2008 Nov;20(11):1927-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.05.002. Epub 2008 May 16. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 18558478 Review. - An EGF receptor-mediated signal attenuates the inhibitory effect of LPA on an adenylate cyclase activity.
Arimura S, Saito Y, Nakata H, Fukushima K, Nishio E, Watanabe Y. Arimura S, et al. Life Sci. 1998;63(17):1563-70. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(98)00423-8. Life Sci. 1998. PMID: 9808067 - Cdc42: new roads to travel.
Cerione RA. Cerione RA. Trends Cell Biol. 2004 Mar;14(3):127-32. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.01.008. Trends Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15003621 Review.
Cited by
- Systems Biology Approaches to Understand the Host-Microbiome Interactions in Neurodegenerative Diseases.
Rosario D, Boren J, Uhlen M, Proctor G, Aarsland D, Mardinoglu A, Shoaie S. Rosario D, et al. Front Neurosci. 2020 Jul 8;14:716. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00716. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32733199 Free PMC article. Review. - Communicating oscillatory networks: frequency domain analysis.
Ihekwaba AE, Sedwards S. Ihekwaba AE, et al. BMC Syst Biol. 2011 Dec 22;5:203. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-203. BMC Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 22192879 Free PMC article. - Cellular harmonics for the morphology-invariant analysis of molecular organization at the cell surface.
Mazloom-Farsibaf H, Zou Q, Hsieh R, Danuser G, Driscoll MK. Mazloom-Farsibaf H, et al. Nat Comput Sci. 2023 Sep;3(9):777-788. doi: 10.1038/s43588-023-00512-4. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Nat Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 38177778 Free PMC article. - Doxorubicin and vinorelbine act independently via p53 expression and p38 activation respectively in breast cancer cell lines.
Liem AA, Appleyard MV, O'Neill MA, Hupp TR, Chamberlain MP, Thompson AM. Liem AA, et al. Br J Cancer. 2003 Apr 22;88(8):1281-4. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600898. Br J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12698197 Free PMC article. - Calpain as an effector of the Gq signaling pathway for inhibition of Wnt/beta -catenin-regulated cell proliferation.
Li G, Iyengar R. Li G, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 1;99(20):13254-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.202355799. Epub 2002 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12239346 Free PMC article.
References
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR. Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science. 1997;276:2042–2045. - PubMed
- Bar-Sagi D, Hall A. Ras and Rho GTPases: a family reunion. Cell. 2000;103:227–238. this issue. - PubMed
- Chen J, Iyengar R. Suppression of Ras-induced transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by activated G alpha s. Science. 1994;263:1278–1281. - PubMed
- Colledge M, Dean RA, Scott GK, Langeberg LK, Huganir RL, Scott JD. Targeting of PKA to glutamate receptors through a MAGUK-AKAP complex. Neuron. 2000;27:107–119. - PubMed
- Davis RJ. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell. 2000;103:239–252. this issue. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources