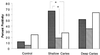Cytokine induction by Streptococcus mutans and pulpal pathogenesis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Cytokine induction by Streptococcus mutans and pulpal pathogenesis
C L Hahn et al. Infect Immun. 2000 Dec.
Abstract
Chronic pulpal inflammation under caries appears to be elicited by bacterial antigens that diffuse into the pulp through dentinal tubules. This prompted the hypothesis that cytokines elicited by antigens from Streptococcus mutans, which frequently dominates shallow lesions, could play a major role in eliciting the initial T-cell response in the pulp. To test this, we examined the ability of S. mutans to stimulate T cells and elicit cytokines and used Lactobacillus casei, which often predominates in deep carious lesions where B cells and plasma cells predominate, as a control. In addition, the presence of cytokines in the pulp was analyzed at the mRNA level. S. mutans elicited potent gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) responses in peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures and reduced the CD4/CD8 ratio by promoting CD8(+) T cells. Multiple inflammatory cytokine mRNAs (IFN-gamma, interleukin 4 [IL-4], and IL-10) were detected in human dental pulp. A higher prevalence of IFN-gamma (67%) than IL-4 (19%) or IL-10 (29%) was obtained in shallow caries, suggesting a type 1 cytokine mechanism in early pulpitis where S. mutans predominates. In contrast, in deep caries no differences in cytokine frequency were observed. Furthermore, the presence of IFN-gamma in the pulp correlated with the presence of S. mutans. The extraordinary induction of type 1 cytokines and the preferential activation of CD8(+) T cells by S. mutans offers an explanation for the etiology of the CD8(+) T-cell-dominant lesion in early pulpitis and suggests that S. mutans may have a major impact on the initial lesion and pulpal pathology.
Figures
FIG. 1
Comparison of S. mutans and L. casei stimulation of IL-10 production in PBMC cultures. The IL-10 concentrations were determined in supernatant fluids from 7-day-old PBMC (106/ml) cultures stimulated with 104 to 106 S. mutans (shaded bars) (n = 6) and L. casei (open bars) (n = 4) bacteria per ml. The error bars represent 95% CIs.
FIG. 2
Comparison of type 1 (IFN-γ) and type 2 (IL-4 and IL-10) cytokine mRNA in pulpal tissues from shallow and deep carious lesions. The presence of detectable cytokine mRNA in the pulps was determined using RT-PCR, and the percentage of positive pulps in the control, shallow-caries, and deep-caries groups is indicated for IFN-γ (shaded bars), IL-4 (striped bars), and IL-10 (open bars). The pulpal tissue was obtained from impacted third molars for controls (n = 16), molars with shallow caries (n = 21), and molars with deep caries (n = 25). ∗, P < 0.05.
Similar articles
- CCL20 production is induced in human dental pulp upon stimulation by Streptococcus mutans and proinflammatory cytokines.
Takahashi K, Nakanishi T, Yumoto H, Adachi T, Matsuo T. Takahashi K, et al. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Aug;23(4):320-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2008.00431.x. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18582332 - Bacterium-dependent induction of cytokines in mononuclear cells and their pathologic consequences in vivo.
Jiang Y, Magli L, Russo M. Jiang Y, et al. Infect Immun. 1999 May;67(5):2125-30. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.5.2125-2130.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10225864 Free PMC article. - Innate immune responses of the dental pulp to caries.
Hahn CL, Liewehr FR. Hahn CL, et al. J Endod. 2007 Jun;33(6):643-51. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2007.01.001. Epub 2007 Mar 6. J Endod. 2007. PMID: 17509400 Review.
Cited by
- Leptin in Dental Pulp and Periapical Tissues: A Narrative Review.
Martin-Gonzalez J, Segura-Egea JJ, Pérez-Pérez A, Cabanillas-Balsera D, Sánchez-Margalet V. Martin-Gonzalez J, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 11;23(4):1984. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041984. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216099 Free PMC article. Review. - Oral Bacterial Signatures in Cerebral Thrombi of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke Treated With Thrombectomy.
Patrakka O, Pienimäki JP, Tuomisto S, Ollikainen J, Lehtimäki T, Karhunen PJ, Martiskainen M. Patrakka O, et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Jun 4;8(11):e012330. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012330. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31117858 Free PMC article. - The Efficacy of Different Antibiotic Compounds in Regenerative Treatment of Immature Necrotic Teeth.
Gharechahi M, Kafi MH, Javidi M, Jafari N, Joibary Moghaddam M. Gharechahi M, et al. Front Dent. 2024 Jan 2;21:1. doi: 10.18502/fid.v21i1.14638. eCollection 2024. Front Dent. 2024. PMID: 38571897 Free PMC article. - Tailored 70S30C Bioactive glass induces severe inflammation as pulpotomy agent in primary teeth: an interim analysis of a randomised controlled trial.
Elhamouly Y, El Backly RM, Talaat DM, Omar SS, El Tantawi M, Dowidar KML. Elhamouly Y, et al. Clin Oral Investig. 2021 Jun;25(6):3775-3787. doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03707-5. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Clin Oral Investig. 2021. PMID: 33409691 Clinical Trial. - S100 and cytokine expression in caries.
McLachlan JL, Sloan AJ, Smith AJ, Landini G, Cooper PR. McLachlan JL, et al. Infect Immun. 2004 Jul;72(7):4102-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.4102-4108.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15213155 Free PMC article.
References
- Abbas A K, Murphy K M, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383:787–793. - PubMed
- Ackermans F, Klein J P, Frank R M. Ultrastructural location of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis antigens in carious human dentine. J Biol Bucc. 1981;9:203–217. - PubMed
- Brannstrom M, Lind P O. Pulpal response to early dental caries. J Dent Res. 1965;44:1045–1050. - PubMed
- Chehimi J, Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12: a bridge between innate resistance and adaptive immunity with a role in infection and acquired immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol. 1994;14:149–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials