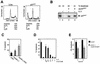Forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1 modulates cytokine-dependent transcriptional regulation of p27(KIP1) - PubMed (original) (raw)
Forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1 modulates cytokine-dependent transcriptional regulation of p27(KIP1)
P F Dijkers et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec.
Abstract
Interleukin-3 (IL-3), IL-5, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor regulate the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of hematopoietic lineages. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) has been implicated in the regulation of these processes. Here we investigate the molecular mechanism by which PI3K regulates cytokine-mediated proliferation and survival in the murine pre-B-cell line Ba/F3. IL-3 was found to repress the expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(KIP1) through activation of PI3K, and this occurs at the level of transcription. This transcriptional regulation occurs through modulation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1, and IL-3 inhibited FKHR-L1 activity in a PI3K-dependent manner. We have generated Ba/F3 cell lines expressing a tamoxifen-inducible active FKHR-L1 mutant [FKHR-L1(A3):ER*]. Tamoxifen-mediated activation of FKHR-L1(A3):ER* resulted in a striking increase in p27(KIP1) promoter activity and mRNA and protein levels as well as induction of the apoptotic program. The level of p27(KIP1) appears to be critical in the regulation of cell survival since mere ectopic expression of p27(KIP1) was sufficient to induce Ba/F3 apoptosis. Moreover, cell survival was increased in cytokine-starved bone marrow-derived stem cells from p27(KIP1) null-mutant mice compared to that in cells from wild-type mice. Taken together, these observations indicate that inhibition of p27(KIP1) transcription through PI3K-induced FKHR-L1 phosphorylation provides a novel mechanism of regulating cytokine-mediated survival and proliferation.
Figures
FIG. 1
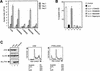
Regulation of IL-3-mediated proliferation and survival. (A) Ba/F3 cells were cultured in the presence of IL-3 without inhibitors or with PD098059 (50 μM), LY294002 (10 μM), SB203580 (10 μM), or rapamycin (20 ng/ml), and cells were counted every 24 h as indicated. (B) Ba/F3 cells were cultured in the absence of IL-3 (bar 1) or in the presence of IL-3 either alone (bar 2) or with LY294002 (10 μM; bar 3) PD098059 (50 μM; bar 4), SB203580 (10 μM; bar 5), or rapamycin (20 ng/ml; bar 6), and the percentages of apoptotic cells were determined after 48 h. (C, left) COS cells were transfected with 8 μg of either the empty vector or the myc-PTEN or myc-PTENcaax vector together with 2 μg of the HA-PKB vector. HA-PKB was immunoprecipitated with an HA antibody (12CA5) and analyzed for activity by immunoblotting with phospho-Ser473 PKB antibody (top). Expression of HA-PKB and mycPTEN was verified by immunoblotting with either 12CA5 (middle) or myc antibody (9E10; bottom). (Right) Ba/F3 cells were electroporated with 2 μg of the spectrin-GFP vector together with either 18 μg of empty vector (pSG5) or 18 μg of the myc-tagged PTENcaax vector. Dead cells were removed 2 h after electroporation by separation through a Ficoll gradient. Twenty-four hours after electroporation cells were fixed and stained with PI, and the DNA content of 5,000 GFP-positive cells was analyzed by FACS. The data depicted are representative of several independent experiments.
FIG. 2
Upregulation of p27KIP1 protein levels correlates with apoptosis. (A) Ba/F3 cells were cultured overnight in the absence or presence of IL-3 without inhibitors or with LY294002 (LY; 10 μM), PD098059 (PD; 50 μM), SB203580 (SB; 10 μM), or rapamycin (RP; 20 ng/ml). Equal amounts of protein were loaded, and the levels of p27KIP1 (top) and RACK1 (bottom) were determined by immunoblotting as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Ba/F3 cells were cultured overnight with IL-3 and cytokine starved for the indicated times in the presence or absence of actinomycin D (5 μg/ml), and p27KIP1 levels were analyzed as for panel A. (C) Ba/F3 cells were cytokine starved overnight and were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times, and levels of p27KIP1 were analyzed as for panel A. (D) Mouse fetal liver cultures were treated with or without cytokines for 24 h. The percentages of apoptotic cells were measured, and equal amounts of protein were analyzed for p27KIP1 expression. (E) Human peripheral blood eosinophils were cultured without cytokines, with IL-5, or with IL-5 and LY294002 (10 μM). Equal amounts of protein were analyzed for levels of p27KIP1 (top) or ERK1 and -2 (bottom) by Western blotting. The percentages of apoptotic cells are shown below. (F) Ba/F3 cells were either cytokine starved or cultured with IL-3 or IL-3 together with LY294002 (10 μM) overnight, equal amounts of protein were immunoprecipitated (IP) with cyclin E antibody, and associated kinase activity was analyzed (top). Equal protein loading was verified by analyzing CDK2 expression (bottom). WCL, whole-cell lysate.
FIG. 3
Cytokine-mediated regulation of p27KIP1 transcription requires PI3K. (A) Ba/F3 cells were either IL-3 starved or IL-3 starved overnight and subsequently stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times. Twenty micrograms of total RNA was used for Northern blotting and hybridized with a p27KIP1 probe (top). Equal RNA loading was verified by GAPDH reprobing (bottom). (B) Ba/F3 cells were IL-3 starved overnight and restimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times with or without preincubation with LY294002 (10 μM) and analyzed as for panel A. (C) Ba/F3 cells were electroporated with 10 μg of either pGL2 (CON), pGL2-TK (TK), pGL2-p27KIP1 (KIP1), or cyclin D1 (D1) luciferase constructs together with 500 ng of tk-renilla plasmid, cultured with or without IL-3 for 24 h, and luciferase activity was analyzed as described in Materials and Methods.
FIG. 4
Analysis of FKHR-L1 phosphorylation and activity in Ba/F3 cells. (A) Ba/F3 cells were cytokine starved and stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times (left) or pretreated with LY294002 (10 μM) for 20 min prior to IL-3 stimulation (right). FKHR-L1 phosphorylation was analyzed using a FKHR-L1(Thr32)-specific antibody (top). Equal protein loading was verified by RACK1 reprobing (bottom). (B) Ba/F3 cells stably expressing myrPKB:ER* were cytokine starved overnight and stimulated with 4-OHT (100 nM) for the indicated times. Phosphorylated myrPKB-ER was analyzed using a PKB(Ser473)-specific antibody (top). Equal PKB levels were verified by reprobing the blot with a PKB antibody (bottom). (C) Ba/F3 cells stably expressing myrPKB:ER* were cytokine starved overnight and stimulated with 4-OHT (100 nM) for the indicated times, and FKHR-L1 phosphorylation was analyzed using an FKHR-L1(Thr32)-specific antibody (top). (D) Ba/F3 cells were electroporated with 12 μg of p27KIP1 luciferase construct together with 4 μg of pSG5-gagPKB, FKHR-L1(wt), or FKHR-L1(A3) or combinations thereof as indicated. The DNA concentration was adjusted to 20 μg with pSG5. Cells were cultured with IL-3, and luciferase activity was analyzed 24 h later as described in Materials and Methods.
FIG. 5
FKHR-L1 directly regulates p27KIP1 transcription. (A) Expression of FKHR-L1 in Ba/F3 cells or Ba/F3 cells stably expressing FKHR-L1(A3):ER* was verified by immunoblotting with FKHR-L1 antibody. (B) Ba/F3 cells stably expressing FKHR-L1(A3):ER* were electroporated with 12 μg of p27KIP1 luciferase construct together with 8 μg of pSG5. Cells were cultured with IL-3 (CON) or with IL-3 and 4-OHT (100 nM), and luciferase activity was analyzed 24 h later as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Ba/F3 cells stably expressing FKHR-L1(A3):ER* were treated with 4-OHT (100 nM) for the indicated times; 20 μg of total RNA was used for Northern blotting and hybridized with a p27KIP1 probe (top). Equal RNA loading was verified by GAPDH reprobing (bottom). (D) Ba/F3 cells and Ba/F3 cells stably expressing FKHR-L1(A3):ER* were cytokine starved overnight and were cultured with IL-3 or with IL-3 and 4-OHT (100 nM). Equal amounts of protein were loaded, and the levels of p27KIP1 (top) and RACK1 (bottom) were determined by immunoblotting as described in Materials and Methods. (E) Ba/F3 cells stably expressing FKHR-L1(A3):ER* were treated with 4-OHT (100 nM) in the absence or presence of actinomycin D (5 μg/ml) for the indicated times and analyzed as for panel D. (F) Ba/F3 cells stably expressing FKHR-L1(A3):ER* were cultured in the absence or presence of IL-3 or IL-3 together with various concentrations 4-OHT overnight and were analyzed as for panel D.
FIG. 6
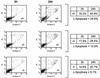
IL-3-mediated survival requires inactivation of FKHR-L1 and downregulation of p27KIP1 levels. (A) Ba/F3 cells were electroporated with 2 μg of spectrin-GFP vector together with either 18 μg of empty vector (pSG5; left) or 18 μg of p27KIP1 vector (right). Dead cells were removed by separation through a Ficoll gradient. Twenty-four hours after electroporation cells were fixed and stained with PI and the DNA contents of 5,000 GFP-positive cells were analyzed by FACS. The data are representative of several independent experiments. (B) Ba/F3 cells were electroporated with 2 μg of LNGFR DNA or 2 μg LNGFR DNA together with 2 or 4 μg of p27KIP1 DNA, and the total amount of DNA was adjusted to 20 μg with pSG5. Dead cells were removed by separating cells through a Ficoll gradient and LNGFR-expressing cells were analyzed 24 h after transfection as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Ba/F3 cells were electroporated with spectrin-GFP (2 μg) together with 18 μg of pSG5 (CON), FKHR-L1, or FKHR-L1(A3) DNAs and analyzed as for panel A. The data represent three independent experiments (± standard errors of the means). (D) Ba/F3 cells stably expressing FKHR-L1(A3):ER* were cytokine starved and cultured with IL-3 or IL-3 together with various concentrations of 4-OHT, and the percentages of apoptotic cells were determined after 48 h by FACS analysis. (E) FKHR-L1(A3):ER-expressing cell lines were electroporated with either 18 μg of pSG5 and 2 μg of spectrin-GFP DNAs (black bars) or 5 μg of kinase-dead CDK4, 5 μg of cyclin D1, 2 μg of spectrin-GFP, and 8 μg of pSG5 DNAs (grey bars). Dead cells were removed by separation through a Ficoll gradient. Cells were treated with 4-OHT and analyzed 24 h later as for panel A. The data are representative of several independent experiments.
FIG. 7
Increased survival of p27KIP1 (−/−) hematopoietic cells after cytokine withdrawal. Hematopoietic stem cells were isolated from either wild-type mice (+/+) or mice lacking one (−/+) or both (−/−) alleles of the p27KIP1 gene and cultured as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were cytokine starved for 24 h, and the percentages of apoptotic cells were analyzed by annexin-V staining. The percentage increase in apoptosis after cytokine withdrawal is shown (Δapoptosis). Data are representative of three independent experiments.
Similar articles
- Cell cycle inhibition by FoxO forkhead transcription factors involves downregulation of cyclin D.
Schmidt M, Fernandez de Mattos S, van der Horst A, Klompmaker R, Kops GJ, Lam EW, Burgering BM, Medema RH. Schmidt M, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Nov;22(22):7842-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.22.7842-7852.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12391153 Free PMC article. - FKHR-L1 can act as a critical effector of cell death induced by cytokine withdrawal: protein kinase B-enhanced cell survival through maintenance of mitochondrial integrity.
Dijkers PF, Birkenkamp KU, Lam EW, Thomas NS, Lammers JW, Koenderman L, Coffer PJ. Dijkers PF, et al. J Cell Biol. 2002 Feb 4;156(3):531-42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200108084. Epub 2002 Jan 28. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11815629 Free PMC article. - PAX3-FKHR transformation increases 26 S proteasome-dependent degradation of p27Kip1, a potential role for elevated Skp2 expression.
Zhang L, Wang C. Zhang L, et al. J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 3;278(1):27-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205424200. Epub 2002 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12401804 - BCR/ABL regulates expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 through the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/AKT pathway.
Gesbert F, Sellers WR, Signoretti S, Loda M, Griffin JD. Gesbert F, et al. J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 15;275(50):39223-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007291200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 11010972 - Forkhead transcription factors are critical effectors of cell death and cell cycle arrest downstream of PTEN.
Nakamura N, Ramaswamy S, Vazquez F, Signoretti S, Loda M, Sellers WR. Nakamura N, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;20(23):8969-82. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.23.8969-8982.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11073996 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Cdc2-like kinase 2 is a key regulator of the cell cycle via FOXO3a/p27 in glioblastoma.
Park SY, Piao Y, Thomas C, Fuller GN, de Groot JF. Park SY, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):26793-805. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8471. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27050366 Free PMC article. - The interaction between acetylation and serine-574 phosphorylation regulates the apoptotic function of FOXO3.
Li Z, Bridges B, Olson J, Weinman SA. Li Z, et al. Oncogene. 2017 Mar 30;36(13):1887-1898. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.359. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27669435 Free PMC article. - Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress Reduces Proliferation in Embryonic Stem Cells via FOXO3A/β-Catenin-Dependent Transcription of p21(cip1).
McClelland Descalzo DL, Satoorian TS, Walker LM, Sparks NR, Pulyanina PY, Zur Nieden NI. McClelland Descalzo DL, et al. Stem Cell Reports. 2016 Jul 12;7(1):55-68. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.06.006. Stem Cell Reports. 2016. PMID: 27411103 Free PMC article. - Complex regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27kip1 in thyroid cancer cells by the PI3K/AKT pathway: regulation of p27kip1 expression and localization.
Motti ML, Califano D, Troncone G, De Marco C, Migliaccio I, Palmieri E, Pezzullo L, Palombini L, Fusco A, Viglietto G. Motti ML, et al. Am J Pathol. 2005 Mar;166(3):737-49. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62295-X. Am J Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15743786 Free PMC article. - Cytokine signaling to the cell cycle.
Quelle FW. Quelle FW. Immunol Res. 2007;39(1-3):173-84. doi: 10.1007/s12026-007-0080-5. Immunol Res. 2007. PMID: 17917064 Review.
References
- Alessi D R, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley D T, Saltiel A R. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27489–27494. - PubMed
- Arai K I, Lee F, Miyajima A, Miyatake S, Arai N, Yokota T. Cytokines: coordinators of immune and inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:783–836. - PubMed
- Bouillet P, Metcalf D, Huang D C, Tarlinton D M, Kay T W, Kontgen F, Adams J M, Strasser A. Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science. 1999;286:1735–1738. - PubMed
- Boussiotis V A, Freeman G J, Taylor P A, Berezovskaya A, Grass I, Blazar B R, Nadler L M. p27kip1 functions as an anergy factor inhibiting interleukin 2 transcription and clonal expansion of alloreactive human and mouse helper T lymphocytes. Nat Med. 2000;6:290–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous