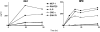Control of chemokine production at the blood-retina barrier - PubMed (original) (raw)
Control of chemokine production at the blood-retina barrier
I J Crane et al. Immunology. 2000 Nov.
Abstract
Chemokine production at the blood-retina barrier probably plays a critical role in determining the influx of tissue-damaging cells from the circulation into the retina during inflammation. The blood-retina barrier comprises the retinal microvascular endothelium and the retinal pigment epithelium. Chemokine expression and production by human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (REC) have never been reported previously, so we examined the in vitro expression and production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), regulated on activation of normal T-cell expressed and secreted (RANTES), macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha, MIP-1beta, interleukin (IL)-8, epithelial cell-derived neutrophil activating protein-78 (ENA-78) and growth related oncogene alpha (GROalpha) in these cells, both unstimulated and stimulated by cytokines likely to be present during the evolution of an inflammatory response. We compared this to expression and production of these chemokines in vitro in human retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE). MCP-1 was expressed and produced constitutively by REC but all the chemokines were produced in greater amounts upon stimulation with the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha). MCP-1 and IL-8 were produced at much higher levels than the other chemokines tested. MIP-1alpha and MIP-1beta were present only at low levels, even after stimulation with IL-1beta and TNF-alpha. Cytokines with greater anti-inflammatory activity, such as IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) and IL-6, had little effect on chemokine production either by REC alone or after stimulation with IL-1beta and TNF-alpha. RPE, although a very different cell type, showed a similar pattern of expression and production of chemokines, indicating the site-specific nature of chemokine production. Chemokine production by REC and RPE is probably significant in selective leucocyte recruitment during the development of inflammation in the retina.
Figures
Figure 1
Time-course of chemokine production in response to interleukin-1β (IL-1β) (0·25 ng/ml, 50 IU/ml) over 48 hr for human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (REC) and human retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE). The chemokine concentration (pg/ml) in culture supernatants was detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), closed squares; regulated on activation of normal T-cell expressed and secreted (RANTES), open squares; interleukin-8 (IL-8), closed circles; growth related oncogene α (GROα), open circles; and epithelial cell-derived neutrophil activating protein-78 (ENA-78), closed triangles. Results shown are from one representative experiment.
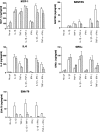
Figure 2
Chemokine production by human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (REC) (open bars) and human retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE) (hatched bars) in response to interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ). Chemokine was detected in supernatants after 24 hr of culture using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). IL-1β was used at 0·25 ng/ml (50 IU/ml), TNF-α at 10 ng/ml (1100 IU/ml) and IFN-γ at 20 ng/ml (136 IU/ml). Results shown are combined from at least three experiments using REC from different donors. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM).
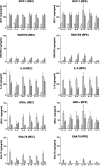
Figure 3
Chemokine production by human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (REC) (left column) and human retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE) (right column) in response to interleukin (IL)-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13 and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) alone (open bars) or in combination with interleukin-1β (IL-1β) (hatched bars) or tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (cross-hatched bars). Chemokine was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in RPE supernatants after 24 hr of culture. IL-1β was used at 0·25 ng/ml, and IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13, TGF-β and TNF-α all at 10 ng/ml. Results shown are combined from at least three experiments using REC and RPE from different donors. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM).
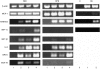
Figure 4
Chemokine mRNA expression as detected by reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR). RNA was extracted from cells 6 hr after stimulation of human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (REC), human retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) (HU) cultures (C, no cDNA). Lane 0, (control) no cDNA; lane 1, unstimulated cultures; lane 2, 0·25 ng/ml of interleukin-1β (IL-1β); lane 3, 10 ng/ml of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α); lane 4, IL-1β (0·25 ng/ml) + TNF-α (10 ng/ml). Results shown for macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α), MIP-1β, regulated on activation of normal T-cell expressed and secreted (RANTES) and epithelial cell-derived neutrophil activating protein-78 (ENA-78) had 5 µl of cDNA in the PCR reaction whereas those for β-actin, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and growth related oncogene α (GROα) had 1 µl of cDNA.
Similar articles
- Suppression of NF-kappaB-dependent proinflammatory gene expression in human RPE cells by a proteasome inhibitor.
Wang XC, Jobin C, Allen JB, Roberts WL, Jaffe GJ. Wang XC, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999 Feb;40(2):477-86. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999. PMID: 9950608 - Regulation of beta-chemokine mRNA expression in adult rat astrocytes by lipopolysaccharide, proinflammatory and immunoregulatory cytokines.
Guo H, Jin YX, Ishikawa M, Huang YM, van der Meide PH, Link H, Xiao BG. Guo H, et al. Scand J Immunol. 1998 Nov;48(5):502-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1998.00422.x. Scand J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9822259 - Cell-associated human retinal pigment epithelium interleukin-8 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1: immunochemical and in-situ hybridization analyses.
Elner VM, Burnstine MA, Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Elner SG. Elner VM, et al. Exp Eye Res. 1997 Dec;65(6):781-9. doi: 10.1006/exer.1997.0380. Exp Eye Res. 1997. PMID: 9441701 - Cytokines and chemokines in uveitis: is there a correlation with clinical phenotype?
Ooi KG, Galatowicz G, Calder VL, Lightman SL. Ooi KG, et al. Clin Med Res. 2006 Dec;4(4):294-309. doi: 10.3121/cmr.4.4.294. Clin Med Res. 2006. PMID: 17210978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Choroidal dendritic cells require activation to present antigen and resident choroidal macrophages potentiate this response.
Forrester JV, Lumsden L, Duncan L, Dick AD. Forrester JV, et al. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005 Mar;89(3):369-77. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2004.054197. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 15722321 Free PMC article. - Characterizing the cellular immune response to subretinal AAV gene therapy in the murine retina.
Chandler LC, McClements ME, Yusuf IH, Martinez-Fernandez de la Camara C, MacLaren RE, Xue K. Chandler LC, et al. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021 May 29;22:52-65. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.05.011. eCollection 2021 Sep 10. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021. PMID: 34485594 Free PMC article. - Polymorphisms of chemokine and chemokine receptor genes in idiopathic immune-mediated posterior segment uveitis.
Ahad MA, Missotten T, Abdallah A, Lympany PA, Lightman S. Ahad MA, et al. Mol Vis. 2007 Mar 23;13:388-96. Mol Vis. 2007. PMID: 17417600 Free PMC article. - Resolution of uveitis.
Wildner G, Diedrichs-Möhring M. Wildner G, et al. Semin Immunopathol. 2019 Nov;41(6):727-736. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00758-z. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Semin Immunopathol. 2019. PMID: 31591678 Review. - CXCL10 is required to maintain T-cell populations and to control parasite replication during chronic ocular toxoplasmosis.
Norose K, Kikumura A, Luster AD, Hunter CA, Harris TH. Norose K, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Jan 21;52(1):389-98. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5819. Print 2011 Jan. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 20811054 Free PMC article.
References
- Springer TA. Traffic signals on endothelium for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:827–72. - PubMed
- Rollins BJ. Chemokines. Blood. 1997;90:909–28. - PubMed
- Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines – CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:97–179. - PubMed
- Baggiolini M, Dahinden CA. CC chemokines in allergic inflammation. Immunol Today. 1994;15:127–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous