Role of the high affinity immunoglobulin E receptor in bacterial translocation and intestinal inflammation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Role of the high affinity immunoglobulin E receptor in bacterial translocation and intestinal inflammation
D Dombrowicz et al. J Exp Med. 2001.
Abstract
A role for immunoglobulin E and its high affinity receptor (Fc epsilon RI) in the control of bacterial pathogenicity and intestinal inflammation has been suggested, but relevant animal models are lacking. Here we compare transgenic mice expressing a humanized Fc epsilon RI (hFc epsilon RI), with a cell distribution similar to that in humans, to Fc epsilon RI-deficient animals. In hFc epsilon RI transgenic mice, levels of colonic interleukin 4 were higher, the composition of fecal flora was greatly modified, and bacterial translocation towards mesenteric lymph nodes was increased. In hFc epsilon RI transgenic mice, 2,4,6-tri-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis was also more pronounced, whereas Fc epsilon RI-deficient animals were protected from colitis, demonstrating that Fc epsilon RI can affect the onset of intestinal inflammation.
Figures
Figure 1
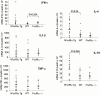
Expression of FcεRIα transcripts (top), β-actin (middle), and IgE productive transcripts (pε; bottom) in hFcεRIα Tg, WT, and FcεRIα−/− mice. Ethidium bromide–stained agarose gels were loaded with amplified PCR products from individual mice.
Figure 2
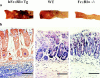
Histology of colon mucosa from hFcεRIα Tg, WT, and FcεRIα−/− mice after May-Grünwald/Giemsa staining of paraffin-embedded 4-μm sections. Bars, 0.2 mm.
Figure 3
Cytokine mRNA levels in the colon of hFcεRIα Tg, WT, and FcεRIα−/− mice. IFN-γ, IL1-β, TNF-α, IL-10, and IL-4 were quantified by competitive RT-PCR from colon mRNA (n = 13 for FcεRIα Tg mice, n = 13 for WT mice, and n = 6 for FcεRIα−/− mice). Results are expressed as number of cytokine mRNA molecules per 104 molecules of β-actin. Individual values, mean, and SD are represented.
Figure 4
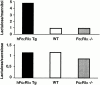
Intestinal permeability in hFcεRIα Tg, WT, and FcεRIα−/− mice. Lactulose/mannitol and lactulose/sucralose ratio in the urine collected over a 24-h period after gavage. Bars represent pools from five mice.
Figure 5
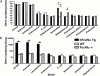
Luminal (a) and MLN (b) flora from hFcεRIα Tg, WT, and FcεRIα−/− mice. Germ number in feces from the three strains of mice were analyzed after culture of both aerobic and anaerobic flora. Results are expressed as mean numbers of bacteria per gram of feces or tissue ± SD (n = 7 for hFcεRIα Tg, n = 8 for WT, and n = 15 for FcεRIα−/− mice; *P < 0.05). Error bars (a) are falling within the top line of each histogram.
Figure 6
Macroscopic (a) and microscopic (b) evaluations of colons from hFcεRIαTg, WT, and FcεRIα−/− mice 48 h after intrarectal TNBS administration. Colons were open along the longitudinal axis for photography. (a) Colons of TNBS-treated hFcεRIα Tg mice display intense inflammation with edema and necrosis compared with the mild inflammation observed in the colon of WT animals and to the absence of inflammation in colons from TNBS-treated FcεRIα−/− mice. One representative colon for each strain of mice is shown. Distal colon is on the left side. (b) 4-μm paraffin-embedded sections were stained with May-Grünwald/Giemsa. Bar, 0.2 mm.
Similar articles
- Transgenic mice expressing the human high-affinity immunoglobulin (Ig) E receptor alpha chain respond to human IgE in mast cell degranulation and in allergic reactions.
Fung-Leung WP, De Sousa-Hitzler J, Ishaque A, Zhou L, Pang J, Ngo K, Panakos JA, Chourmouzis E, Liu FT, Lau CY. Fung-Leung WP, et al. J Exp Med. 1996 Jan 1;183(1):49-56. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.1.49. J Exp Med. 1996. PMID: 8551243 Free PMC article. - Mast cells lacking the high affinity immunoglobulin E receptor are deficient in Fc epsilon RI gamma messenger RNA.
Ryan JJ, Kinzer CA, Paul WE. Ryan JJ, et al. J Exp Med. 1995 Aug 1;182(2):567-74. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.2.567. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7629513 Free PMC article. - Identification of the high affinity receptor binding region in human immunoglobulin E.
Helm BA, Sayers I, Higginbottom A, Machado DC, Ling Y, Ahmad K, Padlan EA, Wilson AP. Helm BA, et al. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 29;271(13):7494-500. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.13.7494. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8631779 - Gene expression profiles for Fc epsilon RI, cytokines and chemokines upon Fc epsilon RI activation in human cultured mast cells derived from peripheral blood.
Wakahara S, Fujii Y, Nakao T, Tsuritani K, Hara T, Saito H, Ra C. Wakahara S, et al. Cytokine. 2001 Nov 21;16(4):143-52. doi: 10.1006/cyto.2001.0958. Cytokine. 2001. PMID: 11792124 - Amino acid residues that influence Fc epsilon RI-mediated effector functions of human immunoglobulin E.
Sayers I, Cain SA, Swan JR, Pickett MA, Watt PJ, Holgate ST, Padlan EA, Schuck P, Helm BA. Sayers I, et al. Biochemistry. 1998 Nov 17;37(46):16152-64. doi: 10.1021/bi981456k. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9819207
Cited by
- IgE-based immunotherapy of cancer: challenges and chances.
Singer J, Jensen-Jarolim E. Singer J, et al. Allergy. 2014 Feb;69(2):137-49. doi: 10.1111/all.12276. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Allergy. 2014. PMID: 24117861 Free PMC article. Review. - Modulation of anti-inflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide stimulated human THP-1 cell line and mouse model at gene expression level with indigenous putative probiotic lactobacilli.
Aparna Sudhakaran V, Panwar H, Chauhan R, Duary RK, Rathore RK, Batish VK, Grover S. Aparna Sudhakaran V, et al. Genes Nutr. 2013 Nov;8(6):637-48. doi: 10.1007/s12263-013-0347-5. Epub 2013 Jun 2. Genes Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23728791 Free PMC article. - Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory efficacy of indigenous probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Lp91 in colitis mouse model.
Duary RK, Bhausaheb MA, Batish VK, Grover S. Duary RK, et al. Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Apr;39(4):4765-75. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1269-1. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 21947851 - Peanut-induced intestinal allergy is mediated through a mast cell-IgE-FcepsilonRI-IL-13 pathway.
Wang M, Takeda K, Shiraishi Y, Okamoto M, Dakhama A, Joetham A, Gelfand EW. Wang M, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Aug;126(2):306-16, 316.e1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.05.017. Epub 2010 Jul 10. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20624645 Free PMC article. - Insights from advances in research of chemically induced experimental models of human inflammatory bowel disease.
Kawada M, Arihiro A, Mizoguchi E. Kawada M, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Nov 14;13(42):5581-93. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i42.5581. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17948932 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Kinet J.P. The high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI)from physiology to pathology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999;17:931–972. - PubMed
- Dombrowicz D., Brini A.T., Flamand V., Hicks E., Snouwaert J.N., Kinet J.P., Koller B.H. Anaphylaxis mediated through a humanized high affinity IgE receptor. J. Immunol. 1996;157:1645–1651. - PubMed
- Dombrowicz D., Lin S., Flamand V., Brini A.T., Koller B.H., Kinet J.P. Allergy-associated FcRbeta is a molecular amplifier of IgE- and IgG-mediated in vivo responses. Immunity. 1998;8:517–529. - PubMed
- Dombrowicz D., Flamand V., Brigman K.K., Koller B.H., Kinet J.P. Abolition of anaphylaxis by targeted disruption of the high affinity immunoglobulin E receptor alpha chain gene. Cell. 1993;75:969–976. - PubMed
- Fiocchi C. Inflammatory bowel diseaseetiology and pathogenesis. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:182–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases