Expression of natural killer receptor alleles at different Ly49 loci occurs independently and is regulated by major histocompatibility complex class I molecules - PubMed (original) (raw)
Expression of natural killer receptor alleles at different Ly49 loci occurs independently and is regulated by major histocompatibility complex class I molecules
D M Tanamachi et al. J Exp Med. 2001.
Abstract
Ly49 receptor genes are expressed by subsets of natural killer (NK) cells in an overlapping fashion, accounting for the capacity of NK subsets to attack host cells that have selectively downregulated self-major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. It was shown previously that most NK cells express only one or the other allele of a given Ly49 gene, while a smaller population expresses both alleles. However, the methods used to detect monoallelic and biallelic cells were nonquantitative. Here, new allele-specific antibodies were used to provide the first quantitative examination of biallelic and monoallelic expression of Ly49A and Ly49G2. The results demonstrate conclusively that most Ly49A(+) and Ly49G2(+) NK cells express the corresponding gene in a monoallelic fashion, with a smaller subset expressing both alleles. Unexpectedly, biallelic Ly49A(+) NK cells were more numerous than predicted by completely independent allelic expression, suggesting some heterogeneity among NK progenitors in the potential to express a given Ly49 gene. The data also show that cells expressing one allele of Ly49G2 may express Ly49A from the same or opposite chromosome with equal likelihood, indicating that the expressed allele is chosen independently for different Ly49 genes. Finally, the data demonstrate that biallelic expression of Ly49A or Ly49G2 occurs least frequently in mice that express ligands for these receptors (H-2(d) mice), and most frequently in class I-deficient mice. Thus, biallelic expression of Ly49 genes is regulated by interactions of NK cell progenitors with MHC class I molecules.
Figures
Figure 1
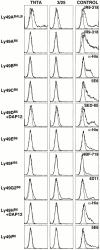
Specificity of TNTA and 3/25 mAbs. TNTA mAb (first column) or 3/25 mAb (second column) was used to stain COS cells transiently transfected with the indicated Ly49 expression constructs (solid lines) or untransfected COS cells (dashed lines). Ly49D and Ly49H constructs were cotransfected with a DAP12 expression construct. Ly49B, Ly49E, and Ly49H cDNAs were epitope (6x-His) tagged. Transiently transfected cells varied in transfection efficiency, as shown by staining with the appropriate Ly49-specific mAb or an anti-his rabbit polyclonal IgG in the case of tagged receptors (third column).
Figure 2
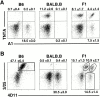
Predominantly monoallelic expression of Ly49A and Ly49G2. Freshly isolated, nylon wool nonadherent splenic cells from B6, BALB.B, and (B6 × BALB.B)F1 mice (all H-2b) were harvested. Gated DX5+CD3−CD8− NK cells were analyzed with (A) the Ly49AB6 specific mAb, A1, versus the Ly49ABALB specific mAb, TNTA, or (B) with Ly49G2B6-specific mAb 3/25 versus 4D11, which recognizes both Ly49G2B6 and Ly49G2BALB alleles. Data represent means ± SD of three or four determinations on cells from individual animals.
Figure 3
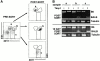
Cell sorting and identification of Ly49G2 populations. Pooled, freshly isolated nylon wool nonadherent spleen cells from (B6 × BALB.B)F1 mice were stained with NK1.1, 3/25, and 4D11. (A) Three populations of NK1.1+ cells were separated by cell sorting: (a) 3/25+4D11low; (b) 3/25+4D11high; and (c) 3/25−4D11+. As tested by postsort analysis, the populations were each of >90% purity. (B) The Ly49G2 alleles expressed by each population were determined by RT-PCR with Ly49G2 specific primers. Before electrophoresis, PCR products were digested with Taqα1, a diagnostic restriction enzyme that cleaves only the Ly49G2BALB cDNA. RT-PCR analysis was performed on cells immediately postsort (top) and after in vitro expansion for 10 d in the presence of IL-2 (bottom). Because the tubulin PCRs were tested only without digestion, the Taqα1 lanes are empty (ND). The experiment was repeated with NK cells from class I–deficient mice with identical results.
Figure 4
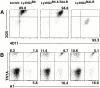
Independent allelic expression of Ly49A and Ly49G2. NK cells expressing Ly49G2B6 only, Ly49G2BALB only, or both Ly49G2B6 and Ly49G2BALB were sorted and expanded for 10–15 d in medium containing IL-2. (A) Reanalysis of the sorted populations with Ly49G2 mAbs demonstrated that they remained >89% pure after the culture. (B) Analysis of the sorted populations using allele-specific Ly49A mAbs. The experiment was repeated with NK cells from class I–deficient mice with similar results.
Figure 5
MHC class I molecules determine the extent of biallelic Ly49 expression. Freshly isolated, nylon wool nonadherent, gated DX5+CD3−CD8− NK cells from MHC-different mice were examined for mono- and biallelic expression of (A) Ly49A and (B) Ly49G2. In each case, Ly49 heterozygous (F1) mice were compared with the parental strains. Data represent means ± SD of three or four determinations on cells from individual animals.
Figure 5
MHC class I molecules determine the extent of biallelic Ly49 expression. Freshly isolated, nylon wool nonadherent, gated DX5+CD3−CD8− NK cells from MHC-different mice were examined for mono- and biallelic expression of (A) Ly49A and (B) Ly49G2. In each case, Ly49 heterozygous (F1) mice were compared with the parental strains. Data represent means ± SD of three or four determinations on cells from individual animals.
Similar articles
- An allele-specific, stochastic gene expression process controls the expression of multiple Ly49 family genes and generates a diverse, MHC-specific NK cell receptor repertoire.
Held W, Kunz B. Held W, et al. Eur J Immunol. 1998 Aug;28(8):2407-16. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199808)28:08<2407::AID-IMMU2407>3.0.CO;2-D. Eur J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9710218 - Expression of the Ly49A gene in murine natural killer cell clones is predominantly but not exclusively mono-allelic.
Held W, Raulet DH. Held W, et al. Eur J Immunol. 1997 Nov;27(11):2876-84. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830271120. Eur J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9394813 - MHC class I-Ly49 interactions shape the Ly49 repertoire on murine NK cells.
Fahlén L, Lendahl U, Sentman CL. Fahlén L, et al. J Immunol. 2001 Jun 1;166(11):6585-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.11.6585. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11359811 - Specificity, tolerance and developmental regulation of natural killer cells defined by expression of class I-specific Ly49 receptors.
Raulet DH, Held W, Correa I, Dorfman JR, Wu MF, Corral L. Raulet DH, et al. Immunol Rev. 1997 Feb;155:41-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1997.tb00938.x. Immunol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9059881 Review. - Regulation of class I major histocompatibility complex receptor expression in natural killer cells: one promoter is not enough!
Pascal V, Stulberg MJ, Anderson SK. Pascal V, et al. Immunol Rev. 2006 Dec;214:9-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2006.00452.x. Immunol Rev. 2006. PMID: 17100872 Review.
Cited by
- Implications of CD94 deficiency and monoallelic NKG2A expression for natural killer cell development and repertoire formation.
Vance RE, Jamieson AM, Cado D, Raulet DH. Vance RE, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jan 22;99(2):868-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.022500599. Epub 2002 Jan 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11782535 Free PMC article. - Differential expression of the Ly49G(B6), but not the Ly49G(BALB), receptor isoform during natural killer cell reconstitution after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Barao I, Wright PW, Sungur CM, Anderson SK, Redelman D, Murphy WJ. Barao I, et al. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013 Oct;19(10):1446-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.07.021. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23911940 Free PMC article. - Regulation of NK cell responsiveness to achieve self-tolerance and maximal responses to diseased target cells.
Joncker NT, Raulet DH. Joncker NT, et al. Immunol Rev. 2008 Aug;224:85-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00658.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18759922 Free PMC article. Review. - The epigenetic stability of the locus control region-deficient IgH locus in mouse hybridoma cells is a clonally varying, heritable feature.
Ronai D, Berru M, Shulman MJ. Ronai D, et al. Genetics. 2004 May;167(1):411-21. doi: 10.1534/genetics.167.1.411. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15166165 Free PMC article. - Characterization of T cell differentiation in the murine gut.
Lambolez F, Azogui O, Joret AM, Garcia C, von Boehmer H, Di Santo J, Ezine S, Rocha B. Lambolez F, et al. J Exp Med. 2002 Feb 18;195(4):437-49. doi: 10.1084/jem.20010798. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 11854357 Free PMC article.
References
- Biron C.A., Nguyen K.B., Pien G.C., Cousens L.P., Salazar-Mather T.P. Natural killer cells in antiviral defensefunction and regulation by innate cytokines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999;17:189–220. - PubMed
- Lanier L.L. NK cell receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998;16:359–393. - PubMed
- Moretta A., Bottino C., Vitale M., Pende D., Biassoni R., Mingari M.C., Moretta L. Receptors for HLA class-I molecules in human natural killer cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:619–648. - PubMed