Control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-kappaB - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-kappaB
A S Baldwin. J Clin Invest. 2001 Feb.
No abstract available
Figures
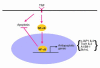
Figure 1
Induction of NF-κB by TNF or other stimuli leads to the transcriptional activation of genes that suppress apoptosis. The proteins encoded by the genes function at different levels in the caspase cascade to block apoptosis.
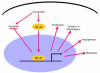
Figure 2
Roles of NF-κB in oncogenesis and in cancer chemo- and radioresistance. Activation of NF-κB blocks apoptosis, induces cell proliferation, potentially blocks differentiation, and promotes metastasis.
Similar articles
- [The Rel/NF-kappa-B transcription factors: complex role in cell regulation].
Bottex-Gauthier C, Pollet S, Favier A, Vidal DR. Bottex-Gauthier C, et al. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2002 Apr;50(3):204-11. doi: 10.1016/s0369-8114(02)00289-4. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2002. PMID: 11980335 Review. French. - The transcription factor NF-kappaB: control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance.
Mayo MW, Baldwin AS. Mayo MW, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Mar 27;1470(2):M55-62. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(00)00002-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10722927 Review. - Regulation of COX-2 protein expression by Akt in endometrial cancer cells is mediated through NF-kappaB/IkappaB pathway.
St-Germain ME, Gagnon V, Parent S, Asselin E. St-Germain ME, et al. Mol Cancer. 2004 Mar 11;3:7. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-3-7. Mol Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15016316 Free PMC article. - NF kappa B/I kappa B proteins. Their role in cell growth, differentiation and development. Madrid, Spain, July 7-10, 1996.
Siebenlist U. Siebenlist U. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Feb 22;1332(1):R7-13. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(96)00038-8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997. PMID: 9061013 No abstract available.
Cited by
- Pathogenesis of human B cell lymphomas.
Shaffer AL 3rd, Young RM, Staudt LM. Shaffer AL 3rd, et al. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:565-610. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075027. Epub 2012 Jan 6. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22224767 Free PMC article. Review. - The NF-kappaB/IL-6 pathway in metastatic androgen-independent prostate cancer: new therapeutic approaches?
Paule B, Terry S, Kheuang L, Soyeux P, Vacherot F, de la Taille A. Paule B, et al. World J Urol. 2007 Oct;25(5):477-89. doi: 10.1007/s00345-007-0175-6. Epub 2007 May 31. World J Urol. 2007. PMID: 17541600 Review. - Pathogenic B-cell receptor signaling in lymphoid malignancies: New insights to improve treatment.
Young RM, Phelan JD, Wilson WH, Staudt LM. Young RM, et al. Immunol Rev. 2019 Sep;291(1):190-213. doi: 10.1111/imr.12792. Immunol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31402495 Free PMC article. Review. - Herpesvirus ateles Tio can replace herpesvirus saimiri StpC and Tip oncoproteins in growth transformation of monkey and human T cells.
Albrecht JC, Biesinger B, Müller-Fleckenstein I, Lengenfelder D, Schmidt M, Fleckenstein B, Ensser A. Albrecht JC, et al. J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(18):9814-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.18.9814-9819.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15331715 Free PMC article. - Gene Therapy Applications to Cancer Treatment.
Scholl SM, Michaelis S, McDermott R. Scholl SM, et al. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2003;2003(1):35-47. doi: 10.1155/S1110724303209037. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 12686721 Free PMC article.
References
- Ghosh S, May M, Kopp E. NF-κB and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune respones. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998; 16:225–260. - PubMed
- Zhong H, Voll R, Ghosh S. Phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 by PKA stimulates transcriptional activity by promoting a novel bivalent interaction with the co-activator CBP/p300. Mol Cell. 1998; 1:661–671. - PubMed
- Gilmore T, Koedood M, Piffat K, White D. Rel/NF-κB/IκB proteins and cancer. Oncogene. 1996; 13:1367–1378. - PubMed
- Rayet B, Gelinas C. Aberrant Rel/NF-κB genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene. 1999; 18:6938–6947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources