NF-kappaB in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
NF-kappaB in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders
M P Mattson et al. J Clin Invest. 2001 Feb.
No abstract available
Figures
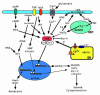
Figure 1
Signaling pathways that regulate NF-κB activity in neurons, and their possible involvement in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders. NF-κB in its inactive form is present in the cytosol as a three-subunit complex, with the prototypical components being p65 and p50 (transcription factor dimer) and IκBα (inhibitory subunit). NF-κB is activated by signals that activate IκB kinase (IKK), resulting in phosphorylation of IκBα; this targets IκBα for degradation in the proteosome and frees the p65-p50 dimer, which then translocates to the nucleus and binds to consensus κB sequences in the enhancer region of κB-responsive genes. Diverse signals can induce NF-κB activation, including TNF-α, sAPPα, NGF, and glutamate; increases in levels of intracellular Ca2+ and reactive oxygen species such as H2O2 can be potent activators of NF-κB. NF-κB induces the expression of several different genes that promote neuron survival, including those encoding manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD), inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins (IAPs), Bcl-2, and calbindin. Several signals that inhibit NF-κB activity are generated in neurons undergoing apoptosis; examples include prostate apoptosis response-4 (Par-4) and the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE). NF-κB is modulated by signals emanating from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria (MIT). AP1, activator protein-1; GRP78, glucose-regulated protein-78; JUNK, Jun NH2-terminal kinase; PKG, cGMP-dependent protein kinase.
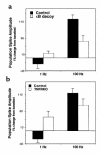
Figure 2
NF-κB in synaptic plasticity. (a) Population spike amplitudes recorded from hippocampal slices from adult mice, pretreated with either scrambled control DNA or κB decoy DNA and stimulated at either 1 or 100 Hz. Note that κB decoy DNA prevents LTD of synaptic transmission induced by stimulation at 1 Hz and attenuated long-term enhancement of synaptic transmission induced by stimulation at 100 Hz. (b) Population spike responses recorded from hippocampal slices from wild-type mice (Control) and mice lacking TNF-α receptors (TNFRKO) after stimulation at either 1 or 100 Hz. Note that LTD of synaptic transmission is not induced by stimulation at 1 Hz in slices from TNFRKO mice, and that long-term enhancement of synaptic transmission is attenuated in slices from TNFRKO mice. Modified from ref..
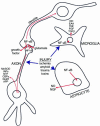
Figure 3
Complex roles for NF-κB in integrating signaling between and within neurons and glial cells. Following brain injury, NF-κB is activated in neurons and glial cells (astrocytes and microglia). Activation of NF-κB in neurons induces production of antiapoptotic gene products and proteins involved in modulating synaptic plasticity. Activation of NF-κB in glial cells results in production of proinflammatory cytokines, and potentially neurotoxic reactive oxygen species and excitotoxins. APP, amyloid precursor protein; CBPs, calcium-binding proteins; EAA, excitatory amino acid; GlutR, glutamate receptors; IAP, inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins; NO, nitric oxide; NTF, neurotrophic factor.
Similar articles
- NF-kappaB functions in the nervous system: from development to disease.
Mémet S. Mémet S. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Oct 30;72(9):1180-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.09.003. Epub 2006 Sep 12. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16997282 Review. - Role of nuclear factor kappa B in neuropathological mechanisms.
Cechetto DF. Cechetto DF. Prog Brain Res. 2001;132:391-404. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(01)32090-3. Prog Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11545005 Review. No abstract available. - NF-kappaB in the survival and plasticity of neurons.
Mattson MP. Mattson MP. Neurochem Res. 2005 Jun-Jul;30(6-7):883-93. doi: 10.1007/s11064-005-6961-x. Neurochem Res. 2005. PMID: 16187223 Review. - Potential roles for tumor necrosis factor and nuclear factor-kappaB in seizure activity.
Albensi BC. Albensi BC. J Neurosci Res. 2001 Oct 15;66(2):151-4. doi: 10.1002/jnr.1206. J Neurosci Res. 2001. PMID: 11592109 Review. No abstract available. - NF-kappaB signalling in cerebral ischaemia.
Schwaninger M, Inta I, Herrmann O. Schwaninger M, et al. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Dec;34(Pt 6):1291-4. doi: 10.1042/BST0341291. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 17073804
Cited by
- Unveiling the LncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Arsenic-Induced Nerve Injury in Rats through High-Throughput Sequencing.
Chu F, Lu C, Jiao Z, Yang W, Yang X, Ma H, Yu H, Wang S, Li Y, Sun D, Sun H. Chu F, et al. Toxics. 2023 Nov 22;11(12):953. doi: 10.3390/toxics11120953. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 38133354 Free PMC article. - Identification of Key Genes Mediated by N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase METTL3 in Ischemic Stroke via Bioinformatics Analysis and Experiments.
Liang T, Zhu L, Yang J, Huang X, Lv M, Liu S, Wen Z, Su L, Zhou L. Liang T, et al. Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jan;67(1):160-174. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00991-w. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38135832 - Dopamine activates NF-κB and primes the NLRP3 inflammasome in primary human macrophages.
Nolan RA, Reeb KL, Rong Y, Matt SM, Johnson HS, Runner K, Gaskill PJ. Nolan RA, et al. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020 Feb;2:100030. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2019.100030. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020. PMID: 33665636 Free PMC article. - Study on the mechanism of andrographolide activation.
Cai Q, Zhang W, Sun Y, Xu L, Wang M, Wang X, Wang S, Ni Z. Cai Q, et al. Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 13;16:977376. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.977376. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36177361 Free PMC article. Review. - Inhibition of the CEBPβ-NFκB interaction by nanocarrier-packaged Carnosic acid ameliorates glia-mediated neuroinflammation and improves cognitive function in an Alzheimer's disease model.
Yi-Bin W, Xiang L, Bing Y, Qi Z, Fei-Tong J, Minghong W, Xiangxiang Z, Le K, Yan L, Ping S, Yufei G, Ye X, Chun-Yan W. Yi-Bin W, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2022 Apr 7;13(4):318. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04765-1. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35393391 Free PMC article.
References
- Baeuerle P, Baltimore D. NF-κB: ten years after. Cell. 1996; 87:13–20. - PubMed
- O’Neill LA, Kaltschmidt C. NF-kappa B: a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends Neurosci. 1997; 20:252–258. - PubMed
- Moerman AM, Mao X, Lucas MM, Barger SW. Characterization of a neuronal κB-binding factor distinct from NF-κB. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999; 67:303–315. - PubMed
- Bruce AJ, et al. Altered neuronal and microglial responses to brain injury in mice lacking TNF receptors. Nat Med. 1996; 2:788–794. - PubMed
- Carter BD, et al. Selective activation of NF-κB by nerve growth factor through the neurotrophin receptor p75. Science. 1996; 272:542–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical