The F-box protein family - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The F-box protein family
E T Kipreos et al. Genome Biol. 2000.
Abstract
The F-box is a protein motif of approximately 50 amino acids that functions as a site of protein-protein interaction. F-box proteins were first characterized as components of SCF ubiquitin-ligase complexes (named after their main components, Skp I, Cullin, and an F-box protein), in which they bind substrates for ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. The F-box motif links the F-box protein to other components of the SCF complex by binding the core SCF component Skp I. F-box proteins have more recently been discovered to function in non-SCF protein complexes in a variety of cellular functions. There are 11 F-box proteins in budding yeast, 326 predicted in Caenorhabditis elegans, 22 in Drosophila, and at least 38 in humans. F-box proteins often include additional carboxy-terminal motifs capable of protein-protein interaction; the most common secondary motifs in yeast and human F-box proteins are WD repeats and leucine-rich repeats, both of which have been found to bind phosphorylated substrates to the SCF complex. The majority of F-box proteins have other associated motifs, and the functions of most of these proteins have not yet been defined.
Figures
Figure 1
The F-box consensus sequence. The consensus was derived from the alignment of 234 sequences used to create the Pfam F-box profile [30]; the single-letter amino-acid code is used. Bold and underlined capital letters signify residues found in over 40% of the F-box sequences; bold, non-underlined, capital letters signify residues found in 20-40% of the F-boxes; bold lower case letters indicate residues found in 15-19% of the F-boxes; and non-bold lower case letters indicate residues found in 10-14% of the F-boxes. A minority of F-boxes contain small insertions in the alignment after positions 11 or 24, or small (1-3 residue gaps) at various locations.
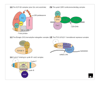
Figure 2
F-box protein functions. (a) The SCF complex. The F-box protein is linked to the SCF complex via interaction between the F-box and Skp1. A ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (Ubc) binds to the SCF complex and transfers ubiquitin (Ub) onto substrates bound by the F-box protein. When the substrate becomes poly-ubiquitinated, it is degraded by the 26S proteasome. (b) Skp1 binds to the F-box of Ctf13, facilitating Ctf13 phosphorylation, which allows Ctf13 to form the structural core of the CBF3 centromere-binding complex. (c) The F-box of Elongin A binds Elongin C (El C). The association of Elongins B and C with A increases Elongin A transcriptional activity. (d) The FOG-2/GLD-1 complex binds the 3' UTR of tra-2 mRNA to translationally repress it. The function of the F-box of FOG-2 is currently unknown. (e) Cyclin F binds to cyclin B1-cdc2 through a direct association of the cyclin F 'cyclin box' with the CRS domain of cyclin B1, and may be required for cyclin B1 nuclear localization. The function of the F-box of cyclin F is unknown. NLS, nuclear localization signal.
References
- Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, Harper JW, Elledge SJ. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell. 1996;86:263–274. This work was the first to recognize the F-box as a widespread protein motif,and demonstrated that the F-box bound to the Skp1 protein. - PubMed
- Cenciarelli C, Chiaur DS, Guardavaccaro D, Parks W, Vidal M, Pagano M. Identification of a family of human F-box proteins. Curr Biol. 1999;9:1177–1179. This paper extended the number of known F-box proteins in humans and demonstrated that F-box proteins without WD or LRR motifs can bind to SCF components in vivo. - PubMed
- Winston JT, Koepp DM, Zhu C, Elledge SJ, Harper JW. A family of mammalian F-box proteins. Curr Biol. 1999;9:1180–1182. Extended the number of known F-box proteins in humans and mice. - PubMed
- Clifford R, Lee M-H, Nayak S, Ohmachi M, Giorgini F, Schedl T. FOG-2, a novel F-box containing protein, associates with the GLD-1 RNA binding protein to direct male sex determination in the C. elegans hermaphrodite germline. Development. 2000. Demonstrates that the F-box protein FOG-2 functions in a protein complex with the RNA binding protein GLD-1 to repress tra-2 mRNA translation. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01-GM55297/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM57587/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA16087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM057587/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA76584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21-CA66229/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055297/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA076584/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases