Declining brain activity in cognitively normal apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 heterozygotes: A foundation for using positron emission tomography to efficiently test treatments to prevent Alzheimer's disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Declining brain activity in cognitively normal apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 heterozygotes: A foundation for using positron emission tomography to efficiently test treatments to prevent Alzheimer's disease
E M Reiman et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001.
Abstract
Cross-sectional positron emission tomography (PET) studies find that cognitively normal carriers of the apolipoprotein E (APOE) epsilon4 allele, a common Alzheimer's susceptibility gene, have abnormally low measurements of the cerebral metabolic rate for glucose (CMRgl) in the same regions as patients with Alzheimer's dementia. In this article, we characterize longitudinal CMRgl declines in cognitively normal epsilon4 heterozygotes, estimate the power of PET to test the efficacy of treatments to attenuate these declines in 2 years, and consider how this paradigm could be used to efficiently test the potential of candidate therapies for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease. We studied 10 cognitively normal epsilon4 heterozygotes and 15 epsilon4 noncarriers 50-63 years of age with a reported family history of Alzheimer's dementia before and after an interval of approximately 2 years. The epsilon4 heterozygotes had significant CMRgl declines in the vicinity of temporal, posterior cingulate, and prefrontal cortex, basal forebrain, parahippocampal gyrus, and thalamus, and these declines were significantly greater than those in the epsilon4 noncarriers. In testing candidate primary prevention therapies, we estimate that between 50 and 115 cognitively normal epsilon4 heterozygotes are needed per active and placebo treatment group to detect a 25% attenuation in these CMRgl declines with 80% power and P = 0.005 in 2 years. Assuming these CMRgl declines are related to the predisposition to Alzheimer's dementia, this study provides a paradigm for testing the potential of treatments to prevent the disorder without having to study thousands of research subjects or wait many years to determine whether or when treated individuals develop symptoms.
Figures
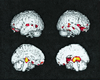
Figure 1
Statistical parametric map of significantly greater 2-year declines in regional CMRgl in cognitively normal APOE ɛ4 heterozygotes than in ɛ4 noncarriers (P < 0.001, uncorrected for multiple comparisons). Significant CMRgl declines (in color) are superimposed onto the left lateral, right lateral, left medial, and right medial surfaces of a spatially standardized volume-rendered MRI.
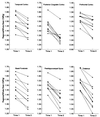
Figure 2
Two-year declines in regional CMRgl in cognitively normal APOE ɛ4 heterozygotes. These data were extracted from locations indicated in Table 2 and used to estimate the number of subjects needed to test the potential efficacy of Alzheimer's prevention therapies shown in Table 3.
Similar articles
- Correlations between apolipoprotein E epsilon4 gene dose and brain-imaging measurements of regional hypometabolism.
Reiman EM, Chen K, Alexander GE, Caselli RJ, Bandy D, Osborne D, Saunders AM, Hardy J. Reiman EM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jun 7;102(23):8299-302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500579102. Epub 2005 Jun 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15932949 Free PMC article. - Hypometabolism in Alzheimer-affected brain regions in cognitively healthy Latino individuals carrying the apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele.
Langbaum JB, Chen K, Caselli RJ, Lee W, Reschke C, Bandy D, Alexander GE, Burns CM, Kaszniak AW, Reeder SA, Corneveaux JJ, Allen AN, Pruzin J, Huentelman MJ, Fleisher AS, Reiman EM. Langbaum JB, et al. Arch Neurol. 2010 Apr;67(4):462-8. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.30. Arch Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20385913 Free PMC article. - Functional brain abnormalities in young adults at genetic risk for late-onset Alzheimer's dementia.
Reiman EM, Chen K, Alexander GE, Caselli RJ, Bandy D, Osborne D, Saunders AM, Hardy J. Reiman EM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 6;101(1):284-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2635903100. Epub 2003 Dec 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14688411 Free PMC article. - Linking brain imaging and genomics in the study of Alzheimer's disease and aging.
Reiman EM. Reiman EM. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Feb;1097:94-113. doi: 10.1196/annals.1379.011. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17413015 Review. - Cerebral blood flow and metabolic abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease.
Matsuda H. Matsuda H. Ann Nucl Med. 2001 Apr;15(2):85-92. doi: 10.1007/BF02988596. Ann Nucl Med. 2001. PMID: 11448080 Review.
Cited by
- Ushering in the study and treatment of preclinical Alzheimer disease.
Langbaum JB, Fleisher AS, Chen K, Ayutyanont N, Lopera F, Quiroz YT, Caselli RJ, Tariot PN, Reiman EM. Langbaum JB, et al. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013 Jul;9(7):371-81. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.107. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23752908 Free PMC article. Review. - Association between GAB2 haplotype and higher glucose metabolism in Alzheimer's disease-affected brain regions in cognitively normal APOEε4 carriers.
Liang WS, Chen K, Lee W, Sidhar K, Corneveaux JJ, Allen AN, Myers A, Villa S, Meechoovet B, Pruzin J, Bandy D, Fleisher AS, Langbaum JB, Huentelman MJ, Jensen K, Dunckley T, Caselli RJ, Kaib S, Reiman EM. Liang WS, et al. Neuroimage. 2011 Feb 1;54(3):1896-902. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.066. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 20888920 Free PMC article. - Correlations between apolipoprotein E epsilon4 gene dose and brain-imaging measurements of regional hypometabolism.
Reiman EM, Chen K, Alexander GE, Caselli RJ, Bandy D, Osborne D, Saunders AM, Hardy J. Reiman EM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jun 7;102(23):8299-302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500579102. Epub 2005 Jun 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15932949 Free PMC article. - Loss of cerebral white matter structural integrity tracks the gray matter metabolic decline in normal aging.
Kochunov P, Ramage AE, Lancaster JL, Robin DA, Narayana S, Coyle T, Royall DR, Fox P. Kochunov P, et al. Neuroimage. 2009 Mar 1;45(1):17-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.11.010. Epub 2008 Nov 25. Neuroimage. 2009. PMID: 19095067 Free PMC article.
References
- Evans D A, Funkenstein H H, Albert M S, Scherr P A, Cook N R, Chown M J, Hebert L E, Hennekens C H, Taylor J O. J Am Med Assoc. 1989;262:2551–2556. - PubMed
- Reiman E M, Caselli R J. Maturitas. 1999;31:185–200. - PubMed
- Terry R D, Katzman R, Bick K L, Sisodia S S, editors. Alzheimer Disease. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999.
- Vassar R, Bennett B D, Babu-Khan S, Kahn S, Mendiaz E A, Denis P, Teplow D B, Ross S, Amarante P, Loeloff R, et al. Science. 1999;286:735–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous