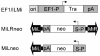Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis in human cells by the Drosophila mobile element Minos - PubMed (original) (raw)
Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis in human cells by the Drosophila mobile element Minos
A G Klinakis et al. EMBO Rep. 2000 Nov.
Abstract
The development of efficient non-viral methodologies for genome-wide insertional mutagenesis and gene tagging in mammalian cells is highly desirable for functional genomic analysis. Here we describe transposon mediated mutagenesis (TRAMM), using naked DNA vectors based on the Drosophila hydei transposable element Minos. By simple transfections of plasmid Minos vectors in HeLa cells, we have achieved high frequency generation of cell lines, each containing one or more stable chromosomal integrations. The Minos-derived vectors insert in different locations in the mammalian genome. Genome-wide mutagenesis in HeLa cells was demonstrated by using a Minos transposon containing a lacZ-neo gene-trap fusion to generate a HeLa cell library of at least 10(5) transposon insertions in active genes. Multiple gene traps for six out of 12 active genes were detected in this library. Possible applications of Minos-based TRAMM in functional genomics are discussed.
Figures
Fig. 1. _Minos_-derived vectors. Minos inverted terminal repeats are shown as block arrows. Arrowheads indicate the direction of transcription of the transposase (Tra) and neo genes. pA is polyadenylation signal; ori and S-P are the SV40 origin of replication and promoter, respectively.
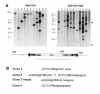
Fig. 2. MiLRneo insertions in individual HeLa clones. (A) Southern blot analysis of individual colonies. Genomic DNA (10 µg) was digested with the enzymes indicated before electrophoresis. The probe used is indicated by a grey bar. Arrowheads indicate the expected positions of diagnostic fragments derived from plasmid vector sequences. Lane H is from non-transfected cells. (B) Sequences flanking MiLRneo insertions. Transposon sequences and the target TA dinucleotide are in upper case.
Fig. 3. MiLRgeo gene-trap insertions. (A) The gene-trap construct MiLRgeo. The probe used for Southern blotting is indicated by a grey bar. (B) Southern blot analysis of individual HeLa lines stably transfected with MiLRgeo. Ten micrograms of DNA were digested with _Eco_RV. Lane H is from non-transfected cells. (C) Fusion cDNA and flanking intron sequences of a gene-trap insertion from clone T4. Transposon sequences and the target TA dinucleotide are in upper case.
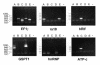
Fig. 4. Trapping of six genes in HeLa cells with MiLRgeo. Each panel shows agarose gel electrophoresis separated, ethidium bromide stained RT–PCR products that were recovered from five independent pools (A–E) of G418-resistant clones. The control lane corresponds to a reaction without template. The panels correspond to genes (accession numbers in brackets): elongation factor 1γ (EF1γ) (Z11531); ribosomal protein 18 (rs18) (X69150); DNA replication licensing factor homolog (hRlf) (D39073); G1 to S phase transition protein 1 homolog (GSPT1) (X17644); heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (hnRNP) (D28877); ATP synthase c-subunit (ATP-c) (X69908). Genes that were not detected are: thymidine kinase (M15205), ATP synthase γ-subunit (D16561), F-actin capping protein (U03271), a putative protein kinase C inhibitor (U51004), hypoxantine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (NM_000194) and cytochrome c core I protein (L16842).
Similar articles
- Minos as a genetic and genomic tool in Drosophila melanogaster.
Metaxakis A, Oehler S, Klinakis A, Savakis C. Metaxakis A, et al. Genetics. 2005 Oct;171(2):571-81. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.041848. Epub 2005 Jun 21. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15972463 Free PMC article. - Introduction of the transposable element Minos into the germ line of Drosophila melanogaster.
Loukeris TG, Arcà B, Livadaras I, Dialektaki G, Savakis C. Loukeris TG, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Oct 10;92(21):9485-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9485. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7568159 Free PMC article. - In vivo transposition of Minos, a Drosophila mobile element, in mammalian tissues.
Zagoraiou L, Drabek D, Alexaki S, Guy JA, Klinakis AG, Langeveld A, Skavdis G, Mamalaki C, Grosveld F, Savakis C. Zagoraiou L, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Sep 25;98(20):11474-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.201392398. Epub 2001 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11562481 Free PMC article. - Transposable elements as tools for genomics and genetics in Drosophila.
Ryder E, Russell S. Ryder E, et al. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003 Apr;2(1):57-71. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/2.1.57. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003. PMID: 15239944 Review. - Germline transgenesis and insertional mutagenesis in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis.
Sasakura Y. Sasakura Y. Dev Dyn. 2007 Jul;236(7):1758-67. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21111. Dev Dyn. 2007. PMID: 17342755 Review.
Cited by
- Minos and Restless transposon insertion mutagenesis of psychrotrophic fungus for red pigment synthesis adaptive to normal temperature.
Lu F, Ren Y, Ding L, Lu J, Zhou X, Liu H, Wang N, Cai M. Lu F, et al. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022 Nov 4;9(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s40643-022-00604-5. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022. PMID: 38647871 Free PMC article. - Asian Citrus Psyllid Expression Profiles Suggest Candidatus Liberibacter Asiaticus-Mediated Alteration of Adult Nutrition and Metabolism, and of Nymphal Development and Immunity.
Vyas M, Fisher TW, He R, Nelson W, Yin G, Cicero JM, Willer M, Kim R, Kramer R, May GA, Crow JA, Soderlund CA, Gang DR, Brown JK. Vyas M, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):e0130328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130328. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26091106 Free PMC article. - Regulation of DNA transposition by CpG methylation and chromatin structure in human cells.
Jursch T, Miskey C, Izsvák Z, Ivics Z. Jursch T, et al. Mob DNA. 2013 May 15;4(1):15. doi: 10.1186/1759-8753-4-15. Mob DNA. 2013. PMID: 23676100 Free PMC article. - Mariner transposons as genetic tools in vertebrate cells.
Delaurière L, Chénais B, Hardivillier Y, Gauvry L, Casse N. Delaurière L, et al. Genetica. 2009 Sep;137(1):9-17. doi: 10.1007/s10709-009-9370-2. Epub 2009 May 29. Genetica. 2009. PMID: 19479327 Review. - Passport, a native Tc1 transposon from flatfish, is functionally active in vertebrate cells.
Clark KJ, Carlson DF, Leaver MJ, Foster LK, Fahrenkrug SC. Clark KJ, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Mar;37(4):1239-47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn1025. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19136468 Free PMC article.
References
- Bellen H.J., O’Kane, C.J., Wilson, C., Grossniklaus, U., Pearson, R.K. and Gehring, W.J. (1989) P-element-mediated enhancer detection: a versatile method to study development in Drosophila. Genes Dev., 3, 1288–1300. - PubMed
- Bier E. et al. (1989) Searching for pattern and mutation in the Drosophila genome with a P-lacZ vector. Genes Dev., 3, 1273–1287. - PubMed
- Bonaldo P., Chowdhury, K., Stoykova, A., Torres, M. and Gruss, P. (1998) Efficient gene trap screening for novel developmental genes using IRES β geo vector and in vitro preselection. Exp. Cell Res., 244, 125–136. - PubMed
- Catteruccia F., Nolan, T., Loukeris, T.G., Blass, Savakis, C., Kafatos, F.C. and Crisanti, A. (2000b) Stable germline transformation of the malaria mosquito Anopheles stephensi. Nature, 405, 959–962 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases