Chunnel vision. Export and efflux through bacterial channel-tunnels - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Chunnel vision. Export and efflux through bacterial channel-tunnels
C Andersen et al. EMBO Rep. 2000 Oct.
Abstract
The Escherichia coli TolC protein is central to toxin export and drug efflux across the inner and outer cell membranes and the intervening periplasmic space. The crystal structure has revealed that TolC assembles into a remarkable alpha-helical trans-periplasmic cylinder (tunnel) embedded in the outer membrane by a contiguous beta-barrel (channel), so providing a large duct open to the outside environment. The channel-tunnel structure is conserved in TolC homologues throughout Gram-negative bacteria, and it is envisaged that they are recruited and opened, through a common mechanism, by substrate-specific inner-membrane complexes.
Figures
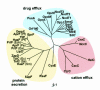
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic tree of the TolC family. The 36 TolC homologues for which function is known, or strongly implicated by the location of their genes in the export or efflux operons, sorted by TREEVIEW (Page, 1996) on the basis of a sequence alignment using MULTIALIN (Corpet, 1988). Abbreviations: Ea, Erwinia amylovora; Ec, Escherichia coli; Ech, Erwinia chrysanthemi; Se, Salmonella enteritidis; Sm, Serratia marcescens; Pa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Pf, Pseudomonas fluorescens. SilC1 may be an exception to the subgrouping as it is reported to be involved in silver efflux. Scale ‘0.1’ indicates 0.1 nucleotide substitutions. Note: the database has a further 20 homologues, with no ascribed function to date.
Fig. 2. The structures of bacterial OM proteins. (i) Top view of the proteins down the OM channel. In the case of TolC this extends to ∼2/3 of the height, i.e. the top 100 Å. (ii) Side view, at right angles to the plane of the OM. (iii) Cross-section of TolC near the tunnel entrance, i.e. the bottom 40 Å. Red, green and blue indicate individual monomers.
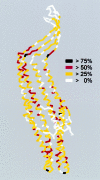
Fig. 3. Sequence conservation of TolC homologues related to the TolC structure. The TolC monomer coloured, as indicated, according to the level of consensus of individual amino acids throughout the known 56 TolC homologues. Alignment was performed using MULTIALIN (Corpet, 1988), consensus scores were calculated using the CLUSTAL function with matrix PAM350.
Fig. 4. Channel-tunnels of the TolC family acting in export and efflux. A model indicating reversible interaction of trimeric TolC homologues (green) with substrate-specific IM complexes containing an adaptor protein (red/blue) and an energy-providing protein of either the traffic ATPase (protein export, yellow) or proton antiporter families (small molecule efflux, purple). Escherichia coli TolC can act in both pathways, while in other bacteria multiple TolC homologues act separately in distinct pathways. In response to substrate engagement [a peptide chain, or hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs (stars)], the trimeric adaptor protein contacts the periplasmic tunnel, possibly via the predicted coiled-coil structures indicated, prompting the conformational change that opens the entrance.
Similar articles
- Channel-tunnels.
Koronakis V, Andersen C, Hughes C. Koronakis V, et al. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001 Aug;11(4):403-7. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(00)00224-4. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001. PMID: 11495730 Review. - Crystal structure of the bacterial membrane protein TolC central to multidrug efflux and protein export.
Koronakis V, Sharff A, Koronakis E, Luisi B, Hughes C. Koronakis V, et al. Nature. 2000 Jun 22;405(6789):914-9. doi: 10.1038/35016007. Nature. 2000. PMID: 10879525 - Channel-tunnels: outer membrane components of type I secretion systems and multidrug efflux pumps of Gram-negative bacteria.
Andersen C. Andersen C. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;147:122-65. doi: 10.1007/s10254-003-0008-y. Epub 2003 Mar 13. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12783268 Review. - Protein export and drug efflux through bacterial channel-tunnels.
Andersen C, Hughes C, Koronakis V. Andersen C, et al. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;13(4):412-6. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00229-5. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11454445 Review. - Structure and function of TolC: the bacterial exit duct for proteins and drugs.
Koronakis V, Eswaran J, Hughes C. Koronakis V, et al. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:467-89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.074104. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15189150 Review.
Cited by
- Kinetic study of membrane protein interactions: from three to two dimensions.
Adrien V, Reffay M, Taulier N, Verchère A, Monlezun L, Picard M, Ducruix A, Broutin I, Pincet F, Urbach W. Adrien V, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 9;14(1):882. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50827-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38195620 Free PMC article. - Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins.
Raetz CR, Whitfield C. Raetz CR, et al. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:635-700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.110601.135414. Epub 2001 Nov 9. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12045108 Free PMC article. Review. - Carboxy-terminal region involved in activity of Escherichia coli TolC.
Yamanaka H, Izawa H, Okamoto K. Yamanaka H, et al. J Bacteriol. 2001 Dec;183(23):6961-4. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.23.6961-6964.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11698388 Free PMC article. - Screening and purification of nanobodies from E. coli culture supernatants using the hemolysin secretion system.
Ruano-Gallego D, Fraile S, Gutierrez C, Fernández LÁ. Ruano-Gallego D, et al. Microb Cell Fact. 2019 Mar 11;18(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1094-0. Microb Cell Fact. 2019. PMID: 30857538 Free PMC article. - Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited.
Nikaido H. Nikaido H. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003 Dec;67(4):593-656. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.4.593-656.2003. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003. PMID: 14665678 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Benz R., Maier, E. and Gentschev, I. (1993) TolC of Escherichia coli functions as an outer membrane channel. Zentralbl. Bakteriol., 278, 187–196. - PubMed
- Buchanan S.K, Smith, B.S., Venkatramani, L., Xia, D., Esser, L., Palnitkar, M., Chakraborty, R., van der Helm, D. and Deisenhofer, J. (1999) Crystal structure of the outer membrane active transporter FepA from Escherichia coli. Nature Struct. Biol., 6, 56–63. - PubMed
- Cowan S.W., Schirmer, T., Rummel, G., Steiert, M., Ghosh, R., Pauptit, R.A., Jansonius, J.N. and Rosenbusch, J.P. (1992) Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E.coli porins. Nature, 358, 727–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases