Evidence for a susceptibility gene for autism on chromosome 2 and for genetic heterogeneity - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2001 Jun;68(6):1514-20.
doi: 10.1086/320588. Epub 2001 May 14.
Affiliations
- PMID: 11353400
- PMCID: PMC1226139
- DOI: 10.1086/320588
Evidence for a susceptibility gene for autism on chromosome 2 and for genetic heterogeneity
J D Buxbaum et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Jun.
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet 2001 Aug;69(2):470
Abstract
Although there is considerable evidence for a strong genetic component to idiopathic autism, several genomewide screens for susceptibility genes have been performed with limited concordance of linked loci, reflecting either numerous genes of weak effect and/or sample heterogeneity. Because decreasing sample heterogeneity would increase the power to identify genes, the effect on evidence for linkage of restricting a sample of autism-affected relative pairs to those with delayed onset (at age >36 mo) of phrase speech (PSD, for phrase speech delay) was studied. In the second stage of a two-stage genome screen for susceptibility loci involving 95 families with two or more individuals with autism or related disorders, a maximal multipoint heterogeneity LOD score (HLOD) of 1.96 and a maximal multipoint nonparametric linkage (NPL) score of 2.39 was seen on chromosome 2q. Restricting the analysis to the subset of families (n=49) with two or more individuals having a narrow diagnosis of autism and PSD generated a maximal multipoint HLOD score of 2.99 and an NPL score of 3.32. The increased scores in the restricted sample, together with evidence for heterogeneity in the entire sample, indicate that the restricted sample comprises a population that is more genetically homogeneous, which could therefore increase the likelihood of positional cloning of susceptibility loci.
Figures
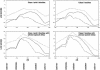
Figure 1
Multipoint analyses of chromosome 2q. Multipoint LOD analyses under dominant (solid lines) and recessive (dashed lines) modes of inheritance were performed (Vieland et al. ; Durner et al. 1999), with penetrance set at 50% (Greenberg et al. 1998) and allowing for locus heterogeneity (HLOD) (Smith ; Durner and Greenberg 1992). This simple approach works well for complex traits, even if true modes of inheritance and numbers of genes contributing to the disease are not known (Vieland et al. 1992_a,_ 1993). All genotyped family members were included in the analyses, and any individual not receiving a research diagnosis of autism, borderline autism, or Asperger disorder was defined as phenotypically unknown. Disease-allele frequency was arbitrarily set at .1 for recessive inheritance and .006 for dominant inheritance. Multipoint linkage analyses using nonparametric estimates of sharing were also performed using NPL (dotted lines) with GENEHUNTER (Kruglyak et al. 1996).
Similar articles
- Phenotypic homogeneity provides increased support for linkage on chromosome 2 in autistic disorder.
Shao Y, Raiford KL, Wolpert CM, Cope HA, Ravan SA, Ashley-Koch AA, Abramson RK, Wright HH, DeLong RG, Gilbert JR, Cuccaro ML, Pericak-Vance MA. Shao Y, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Apr;70(4):1058-61. doi: 10.1086/339765. Epub 2002 Mar 1. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 11875756 Free PMC article. - Evidence for a prostate cancer-susceptibility locus on chromosome 20.
Berry R, Schroeder JJ, French AJ, McDonnell SK, Peterson BJ, Cunningham JM, Thibodeau SN, Schaid DJ. Berry R, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Jul;67(1):82-91. doi: 10.1086/302994. Epub 2000 May 16. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10820130 Free PMC article. - The genetics of autism.
Muhle R, Trentacoste SV, Rapin I. Muhle R, et al. Pediatrics. 2004 May;113(5):e472-86. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.5.e472. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15121991 Review. - Genetic advances in autism: heterogeneity and convergence on shared pathways.
Bill BR, Geschwind DH. Bill BR, et al. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009 Jun;19(3):271-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.04.004. Epub 2009 May 26. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2009. PMID: 19477629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A Novel Stratification Method in Linkage Studies to Address Inter- and Intra-Family Heterogeneity in Autism.
Talebizadeh Z, Arking DE, Hu VW. Talebizadeh Z, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Jun 26;8(6):e67569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067569. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840741 Free PMC article. - Stratification based on language-related endophenotypes in autism: attempt to replicate reported linkage.
Spence SJ, Cantor RM, Chung L, Kim S, Geschwind DH, Alarcón M. Spence SJ, et al. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2006 Sep 5;141B(6):591-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30329. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2006. PMID: 16752361 Free PMC article. - Evidence for a language quantitative trait locus on chromosome 7q in multiplex autism families.
Alarcón M, Cantor RM, Liu J, Gilliam TC, Geschwind DH; Autism Genetic Research Exchange Consortium. Alarcón M, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Jan;70(1):60-71. doi: 10.1086/338241. Epub 2001 Dec 6. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 11741194 Free PMC article. - An estimating function approach to linkage heterogeneity.
Gao H, Zhou Y, Ma W, Liu H, Zhao L. Gao H, et al. J Genet. 2013 Dec;92(3):413-21. doi: 10.1007/s12041-013-0282-7. J Genet. 2013. PMID: 24371163 - Clinical heterogeneity among people with high functioning autism spectrum conditions: evidence favouring a continuous severity gradient.
Ring H, Woodbury-Smith M, Watson P, Wheelwright S, Baron-Cohen S. Ring H, et al. Behav Brain Funct. 2008 Feb 20;4:11. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-4-11. Behav Brain Funct. 2008. PMID: 18289376 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for autism/autistic disorder [MIM <209850>]).
References
- Ashley-Koch A, Wolpert CM, Menold MM, Zaeem L, Basu S, Donnelly SL, Ravan SA, Powell CM, Qumsiyeh MB, Aylsworth AS, Vance JM, Gilbert JR, Wright HH, Abramson RK, DeLong GR, Cuccaro ML, Pericak-Vance MA (1999) Genetic studies of autistic disorder and chromosome 7. Genomics 61:227–236 - PubMed
- Auranen M, Nieminen T, Majuri S, Vanhala R, Peltonen L, Jarvela I (2000) Analysis of autism susceptibility gene loci on chromosomes 1p, 4p, 6q, 7q, 13q, 15q, 16p, 17q, 19q and 22q in Finnish multiplex families. Mol Psychiatry 5:320–322 - PubMed
- Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, Yuzda E, Rutter M (1995) Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med 25:63–77 - PubMed
- Barrett S, Beck JC, Bernier R, Bisson E, Braun TA, Casavant TL, Childress D, et al (1999) An autosomal genomic screen for autism: collaborative linkage study of autism. Am J Med Genet 88:609–615 - PubMed
- Bass MP, Menold MM, Joyner KL, Wolpert CM, Donnelly SL, Ravan SA, McClain C, vonWendt L, Gilbert JR, Wright HH, Abramson RK, DeLong GR, Cuccaro ML, Pericak-Vance MA (2000) Association analysis of GI candidate genes in autistic disorder. Am J Hum Genet 67 Suppl:S49
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources