Oxacillinase-mediated resistance to cefepime and susceptibility to ceftazidime in Pseudomonas aeruginosa - PubMed (original) (raw)
Oxacillinase-mediated resistance to cefepime and susceptibility to ceftazidime in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D Aubert et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Jun.
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate SOF-1 was resistant to cefepime and susceptible to ceftazidime. This resistance phenotype was explained by the expression of OXA-31, which shared 98% amino acid identity with a class D beta-lactamase, OXA-1. The oxa-31 gene was located on a ca. 300-kb nonconjugative plasmid and on a class 1 integron. No additional efflux mechanism for cefepime was detected in P. aeruginosa SOF-1. Resistance to cefepime and susceptibility to ceftazidime in P. aeruginosa were conferred by OXA-1 as well.
Figures
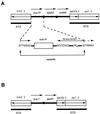
FIG. 1
Structure of the class 1 integrons that contain oxa-31 (A) and oxa-1 (B) cassettes. The arrows indicate the transcriptional orientations of the ORFs.
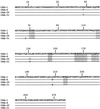
FIG. 2
Comparison of the amino acid sequence of β-lactamase OXA-31 to those of OXA-1, OXA-4, and OXA-30. Dashes indicate identical amino acids. The numbering is according to DBL (13). The highlighted boxes indicate conserved regions within class D β-lactamases.
FIG. 3
Intracellular accumulation of cefepime and norfloxacin in P. aeruginosa clinical isolate SOF-1. The intracellular concentrations of radiolabeled norfloxacin (A) and cefepime (B) were measured in cells of P. aeruginosa SOF-1 with (●) or without (□) the energy uncoupler CCCP. Values are means of two independent experiments.
Similar articles
- In vivo selection of oxacillinase-mediated ceftazidime resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Leotard S, Poirel L, Leblanc PE, Nordmann P. Leotard S, et al. Microb Drug Resist. 2001 Fall;7(3):273-5. doi: 10.1089/10766290152652828. Microb Drug Resist. 2001. PMID: 11759089 - Comparative in-vitro activities of newer cephalosporins cefclidin, cefepime, and cefpirome against ceftazidime- or imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Watanabe N, Hiruma R, Katsu K. Watanabe N, et al. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Nov;30(5):633-41. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.5.633. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992. PMID: 1493980 - Mechanisms of resistance in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa less susceptible to cefepime than to ceftazidime.
Campo Esquisabel AB, Rodríguez MC, Campo-Sosa AO, Rodríguez C, Martínez-Martínez L. Campo Esquisabel AB, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011 Dec;17(12):1817-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03530.x. Epub 2011 May 23. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011. PMID: 21599797 - [New antimicrobial agent series IL: cefepime].
Hara K. Hara K. Jpn J Antibiot. 1996 Aug;49(8):766-81. Jpn J Antibiot. 1996. PMID: 8910134 Review. Japanese. No abstract available. - [New antimicrobial agent series XVII: Ceftazidime].
Ishibiki K. Ishibiki K. Jpn J Antibiot. 1986 Nov;39(11):2819-30. Jpn J Antibiot. 1986. PMID: 3102806 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Involvement of the MexXY-OprM efflux system in emergence of cefepime resistance in clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Hocquet D, Nordmann P, El Garch F, Cabanne L, Plésiat P. Hocquet D, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Apr;50(4):1347-51. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.4.1347-1351.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16569851 Free PMC article. - Genetic and biochemical characterization of a chromosome-encoded carbapenem-hydrolyzing ambler class D beta-lactamase from Shewanella algae.
Héritier C, Poirel L, Nordmann P. Héritier C, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 May;48(5):1670-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.5.1670-1675.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15105119 Free PMC article. - Modes and modulations of antibiotic resistance gene expression.
Depardieu F, Podglajen I, Leclercq R, Collatz E, Courvalin P. Depardieu F, et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007 Jan;20(1):79-114. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00015-06. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17223624 Free PMC article. Review. - Inhibition of OXA-1 beta-lactamase by penems.
Bethel CR, Distler AM, Ruszczycky MW, Carey MP, Carey PR, Hujer AM, Taracila M, Helfand MS, Thomson JM, Kalp M, Anderson VE, Leonard DA, Hujer KM, Abe T, Venkatesan AM, Mansour TS, Bonomo RA. Bethel CR, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Sep;52(9):3135-43. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01677-07. Epub 2008 Jun 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18559643 Free PMC article. - Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Narrative Review of Antibiogram Interpretation and Emerging Treatments.
Giovagnorio F, De Vito A, Madeddu G, Parisi SG, Geremia N. Giovagnorio F, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Nov 12;12(11):1621. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12111621. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Chen H Y, Yuan M, Livermore D M. Mechanisms of resistance to β-lactam antibiotics amongst Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates collected in the UK in 1993. J Med Microbiol. 1995;43:300–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources