A genomewide screen for autism susceptibility loci - PubMed (original) (raw)
A genomewide screen for autism susceptibility loci
J Liu et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Aug.
Abstract
We report the analysis of 335 microsatellite markers genotyped in 110 multiplex families with autism. All families include at least two "affected" siblings, at least one of whom has autism; the remaining affected sibs carry diagnoses of either Asperger syndrome or pervasive developmental disorder. Affected sib-pair analysis yielded multipoint maximum LOD scores (MLS) that reach the accepted threshold for suggestive linkage on chromosomes 5, X, and 19. Nominal evidence for linkage (point-wise P<.05) was obtained on chromosomes 2, 3, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 15, 16, 18, and 20, and secondary loci were found on chromosomes 5 and 19. Analysis of families sharing alleles at the putative X chromosomal linked locus and one or more other putative linked loci produced an MLS of 3.56 for the DXS470-D19S174 marker combination. In an effort to increase power to detect linkage, scan statistics were used to evaluate the significance of peak LOD scores based on statistical evidence at adjacent marker loci. This analysis yielded impressive evidence for linkage to autism and autism-spectrum disorders with significant genomewide P values <.05 for markers on chromosomes 5 and 8 and with suggestive linkage evidence for a marker on chromosome 19.
Figures
Figure 1
Chromosome-wise results from MAPMAKER/SIBS multipoint ASP analysis. Solid lines represent results based on use of the narrow diagnosis, and dashed lines represent results based on use of the broad diagnosis.
Figure 1
Chromosome-wise results from MAPMAKER/SIBS multipoint ASP analysis. Solid lines represent results based on use of the narrow diagnosis, and dashed lines represent results based on use of the broad diagnosis.
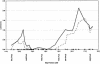
Figure 2
LOD scores from multipoint ASP analysis of 160 nuclear families. Microsatellite markers used in the original genome scan are shown as unfilled triangles along the X axis. New microsatellite markers not included in the original scan are depicted as blackened triangles. Solid lines represent results based on use of the narrow diagnosis, and dashed lines represent results based on use of the broad diagnosis.
Similar articles
- A genomewide screen of 345 families for autism-susceptibility loci.
Yonan AL, Alarcón M, Cheng R, Magnusson PK, Spence SJ, Palmer AA, Grunn A, Juo SH, Terwilliger JD, Liu J, Cantor RM, Geschwind DH, Gilliam TC. Yonan AL, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Oct;73(4):886-97. doi: 10.1086/378778. Epub 2003 Sep 17. Am J Hum Genet. 2003. PMID: 13680528 Free PMC article. - A genomewide scan identifies two novel loci involved in specific language impairment.
SLI Consortium. SLI Consortium. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Feb;70(2):384-98. doi: 10.1086/338649. Epub 2002 Jan 4. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 11791209 Free PMC article. - A genomewide screen for autism: strong evidence for linkage to chromosomes 2q, 7q, and 16p.
International Molecular Genetic Study of Autism Consortium (IMGSAC). International Molecular Genetic Study of Autism Consortium (IMGSAC). Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Sep;69(3):570-81. doi: 10.1086/323264. Epub 2001 Jul 30. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11481586 Free PMC article. - The genetics of autism.
Muhle R, Trentacoste SV, Rapin I. Muhle R, et al. Pediatrics. 2004 May;113(5):e472-86. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.5.e472. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15121991 Review. - [Genetic factors in Asperger syndrome].
Sasaki T. Sasaki T. Nihon Rinsho. 2007 Mar;65(3):443-8. Nihon Rinsho. 2007. PMID: 17354555 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
- Protein Biomarkers of Autism Spectrum Disorder Identified by Computational and Experimental Methods.
Yao F, Zhang K, Feng C, Gao Y, Shen L, Liu X, Ni J. Yao F, et al. Front Psychiatry. 2021 Feb 25;12:554621. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.554621. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33716802 Free PMC article. - Contribution of common and rare variants of the PTCHD1 gene to autism spectrum disorders and intellectual disability.
Torrico B, Fernàndez-Castillo N, Hervás A, Milà M, Salgado M, Rueda I, Buitelaar JK, Rommelse N, Oerlemans AM, Bralten J, Freitag CM, Reif A, Battaglia A, Mazzone L, Maestrini E, Cormand B, Toma C. Torrico B, et al. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015 Dec;23(12):1694-701. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2015.37. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 25782667 Free PMC article. - Recurrence rates provide evidence for sex-differential, familial genetic liability for autism spectrum disorders in multiplex families and twins.
Werling DM, Geschwind DH. Werling DM, et al. Mol Autism. 2015 May 13;6:27. doi: 10.1186/s13229-015-0004-5. eCollection 2015. Mol Autism. 2015. PMID: 25973164 Free PMC article. - Alterations of presynaptic proteins in autism spectrum disorder.
Yeo XY, Lim YT, Chae WR, Park C, Park H, Jung S. Yeo XY, et al. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Nov 17;15:1062878. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1062878. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36466804 Free PMC article. Review. - Presence of large deletions in kindreds with autism.
Yu CE, Dawson G, Munson J, D'Souza I, Osterling J, Estes A, Leutenegger AL, Flodman P, Smith M, Raskind WH, Spence MA, McMahon W, Wijsman EM, Schellenberg GD. Yu CE, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Jul;71(1):100-15. doi: 10.1086/341291. Epub 2002 Jun 7. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 12058345 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
- Autism Genetic Resource Exchange, http://www.agre.org (for DNA samples)
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for fluorescence-labeled genome screening set)
- Cure Autism Now Foundation, http://www.canfoundation.org (for recruitment of families affected by autism)
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for autism [MIM209850], fragile X syndrome [MIM <309550>] and tuberous sclerosis [MIM191100])
References
- Adams P (1994) LABMAN and LINKMAN: a data management system specifically designed for genome searches of complex diseases. Genet Epidemiol 11:87–98 - PubMed
- Aita VM, Liu J, Knowles JA, Terwilliger JD, Baltazar R, Grunn A, Loth JE, Kanyas K, Lerer B, Endicott J, Wang Z, Penchaszadeh G, Gilliam TC, Baron M (1999) A comprehensive linkage analysis of chromosome 21q22 supports prior evidence for a putative bipolar affective disorder locus. Am J Hum Genet 64:210–217 - PMC - PubMed
- Anderson GM, Freedman DX, Cohen DJ, Volkmar FR, Hoder EL, McPhedran P, Minderaa RB, Hansen CR, Young JG (1987) Whole blood serotonin in autistic and normal subjects. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 28:885–900 - PubMed
- Anderson MA, Gusella JF (1984) Use of cyclosporin A in establishing Epstein-Barr virus–transformed human lymphoblastoid cell lines. In Vitro 20:856–858 - PubMed
- Ashley-Koch A, Wolpert CM, Menold MM, Zaeem L, Basu S, Donnelly SL, Ravan SA, Powell CM, Qumsiyeh MB, Aylsworth AS, Vance JM, Gilbert JR, Wright HH, Abramson RK, DeLong GR, Cuccaro ML, Pericak-Vance MA (1999) Genetic studies of autistic disorder and chromosome 7. Genomics 61:227–236 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases