A role for dopamine D1 receptors of the nucleus accumbens shell in conditioned taste aversion learning - PubMed (original) (raw)
A role for dopamine D1 receptors of the nucleus accumbens shell in conditioned taste aversion learning
S Fenu et al. J Neurosci. 2001.
Abstract
The involvement of dopamine (DA) in conditioned taste aversion (CTA) learning was studied with saccharin or sucrose as the conditioned stimulus (CS) and intraperitoneal lithium as the unconditioned stimulus (US). The dopamine D(1) antagonist R(+)-7-chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine hydrochloride (SCH 23390) (12.5-50 microg/kg, s.c.), given 5 min after the CS, impaired the acquisition of CTA in a paradigm consisting of three or a single CS-lithium association. SCH 23390 failed to impair CTA acquisition given 45 min after, 30 min before, or right before the CS. (-)-trans-6,7,7a,8,9,13b-hexahydro-3-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-methyl-5a-benzo-(d)-naphtho-(2,1b) azepine (SCH 39166) (12.5-50.0 microg/kg, s.c), a SCH 23390 analog that does not bind to 5HT(2) receptors, also impaired CTA. No significant impairment of CTA was obtained after administration of the specific D(2)/D(3) antagonist raclopride (100 and 300 microg/kg, s.c.). The ability of SCH 23390 to impair CTA learning was confirmed by its ability to reduce the conditional aversive reactions to a gustatory CS (sweet chocolate) as estimated in a taste reactivity paradigm. SCH 39166 impaired CTA also when infused in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) shell 5 min after the CS. No impairment was obtained from the NAc core or from the bed nucleus stria terminalis. The results indicate that D(1) receptor blockade impairs CTA learning by disrupting the formation of a short-term memory trace of the gustatory CS and that endogenous dopamine acting on D(1) receptors in the NAc shell plays a role in short-term memory processes related to associative gustatory learning.
Figures
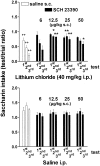
Fig. 1.
Effect of systemic SCH 23390 or saline on saccharin intake conditioned by multiple association with lithium chloride (top panel) or unconditioned (bottom panel). SCH 23390 was given subcutaneously 5 min after saccharin, whereas lithium chloride was given 30 min thereafter. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of test per trial ratio of saccharin intake in 20 min.+p < 0.05 or++p < 0.005 versus intraperitoneal saline; *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.005 versus lithium.
Fig. 2.
Effect of SCH 23390 and SCH 39166 on the intake of saccharin or sucrose either unconditioned or conditioned by lithium chloride. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of test per trial ratio of saccharin intake in 20 min. a, 6.0 μg/kg, s.c.; b, 12.5 μg/kg, s.c.; c, 25 μg/kg, s.c.; d, 50 μg/kg, s.c.++p < 0.005 versus intraperitoneal saline; *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.005 versus lithium.
Fig. 3.
Effect of delay between systemic SCH 23390 and saccharin (top panel) or sucrose (bottom panel) on CTA learning.++p < 0.005 versus intraperitoneal saline; **p < 0.005 versus lithium.
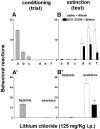
Fig. 4.
Effect of SCH 23390 (25 μg/kg, s.c.) on the acquisition of aversive reactions to chocolate induced by a single association with lithium chloride (125 mg/kg, i.p.). Conditioning (trial): hedonic and aversive reactions to chocolate (A, individual; A′, total). Extinction (test): aversive and hedonic reactions to chocolate after saline (open bars) or SCH 23390 (filled bars) plus lithium (B, individual; B′, total). Each bar represents the means ± SEM of hedonic and aversive reactions.a, Rhythmic tongue protrusion; _b,_sniffing; c, paw licks; d, gapes;e, chin rubs; f, paw tread. *p < 0.05 versus subcutaneous saline.
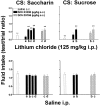
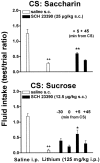
Fig. 5.
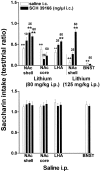
Effect of infusion of SCH 39166 or saline in the NAc shell, NAc core, LHA, and BNST on saccharin intake conditioned by lithium chloride (80 or 125 mg/kg, i.p; top panel) or unconditioned (bottom panel). Differences between groups were evaluated by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test.++p < 0.005 versus intraperitoneal saline; *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.005 versus lithium.
Fig. 6.
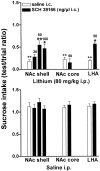
Effect of infusion of SCH 39166 or saline in the NAc shell, NAc core, LHA, and BNST on sucrose intake conditioned by lithium chloride (80 or 125 mg/kg, i.p.; top panel) or unconditioned (bottom panel). Differences between groups were evaluated by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test.++p < 0.005 versus saline; *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.005 versus lithium.
Fig. 7.
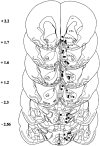
Brain sections showing intracerebral injection sites. Section levels are according to Paxinos and Watson (1999).Filled circles, Correct injection sites; filled squares, incorrect injection sites (cc, corpus callosum; Cpu, caudate putamen; _NAc Sh,_nucleus accumbens shell; NAc Co, nucleus accumbens core;LHA, lateral hypothalamic area).
Similar articles
- Dopamine and learned food preferences.
Sclafani A, Touzani K, Bodnar RJ. Sclafani A, et al. Physiol Behav. 2011 Jul 25;104(1):64-8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.04.039. Epub 2011 May 1. Physiol Behav. 2011. PMID: 21549727 Free PMC article. Review. - Facilitation of conditioned taste aversion learning by systemic amphetamine: role of nucleus accumbens shell dopamine D1 receptors.
Fenu S, Di Chiara G. Fenu S, et al. Eur J Neurosci. 2003 Oct;18(7):2025-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02899.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14622235 - Differential involvement of dopamine D1 receptors in morphine- and lithium-conditioned saccharin avoidance.
Fenu S, Rivas E, Di Chiara G. Fenu S, et al. Physiol Behav. 2009 Jan 8;96(1):73-7. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2008.08.017. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Physiol Behav. 2009. PMID: 18790704 - Role of NMDA, opioid and dopamine D1 and D2 receptor signaling in the acquisition of a quinine-conditioned flavor avoidance in rats.
Rotella FM, Badalia A, Duenas SM, Hossain M, Saeed S, Touzani K, Sclafani A, Bodnar RJ. Rotella FM, et al. Physiol Behav. 2014 Apr 10;128:133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.01.014. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Physiol Behav. 2014. PMID: 24508751 - Molecular signals into the insular cortex and amygdala during aversive gustatory memory formation.
Bermúdez-Rattoni F, Ramírez-Lugo L, Gutiérrez R, Miranda MI. Bermúdez-Rattoni F, et al. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2004 Feb;24(1):25-36. doi: 10.1023/b:cemn.0000012722.45805.c8. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15049508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Role of the dopaminergic system in the acquisition, expression and reinstatement of MDMA-induced conditioned place preference in adolescent mice.
Vidal-Infer A, Roger-Sánchez C, Daza-Losada M, Aguilar MA, Miñarro J, Rodríguez-Arias M. Vidal-Infer A, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043107. Epub 2012 Aug 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22916213 Free PMC article. - Morphine-conditioned single-trial place preference: role of nucleus accumbens shell dopamine receptors in acquisition, but not expression.
Fenu S, Spina L, Rivas E, Longoni R, Di Chiara G. Fenu S, et al. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006 Aug;187(2):143-53. doi: 10.1007/s00213-006-0415-2. Epub 2006 May 25. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006. PMID: 16724186 - NMDA and muscarinic receptors of the nucleus accumbens have differential effects on taste memory formation.
Ramírez-Lugo L, Zavala-Vega S, Bermúdez-Rattoni F. Ramírez-Lugo L, et al. Learn Mem. 2006 Jan-Feb;13(1):45-51. doi: 10.1101/lm.103206. Learn Mem. 2006. PMID: 16452653 Free PMC article. - Dopamine and learned food preferences.
Sclafani A, Touzani K, Bodnar RJ. Sclafani A, et al. Physiol Behav. 2011 Jul 25;104(1):64-8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.04.039. Epub 2011 May 1. Physiol Behav. 2011. PMID: 21549727 Free PMC article. Review. - The Mesoaccumbens Pathway: A Retrograde Labeling and Single-Cell Axon Tracing Analysis in the Mouse.
Rodríguez-López C, Clascá F, Prensa L. Rodríguez-López C, et al. Front Neuroanat. 2017 Mar 27;11:25. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00025. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 28396627 Free PMC article.
References
- Acquas E, Di Chiara G. D1 receptors blockade stereospecifically impairs the acquisition of drug-conditioned place-preference and place-aversion. Behav Pharmacol. 1994;5:555–569. - PubMed
- Acquas E, Carboni E, Leone P, Di Chiara G. SCH 23390 blocks drug-conditioned place-preference and place-aversion: anhedonia (lack of reward) or apathy (lack of motivation) after dopamine-receptor blockade? Psychopharmacology. 1989;99:151–155. - PubMed
- Bassareo V, Di Chiara G. Modulation of feeding-induced activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by appetitive stimuli and its relation to motivational state. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:4389–4397. - PubMed
- Beninger RJ. The role of dopamine in locomotor activity and learning. Brain Res Rev. 1983;6:173–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous