Glutamate-induced transient modification of the postsynaptic density - PubMed (original) (raw)
Glutamate-induced transient modification of the postsynaptic density
A Dosemeci et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001.
Abstract
Depolarization of rat hippocampal neurons with a high concentration of external potassium induces a thickening of postsynaptic densities (PSDs) within 1.5-3 min. After high-potassium treatment, PSDs thicken 2.1-fold in cultured neurons and 1.4-fold in hippocampal slices compared with their respective controls. Thin-section immunoelectron microscopy of hippocampal cultures indicates that at least part of the observed thickening of PSDs can be accounted for by an accumulation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) on their cytoplasmic faces. Indeed, PSD-associated gold label for CaMKII increases 5-fold after depolarization with potassium. The effects of high-potassium treatment on the composition and structure of the PSDs are mimicked by direct application of glutamate. In cultures, glutamate-induced thickening of PSDs and the accumulation of CaMKII on PSDs are reversed within 5 min of removal of glutamate and Ca(2+) from the extracellular medium. These results suggest that PSDs are dynamic structures whose thickness and composition are subject to rapid and transient changes during synaptic activity.
Figures
Figure 1
Measurement of the thickness and the amount of gold label associated with PSDs. A cytoplasmic outline of the PSD was traced by hand. This area was then enclosed by tracing the postsynaptic membrane separately. The average thickness of the PSD was calculated by dividing the outlined area by the length of the postsynaptic membrane. The intensity of the gold label was estimated as the number of silver-enhanced gold particles within the outline around the PSD divided by the length of the corresponding postsynaptic membrane.
Figure 2
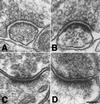
Brief depolarization with high K+ induces thickening of PSDs in hippocampal cultures (A and B) and hippocampal slices (C and D). Hippocampal cultures were incubated for 3 min either in normal incubation medium (A) or in medium containing 90 mM KCl (B) before fixation. After recovery hippocampal slices were perfused for 90 s in either normal ACSF (C) or in ACSF containing 90 mM KCl (D) and fixed immediately. In media containing 90 mM KCl, osmolarity was adjusted by an equivalent reduction in [NaCl]. (Bar = 100 nm.)
Figure 3
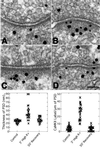
Reversible thickening of PSDs induced by high K+ is accompanied by a reversible increase in CaMKII labeling. Cultures were incubated in either normal incubation medium (A) or medium containing 90 mM KCl (B and C) and fixed immediately. One group of cultures was allowed to recover for 30 min after exposure to high K+ (D). After fixation, samples were immunogold labeled with an antibody against CaMKII. Silver-enhanced gold particles appear as black grains of variable size. (Bar = 100 nm.) (Bottom) Scatter plots show measurements of the thickness (Bottom Left) and CaMKII label intensity (Bottom Right) of PSDs in parallel experiments. Each point corresponds to a measurement from an individual PSD. Between 22 and 24 PSDs were analyzed per group.
Figure 4
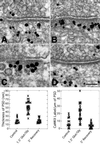
Glutamate/glycine application mimics the effects of high-K+ depolarization. Cultures were incubated in either normal incubation medium (A) or the same medium containing 100 mM glutamate/10 mM glycine for 90 s (B and C). After exposure to glutamate, one group of samples was washed and incubated for an additional 5 min in Ca2+-free incubation medium (D). A, B and C, D represent pairs from two separate experiments. (Bar = 100 nm.) (Bottom) Measurements of the thickness of the PSDs (Bottom Left) and intensity of CaMKII gold label (Bottom Right) are presented as scatter plots. Each point corresponds to a measurement from an individual PSD. Between 15 and 20 PSDs were analyzed per group.
Figure 5
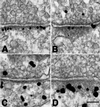
Immunogold labeling pattern for PSD-95 is distinct from that for CaMKII. Cultures were labeled with an antibody against PSD-95 (A and B) or with an antibody against CaMKII (C and D) after 3-min exposure to either normal incubation medium (A and C) or medium containing 100 μM glutamate/10 μM glycine (B and D). (Bar = 100 nm.)
Similar articles
- Inhibition of phosphatase activity prolongs NMDA-induced modification of the postsynaptic density.
Dosemeci A, Vinade L, Winters CA, Reese TS, Tao-Cheng JH. Dosemeci A, et al. J Neurocytol. 2002 Sep-Nov;31(8-9):605-12. doi: 10.1023/a:1025735410738. J Neurocytol. 2002. PMID: 14501202 - Effects of CaMKII inhibitor tatCN21 on activity-dependent redistribution of CaMKII in hippocampal neurons.
Tao-Cheng JH, Yang Y, Bayer KU, Reese TS, Dosemeci A. Tao-Cheng JH, et al. Neuroscience. 2013 Aug 6;244:188-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.03.063. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23583761 Free PMC article. - Translocation of autophosphorylated calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II to the postsynaptic density.
Strack S, Choi S, Lovinger DM, Colbran RJ. Strack S, et al. J Biol Chem. 1997 May 23;272(21):13467-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.21.13467. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9153188 - Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II clusters in adult rat hippocampal slices.
Tao-Cheng JH, Vinade L, Pozzo-Miller LD, Reese TS, Dosemeci A. Tao-Cheng JH, et al. Neuroscience. 2002;115(2):435-40. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00451-7. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 12421609 - Direct visualization of CaMKII at postsynaptic densities by electron microscopy tomography.
Fera A, Dosemeci A, Sousa AA, Yang C, Leapman RD, Reese TS. Fera A, et al. J Comp Neurol. 2012 Dec 15;520(18):4218-25. doi: 10.1002/cne.23151. J Comp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22627922
Cited by
- Subcellular organization of camkii in rat hippocampal pyramidal neurons.
Ding JD, Kennedy MB, Weinberg RJ. Ding JD, et al. J Comp Neurol. 2013 Oct 15;521(15):3570-83. doi: 10.1002/cne.23372. J Comp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23749614 Free PMC article. - Differentiation and Characterization of Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses by Cryo-electron Tomography and Correlative Microscopy.
Tao CL, Liu YT, Sun R, Zhang B, Qi L, Shivakoti S, Tian CL, Zhang P, Lau PM, Zhou ZH, Bi GQ. Tao CL, et al. J Neurosci. 2018 Feb 7;38(6):1493-1510. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1548-17.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 8. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29311144 Free PMC article. - Ultrastructural localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in tree shrew nucleus accumbens core and shell.
McCollum LA, Roberts RC. McCollum LA, et al. Neuroscience. 2014 Jun 20;271:23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.04.024. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24769226 Free PMC article. - Coordination between Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II and Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase in Neurons.
Araki S, Osuka K, Takata T, Tsuchiya Y, Watanabe Y. Araki S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 27;21(21):7997. doi: 10.3390/ijms21217997. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33121174 Free PMC article. Review. - Occurrence of Ordered and Disordered Structural Elements in Postsynaptic Proteins Supports Optimization for Interaction Diversity.
Kiss-Tóth A, Dobson L, Péterfia B, Ángyán AF, Ligeti B, Lukács G, Gáspári Z. Kiss-Tóth A, et al. Entropy (Basel). 2019 Aug 6;21(8):761. doi: 10.3390/e21080761. Entropy (Basel). 2019. PMID: 33267475 Free PMC article.
References
- Benveniste H, Drejer J, Schousboe A, Diemer N H. J Neurochem. 1984;43:1369–1374. - PubMed
- Globus M Y, Busto R, Dietrich W D, Martinez E, Valdes I, Ginsberg M D. J Neurochem. 1988;51:1455–1464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous