Dominant intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy maps to chromosome 19p12-p13.2 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Dominant intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy maps to chromosome 19p12-p13.2
M L Kennerson et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Oct.
Abstract
The hereditary disorders of peripheral nerve form one of the most common groups of human genetic diseases, collectively called Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) neuropathy. Using linkage analysis we have identified a new locus for a form of CMT that we have called "dominant intermediate CMT" (DI-CMT). A genomewide screen using 383 microsatellite markers showed strong linkage to the short arm of chromosome 19 (maximum LOD score 4.3, with a recombination fraction (straight theta) of 0, at D19S221 and maximum LOD score 5.28, straight theta=0, at D19S226). Haplotype analysis performed with 14 additional markers placed the DI-CMT locus within a 16.8-cM region flanked by the markers D19S586 and D19S546. Multipoint linkage analysis suggested the most likely location at D19S226 (maximum multipoint LOD score 6.77), within a 10-cM confidence interval. This study establishes the presence of a locus for DI-CMT on chromosome 19p12-p13.2.
Figures
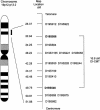
Figure 1
Genetic map (sex averaged) of chromosome 19 markers used in this study. The genetic distances were obtained from the Marshfield map. Loci that appear on the same line map to the same genetic location. The order of these markers was obtained from the chromosome 19 p-arm metric physical map. Markers defining the DI-CMT genetic interval are shown in boldface.
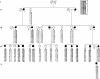
Figure 2
Haplotype analysis of markers from chromosome 19p12-p13.2 in family (DI-CMT310) with autosomal dominant intermediate CMT. The haplotype segregating with the disease is boxed. The markers are presented in order from telomere (top) to centromere (bottom). Blackened symbols denote affected individuals, and unblackened symbols denote unaffected individuals. Individuals are numbered consecutively in each generation, from left to right. Individuals IV-1 and IV-12 define the centromeric boundary of the disease at D19S546, whereas individual IV-16 defines the telomeric boundary at D19S586.
Figure 3
Multipoint localization of dominant intermediate CMT. Genetic location (distance, in cM, from the telomere of chromosome 19p) is plotted against the multipoint LOD score. Markers used in the multipoint analysis are shown. A maximum multipoint LOD score of 6.77 was obtained for D19S226 at 42.28 cM. The markers D19S586 and D19S199 flank the 10-cM confidence interval.
Similar articles
- Refined localization of dominant intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy and exclusion of seven known candidate genes in the region.
Zhu D, Kennerson M, Merory J, Chrast R, Verheijen M, Lemke G, Nicholson G. Zhu D, et al. Neurogenetics. 2003 Aug;4(4):179-83. doi: 10.1007/s10048-003-0147-y. Epub 2003 May 22. Neurogenetics. 2003. PMID: 12761657 - A new locus for autosomal dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 (CMT2L) maps to chromosome 12q24.
Tang BS, Luo W, Xia K, Xiao JF, Jiang H, Shen L, Tang JG, Zhao GH, Cai F, Pan Q, Dai HP, Yang QD, Xia JH, Evgrafov OV. Tang BS, et al. Hum Genet. 2004 May;114(6):527-33. doi: 10.1007/s00439-004-1102-1. Epub 2004 Mar 12. Hum Genet. 2004. PMID: 15021985 - Localization of the gene for the intermediate form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth to chromosome 10q24.1-q25.1.
Verhoeven K, Villanova M, Rossi A, Malandrini A, De Jonghe P, Timmerman V. Verhoeven K, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Oct;69(4):889-94. doi: 10.1086/323742. Epub 2001 Aug 30. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11533914 Free PMC article. - Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related inherited neuropathies.
Murakami T, Garcia CA, Reiter LT, Lupski JR. Murakami T, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996 Sep;75(5):233-50. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199609000-00001. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996. PMID: 8862346 Review.
Cited by
- Refined localization of dominant intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy and exclusion of seven known candidate genes in the region.
Zhu D, Kennerson M, Merory J, Chrast R, Verheijen M, Lemke G, Nicholson G. Zhu D, et al. Neurogenetics. 2003 Aug;4(4):179-83. doi: 10.1007/s10048-003-0147-y. Epub 2003 May 22. Neurogenetics. 2003. PMID: 12761657 - Adult-onset autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia linked to a GTPase-effector domain mutation of dynamin 2.
Sambuughin N, Goldfarb LG, Sivtseva TM, Davydova TK, Vladimirtsev VA, Osakovskiy VL, Danilova AP, Nikitina RS, Ylakhova AN, Diachkovskaya MP, Sundborger AC, Renwick NM, Platonov FA, Hinshaw JE, Toro C. Sambuughin N, et al. BMC Neurol. 2015 Oct 30;15:223. doi: 10.1186/s12883-015-0481-3. BMC Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26517984 Free PMC article. - Intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: an electrophysiological reappraisal and systematic review.
Berciano J, García A, Gallardo E, Peeters K, Pelayo-Negro AL, Álvarez-Paradelo S, Gazulla J, Martínez-Tames M, Infante J, Jordanova A. Berciano J, et al. J Neurol. 2017 Aug;264(8):1655-1677. doi: 10.1007/s00415-017-8474-3. Epub 2017 Mar 31. J Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28364294 - [A new locus for an autosomal dominant, non-syndromic hearing impairment (DFNA57) located on chromosome 19p13.2 and overlapping with DFNB15].
Bönsch D, Schmidt CM, Scheer P, Bohlender J, Neumann C, am Zehnhoff-Dinnesen A, Deufel T. Bönsch D, et al. HNO. 2008 Feb;56(2):177-82. doi: 10.1007/s00106-007-1633-6. HNO. 2008. PMID: 18066515 German. - Phenotypic spectrum of dynamin 2 mutations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy.
Claeys KG, Züchner S, Kennerson M, Berciano J, Garcia A, Verhoeven K, Storey E, Merory JR, Bienfait HM, Lammens M, Nelis E, Baets J, De Vriendt E, Berneman ZN, De Veuster I, Vance JM, Nicholson G, Timmerman V, De Jonghe P. Claeys KG, et al. Brain. 2009 Jul;132(Pt 7):1741-52. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp115. Epub 2009 Jun 5. Brain. 2009. PMID: 19502294 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/Map_Markers/maps/IndexMapF...
- Chromosome 19 p Arm Metric Physical Map, Lawrence Livermore Laboratory, http://greengenes.llnl.gov/genome-bin/loadmap?region=mp
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (for PMP22 [accession number L03203], Cx32/GJB1 [accession number XM_047682], MPZ/Po [accession number D10537 D90501], EGR2 [accession number AF139463], MTMR2 [accession number NM_003912], NDRG1 [accession number XM_051273], NTRK1/TrkA [accession number XM_043533], PRX [accession number XM_047407], NEFL [accession number X05608], KIF1Bβ [accession number AB023656])
- Genome Database, http://www.gdb.org/
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for CMT1A [MIM <118220>], CMT1B [MIM <118200>], CMT1X [MIM <302800>], CMT2A [MIM <118210>], CMT2B [ MIM <600882>], CMT2C [MIM <606071>], CMT2D [MIM <601472>], and CMT2E [162280])
References
- Bergoffen J, Scherer SS, Wang S, Scott MO, Bone LJ, Paul DL, Chen K, Lensch MW, Chance PF, Fischbeck KH (1993) Connexin mutations in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Science 262:2039–2042 - PubMed
- Bodzioch M, Lapicka K, Aslanidis C, Kacinski M, Schmitz G (2001) Two novel mutant alleles of the gene encoding neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 1 (ntrk1) in a patient with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis: a splice junction mutation in intron 5 and cluster of four mutations in exon 15. Hum Mutat 17:72 - PubMed
- Bolino A, Muglia M, Conforti FL, LeGuern E, Salih MA, Georgiou DM, Christodoulou K, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I, Mandich P, Schenone A, Gambardella A, Bono F, Quattrone A, Devoto M, Monaco AP (2000) Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4B is caused by mutations in the gene encoding myotubularin-related protein-2. Nat Genet 25:17–19 - PubMed
- Conneally PM, Edwards JH, Kidd KK, Lalouel JM, Morton NE, Ott J, White R (1985) Report of the committee on methods of linkage analysis and reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet 40:356–359 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases