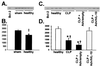Targeted adenovirus-induced expression of IL-10 decreases thymic apoptosis and improves survival in murine sepsis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Targeted adenovirus-induced expression of IL-10 decreases thymic apoptosis and improves survival in murine sepsis
C Oberholzer et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001.
Abstract
Sepsis remains a significant clinical conundrum, and recent clinical trials with anticytokine therapies have produced disappointing results. Animal studies have suggested that increased lymphocyte apoptosis may contribute to sepsis-induced mortality. We report here that inhibition of thymocyte apoptosis by targeted adenovirus-induced thymic expression of human IL-10 reduced blood bacteremia and prevented mortality in sepsis. In contrast, systemic administration of an adenovirus expressing IL-10 was without any protective effect. Improvements in survival were associated with increases in Bcl-2 expression and reductions in caspase-3 activity and thymocyte apoptosis. These studies demonstrate that thymic apoptosis plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of sepsis and identifies a gene therapy approach for its therapeutic intervention.
Figures
Figure 1
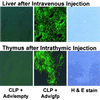
Histological GFP-positive cells. Mice were injected i.v. (Upper) or intrathymically (Lower) with 1010 particles of an adenoviral vector containing an empty cassette or expressing GFP. Tissues were examined 24 h later for GFP fluorescence or by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. (Magnification: ×100.)
Figure 2
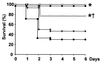
Survival rate of different treatment and nontreatment groups. Survival rate of mice undergoing CLP without treatment (●) was compared with that of animals pretreated intrathymically with 105 particles of an adenoviral vector expressing hIL-10 (Adv/hIL-10) (○) 24 h before CLP and mice pretreated with an equivalent number of adenoviral particles containing an empty cassette (▾). Transgenic mice overexpressing Bcl-2 in T cells (■) as well as sham mice (▿) had a survival of 100%. *, P < 0.05 CLP vs. treatment or sham; †, P < 0.05 Adv/hIL-10 vs. Adv/empty, by Kaplan-Meier, log rank.
Figure 3
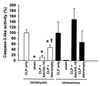
Caspase-3-like activity in the thymus of septic mice. Caspase-3-like activity was determined in the thymus from septic mice (n = 10/group) 24 h after CLP and 48 h after intrathymic or i.v. pretreatment. Data from several experiments were combined, and the rate of caspase-3 activity in the thymus of septic mice was normalized to 100%. Statistical comparisons could not be performed between groups of mice treated intrathymically and i.v. because of the effect of a prior surgery (thoracotomy) on subsequent thymic caspase activity. Data were normalized (100%) for values from sham, septic mice [2,329 relative fluorescence intensity (RFI) for intrathymic and 301 RFI for i.v. injections]. *,P < 0.05 CLP vs. treatment or sham; †,P < 0.05 Adv/hIL-10 vs. Adv/empty, by one-way ANOVA and Fischer's least significant difference posthoc test.
Figure 4
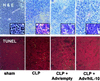
In situ TUNEL staining and histological examination of thymi from mice after CLP. Thymi were harvested from mice 24 h after CLP, and tissues were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), or by 3′ end labeling of apoptotic nuclei (TUNEL) staining as described in Materials and Methods. Increased numbers of cells undergoing apoptosis were seen in mice after CLP. Mice pretreated intrathymically with 105 particles of Adv/empty had similar numbers of apoptotic cells, as determined by TUNEL staining. In mice pretreated with 105 particles of Adv/hIL-10, there was a marked reduction in the numbers of apoptotic cells. In the hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections (see Insets for greater detail), apoptotic cells (fragmented and pyknotic) were seen primarily in the thymus of untreated mice and mice pretreated with Adv/empty. [Magnification: ×100 and ×1,000 for _Insets_].)
Figure 5
Bcl-2 expression in thymus as determined by Western blot analysis. Bcl-2 levels were examined in the thymus of healthy mice and mice after a CLP. Mice were pretreated intrathymically with either Adv/hIL-10 or Adv/empty at a dose of 105 particles. Bcl-2 levels were determined by Western blot analysis (A and_C_), and the relative quantities of Bcl-2 were determined by densitometric analysis (B and D). *, P < 0.05 healthy vs. CLP; †,P < 0.05 Adv/hIL-10 vs. Adv/empty or CLP; ‡,P < 0.05 healthy vs. sham. As a positive control for detecting murine Bcl-2, M1 cell lysate (ATCC TIB 192) was used.
Similar articles
- Endogenous IL-10 regulates sepsis-induced thymic apoptosis and improves survival in septic IL-10 null mice.
Tschoeke SK, Oberholzer C, LaFace D, Hutchins B, Moldawer LL, Oberholzer A. Tschoeke SK, et al. Scand J Immunol. 2008 Dec;68(6):565-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2008.02176.x. Epub 2008 Oct 8. Scand J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18959626 Free PMC article. - Functional modification of dendritic cells with recombinant adenovirus encoding interleukin 10 for the treatment of sepsis.
Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C, Efron PA, Scumpia PO, Uchida T, Bahjat K, Ungaro R, Tannahill CL, Murday M, Bahjat FR, Tsai V, Hutchins B, Moldawer LL, Laface D, Clare-Salzler MJ. Oberholzer A, et al. Shock. 2005 Jun;23(6):507-15. Shock. 2005. PMID: 15897802 - IL-10 mediation of activation-induced TH1 cell apoptosis and lymphoid dysfunction in polymicrobial sepsis.
Ayala A, Chung CS, Song GY, Chaudry IH. Ayala A, et al. Cytokine. 2001 Apr 7;14(1):37-48. doi: 10.1006/cyto.2001.0848. Cytokine. 2001. PMID: 11298491 - Considering immunomodulatory therapies in the septic patient: should apoptosis be a potential therapeutic target?
Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C, Minter RM, Moldawer LL. Oberholzer A, et al. Immunol Lett. 2001 Jan 15;75(3):221-4. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(00)00307-2. Immunol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11166379 Review. - Biology of interleukin-10 and its regulatory roles in sepsis syndromes.
Scumpia PO, Moldawer LL. Scumpia PO, et al. Crit Care Med. 2005 Dec;33(12 Suppl):S468-71. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000186268.53799.67. Crit Care Med. 2005. PMID: 16340424 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- The role of G protein-coupled receptor in neutrophil dysfunction during sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Wang Y, Zhu CL, Li P, Liu Q, Li HR, Yu CM, Deng XM, Wang JF. Wang Y, et al. Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 20;14:1112196. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1112196. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36891309 Free PMC article. Review. - Recent advances in neutrophil chemotaxis abnormalities during sepsis.
Zhou YY, Sun BW. Zhou YY, et al. Chin J Traumatol. 2022 Nov;25(6):317-324. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2022.06.002. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Chin J Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 35786510 Free PMC article. Review. - miR-21 Regulates Immune Balance Mediated by Th17/Treg in Peripheral Blood of Septic Rats during the Early Phase through Apoptosis Pathway.
Liu C, Zou Q. Liu C, et al. Biochem Res Int. 2022 Apr 27;2022:9948229. doi: 10.1155/2022/9948229. eCollection 2022. Biochem Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35528843 Free PMC article. - Role of the adaptive immune response in sepsis.
Brady J, Horie S, Laffey JG. Brady J, et al. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2020 Dec 18;8(Suppl 1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40635-020-00309-z. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2020. PMID: 33336293 Free PMC article. Review. - Priming with FLO8-deficient Candida albicans induces Th1-biased protective immunity against lethal polymicrobial sepsis.
Lv QZ, Li DD, Han H, Yang YH, Duan JL, Ma HH, Yu Y, Chen JY, Jiang YY, Jia XM. Lv QZ, et al. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021 Aug;18(8):2010-2023. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00576-6. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33154574 Free PMC article.
References
- Abraham E, Anzueto A, Gutierrez G, Tessler S, San Pedro G, Wunderink R, Dal Nogare A, Nasraway S, Berman S, Cooney R, et al. Lancet. 1998;351:929–933. - PubMed
- Fisher C J, Jr, Dhainaut J F, Opal S M, Pribble J P, Balk R A, Slotman G J, Iberti T J, Rackow E C, Shapiro M J, Greenman R L, et al. J Am Med Assoc. 1994;271:1836–1843. - PubMed
- Oberholzer C, Oberholzer A, Clare-Salzler M, Moldawer L L. FASEB J. 2001;15:879–892. - PubMed
- Hotchkiss R S, Swanson P E, Freeman B D, Tinsley K W, Cobb J P, Matuschak G M, Buchman T G, Karl I E. Crit Care Med. 1999;27:1230–1251. - PubMed
- Fukuzuka K, Edwards C K, 3rd, Clare-Salzler M, Copeland E M, 3rd, Moldawer L L, Mozingo D W. Am J Physiol. 2000;278:R1005–R1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 HL008912/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM040586/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HL-08912/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM-40586/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials