Reduced expression of CD44 on monocytes and neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus: relations with apoptotic neutrophils and disease activity - PubMed (original) (raw)
Reduced expression of CD44 on monocytes and neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus: relations with apoptotic neutrophils and disease activity
A P Cairns et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Oct.
Abstract
Background: Increased numbers of apoptotic neutrophils, and impaired monocyte/macrophage clearance of apoptotic cells, have been demonstrated in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). CD44 is implicated in the clearance of apoptotic neutrophils.
Objective: To determine the expression of CD44 on peripheral blood monocytes and neutrophils in SLE, and examine the relations with disease activity and numbers of circulating apoptotic neutrophils.
Methods: Peripheral blood was sampled from 31 patients with SLE, 19 healthy normal subjects, and 19 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Monocyte and neutrophil density of surface CD44 expression was determined by immunofluorescence labelling and flow cytometry, and results expressed as mean channel fluorescence (MCF) values. Neutrophil apoptosis was measured by morphology in 15 patients with SLE, nine with RA, and six normal subjects.
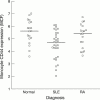
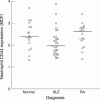
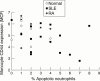
Results: Monocyte CD44 expression was significantly lower in SLE (median MCF 4.71) than in healthy normal subjects (median MCF 5.61) and controls with RA (median MCF 5.39). Neutrophil CD44 expression was also significantly lower in SLE (median MCF 1.95) than in healthy normal subjects (median MCF 2.37) and controls with RA (median MCF 2.60). Monocyte, but not neutrophil, CD44 expression correlated negatively with the percentage of apoptotic neutrophils. There was no significant correlation of monocyte or neutrophil CD44 expression in SLE with disease activity or damage.
Conclusions: Monocyte and neutrophil CD44 expression is reduced in SLE, and this may contribute to the impaired recognition and clearance of apoptotic neutrophils by monocyte derived macrophages.
Figures
Figure 1
(A) Flow cytometry scatter plot demonstrating the three leucocyte populations—from left to right: lymphocytes, monocytes (gated), and neutrophils; (B) gated monocyte IgG isotype control histogram; (C) gated monocyte CD44 staining histogram—in this sample 99.3% of gated cells express CD44 with a mean channel fluorescence of 6.74.
Figure 2
Monocyte CD44 expression in normal subjects, patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Each point represents one patient, and the median value for each group is shown.
Figure 3
Neutrophil CD44 expression in normal subjects, patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Each point represents one patient, and the median value for each group is shown.
Figure 4
Scatter plot showing the negative correlation of monocyte CD44 expression with percentage apoptotic neutrophils (rs=−0.41, p=0.026). Data from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and normal subjects are included, and each point represents one patient. MCF = mean channel fluorescence.
Similar articles
- Increased apoptotic peripheral blood neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus: relations with disease activity, antibodies to double stranded DNA, and neutropenia.
Courtney PA, Crockard AD, Williamson K, Irvine AE, Kennedy RJ, Bell AL. Courtney PA, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 May;58(5):309-14. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.5.309. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999. PMID: 10225817 Free PMC article. - Characterization of the impairment of the uptake of apoptotic polymorphonuclear cells by monocyte subpopulations in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Mikołajczyk TP, Skiba D, Batko B, Krezelok M, Wilk G, Osmenda G, Pryjma JR, Guzik TJ. Mikołajczyk TP, et al. Lupus. 2014 Nov;23(13):1358-69. doi: 10.1177/0961203314541316. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Lupus. 2014. PMID: 24969081 - Increased apoptotic neutrophils and macrophages and impaired macrophage phagocytic clearance of apoptotic neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Ren Y, Tang J, Mok MY, Chan AW, Wu A, Lau CS. Ren Y, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Oct;48(10):2888-97. doi: 10.1002/art.11237. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 14558095 - Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Same Foe Different M.O.
Fresneda Alarcon M, McLaren Z, Wright HL. Fresneda Alarcon M, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 4;12:649693. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.649693. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33746988 Free PMC article. Review. - [Role of neutrophil dysfunction in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus].
Smirnova EV, Krasnova TN, Proskurnina EV, Mukhin NA. Smirnova EV, et al. Ter Arkh. 2017;89(12):110-113. doi: 10.17116/terarkh20178912110-113. Ter Arkh. 2017. PMID: 29411769 Review. Russian.
Cited by
- The role of defective clearance of apoptotic cells in systemic autoimmunity.
Muñoz LE, Lauber K, Schiller M, Manfredi AA, Herrmann M. Muñoz LE, et al. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010 May;6(5):280-9. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.46. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20431553 Review. - Autologous tolerogenic dendritic cells derived from monocytes of systemic lupus erythematosus patients and healthy donors show a stable and immunosuppressive phenotype.
Obreque J, Vega F, Torres A, Cuitino L, Mackern-Oberti JP, Viviani P, Kalergis A, Llanos C. Obreque J, et al. Immunology. 2017 Dec;152(4):648-659. doi: 10.1111/imm.12806. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28763099 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The role of hsa_circ_0008945 in juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus.
Wang Q, Xu B, Zhang Q, Wang H, Chen S, Chen T, Liang S. Wang Q, et al. BMC Med Genomics. 2023 May 9;16(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01524-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37161408 Free PMC article. - Breaking immunological tolerance in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Pieterse E, van der Vlag J. Pieterse E, et al. Front Immunol. 2014 Apr 9;5:164. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00164. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24782867 Free PMC article. Review. - Imaging Cytometry of Human Leukocytes with Third Harmonic Generation Microscopy.
Wu CH, Wang TD, Hsieh CH, Huang SH, Lin JW, Hsu SC, Wu HT, Wu YM, Liu TM. Wu CH, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 15;6:37210. doi: 10.1038/srep37210. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27845443 Free PMC article.
References
- J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Jul;105(1):124-7 - PubMed
- Lupus. 1999;8(7):508-13 - PubMed
- Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Apr;59(4):283-8 - PubMed
- Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Aug;43(8):1719-28 - PubMed
- J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1820-5 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous