Lymphatic vessels as targets of tumor therapy? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Lymphatic vessels as targets of tumor therapy?
T Karpanen et al. J Exp Med. 2001.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
Tumor lymphangiogenesis and its inhibition. VEGF-C and VEGF-D produced by tumor cells or associated inflammatory cells induce the growth of lymphatic vessels in the tumor periphery. These factors may also contribute to angiogenesis induced by VEGF. Tumor cells grow inside of the lymphatic vessels, which provide a route for tumor metastasis. Shown in the top part are various approaches to inhibit tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis by blocking VEGFR-3 signaling.
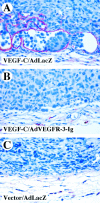
Figure 2
Inhibition of tumor lymphangiogenesis by adenovirally encoded soluble VEGFR-3. MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells were stably transfected with a VEGF-C expression plasmid (A and B) or an empty vector (C) and 107 cells were injected into the mammary fad pads of ovariectomized SCID mice carrying slow-release estrogen pellets. The mice were injected intravenously with 109 PFU of an adenovirus encoding soluble VEGFR-3 (B) or control adenovirus (A and C). See reference 4 for further details.
Comment on
- Isolation and characterization of dermal lymphatic and blood endothelial cells reveal stable and functionally specialized cell lineages.
Kriehuber E, Breiteneder-Geleff S, Groeger M, Soleiman A, Schoppmann SF, Stingl G, Kerjaschki D, Maurer D. Kriehuber E, et al. J Exp Med. 2001 Sep 17;194(6):797-808. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.6.797. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11560995 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Vascular endothelial growth factors C and D and their VEGFR-2 and 3 receptors in blood and lymphatic vessels in healthy and arthritic synovium.
Paavonen K, Mandelin J, Partanen T, Jussila L, Li TF, Ristimaki A, Alitalo K, Konttinen YT. Paavonen K, et al. J Rheumatol. 2002 Jan;29(1):39-45. J Rheumatol. 2002. PMID: 11824969 - Isolation and characterization of dermal lymphatic and blood endothelial cells reveal stable and functionally specialized cell lineages.
Kriehuber E, Breiteneder-Geleff S, Groeger M, Soleiman A, Schoppmann SF, Stingl G, Kerjaschki D, Maurer D. Kriehuber E, et al. J Exp Med. 2001 Sep 17;194(6):797-808. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.6.797. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11560995 Free PMC article. - Endothelial receptor tyrosine kinases involved in blood vessel development and tumor angiogenesis.
Breier G. Breier G. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;476:57-66. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4221-6_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000. PMID: 10949655 Review. No abstract available. - Signalling via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 is sufficient for lymphangiogenesis in transgenic mice.
Veikkola T, Jussila L, Makinen T, Karpanen T, Jeltsch M, Petrova TV, Kubo H, Thurston G, McDonald DM, Achen MG, Stacker SA, Alitalo K. Veikkola T, et al. EMBO J. 2001 Mar 15;20(6):1223-31. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.6.1223. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11250889 Free PMC article. - Lymphatic versus blood vascular endothelial growth factors and receptors in humans.
Partanen TA, Paavonen K. Partanen TA, et al. Microsc Res Tech. 2001 Oct 15;55(2):108-21. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1162. Microsc Res Tech. 2001. PMID: 11596156 Review.
Cited by
- Cancer metastasis through the lymphatic versus blood vessels.
Leong SP, Witte MH. Leong SP, et al. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024 Aug;41(4):387-402. doi: 10.1007/s10585-024-10288-0. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024. PMID: 38940900 Free PMC article. Review. - High VEGFR3 Expression Reduces Doxorubicin Efficacy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
Torres-Ruiz S, Tormo E, Garrido-Cano I, Lameirinhas A, Rojo F, Madoz-Gúrpide J, Burgués O, Hernando C, Bermejo B, Martínez MT, Lluch A, Cejalvo JM, Eroles P. Torres-Ruiz S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3601. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043601. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835014 Free PMC article. - Molecular mechanisms of cancer metastasis via the lymphatic versus the blood vessels.
Leong SP, Naxerova K, Keller L, Pantel K, Witte M. Leong SP, et al. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2022 Feb;39(1):159-179. doi: 10.1007/s10585-021-10120-z. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2022. PMID: 34767139 Free PMC article. Review. - The lymphatic system and sentinel lymph nodes: conduit for cancer metastasis.
Leong SP, Pissas A, Scarato M, Gallon F, Pissas MH, Amore M, Wu M, Faries MB, Lund AW. Leong SP, et al. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2022 Feb;39(1):139-157. doi: 10.1007/s10585-021-10123-w. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2022. PMID: 34651243 Free PMC article. Review. - Tumor-Draining Lymph Secretome En Route to the Regional Lymph Node in Breast Cancer Metastasis.
Mohammed SI, Torres-Luquis O, Zhou W, Lanman NA, Espina V, Liotta L. Mohammed SI, et al. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2020 Mar 25;12:57-67. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S236168. eCollection 2020. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2020. PMID: 32273752 Free PMC article.
References
- Skobe M., Hawighorst T., Jackson D.G., Prevo R., Janes L., Velasco P., Riccardi L., Alitalo K., Claffey K., Detmar M. Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Med. 2001;7:192–198. - PubMed
- Stacker S.A., Caesar C., Baldwin M.E., Thornton G.E., Williams R.A., Prevo R., Jackson D.G., Nishikawa S., Kubo H., Achen M.G. VEGF-D promotes the metastatic spread of tumor cells via the lymphatics. Nat. Med. 2001;7:186–191. - PubMed
- Karpanen T., Egeblad M., Karkkainen M.J., Kubo H., Yla-Herttuala S., Jaattela M., Alitalo K. Vascular endothelial growth factor C promotes tumor lymphangiogenesis and intralymphatic tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1786–1790. - PubMed
- Jeltsch M., Kaipainen A., Joukov V., Meng X., Lakso M., Rauvala H., Swartz M., Fukumura D., Jain R.K., Alitalo K. Hyperplasia of lymphatic vessels in VEGF-C transgenic mice. Science. 1997;276:1423–1425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous