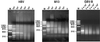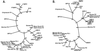A virus discovery method incorporating DNase treatment and its application to the identification of two bovine parvovirus species - PubMed (original) (raw)
A virus discovery method incorporating DNase treatment and its application to the identification of two bovine parvovirus species
T Allander et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001.
Abstract
Identification of previously unrecognized viral agents in serum or plasma samples is of great medical interest but remains a major challenge, primarily because of abundant host DNA. The current methods, library screening or representational difference analysis (RDA), are very laborious and require selected sample sets. We have developed a simple and reproducible method for discovering viruses in single serum samples that is based on DNase treatment of the serum followed by restriction enzyme digestion and sequence-independent single primer amplification (SISPA) of the fragments, and have evaluated its performance on known viruses. Both DNA viruses and RNA viruses at a concentration of approximately 10(6) genome equivalents per ml were reproducibly identified in 50 microl of serum. While evaluating the method, two previously unknown parvoviruses were discovered in the bovine sera used as diluent. The near complete genome sequence of each virus was determined; their classification as two species (provisionally named bovine parvoviruses 2 and 3) was confirmed by phylogenetic analysis. Both viruses were found to be frequent contaminants of commercial bovine serum. DNase treatment of serum samples may prove to be a very useful tool for virus discovery. The DNase-SISPA method is suitable for screening of a large number of samples and also enables rapid sequence determination of high-titer viruses.
Figures
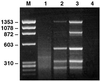
Figure 1
The effect of DNase treatment and filtering of serum on detection of HBV by SISPA. An HBV-containing serum sample diluted to 108 GE/ml was pretreated in different ways before DNA extraction and SISPA. Products were separated on an agarose gel. The six bands in lane 3 were verified to have HBV sequence. Lane 1, no treatment; Lane 2, DNase treatment only; Lane 3, filtering (0.22 μm) and DNase treatment; Lane 4, negative PCR control (no template); M, molecular weight marker PhiX 174 (_Hae_III fragments).
Figure 2
Detection levels of different virus genomes by DNase-SISPA. HBV, bacteriophage M13, and GBV-B were diluted in 10-fold increments in bovine serum and subjected to the DNase-SISPA procedure. Products were separated on an agarose gel. The virus titer (GE/ml) is shown above each lane. M, molecular weight marker PhiX 174 (_Hae_III fragments).
Figure 3
Overview of the BPV-2 (A) and BPV-3 (B) genomes as deposited in GenBank. The actual sizes and sequences of the transcripts and proteins of the indicated ORFs have not been investigated. NS, nonstructural gene.
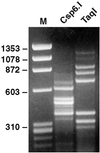
Figure 4
The use of DNase-SISPA for obtaining the sequence of unknown viruses, illustrated by SISPA products of a serum containing 108 GE/ml of BPV-3. (Left) Marker. (Center) SISPA based on digestion with _Csp_6.I. (Right) SISPA based on digestion with_Taq_I.
Figure 5
Phylogenetic trees of full-length nucleotide sequences (A) and truncated ORF2 amino acid sequences (B) of parvoviruses (Parvovirinae subfamily), including BPV-2 and BPV-3. Bootstrap values >70% are indicated.
Similar articles
- Identification and genomic characterization of a novel porcine parvovirus (PPV6) in China.
Ni J, Qiao C, Han X, Han T, Kang W, Zi Z, Cao Z, Zhai X, Cai X. Ni J, et al. Virol J. 2014 Dec 2;11:203. doi: 10.1186/s12985-014-0203-2. Virol J. 2014. PMID: 25442288 Free PMC article. - A novel parvovirus isolated from Manchurian chipmunks.
Yoo BC, Lee DH, Park SM, Park JW, Kim CY, Lee HS, Seo JS, Park KJ, Ryu WS. Yoo BC, et al. Virology. 1999 Jan 20;253(2):250-8. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9518. Virology. 1999. PMID: 9918883 - New DNA viruses identified in patients with acute viral infection syndrome.
Jones MS, Kapoor A, Lukashov VV, Simmonds P, Hecht F, Delwart E. Jones MS, et al. J Virol. 2005 Jul;79(13):8230-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.13.8230-8236.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15956568 Free PMC article. - Identification of a Novel Parvovirus in the Arctic Wolf (Canis lupus arctos).
Dai Z, Lu Q, Sun M, Chen H, Zhu R, Wang H. Dai Z, et al. Pol J Microbiol. 2024 Sep 13;73(3):395-401. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2024-035. eCollection 2024 Sep 1. Pol J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39268953 Free PMC article. - Two novel circo-like viruses detected in human feces: complete genome sequencing and electron microscopy analysis.
Castrignano SB, Nagasse-Sugahara TK, Kisielius JJ, Ueda-Ito M, Brandão PE, Curti SP. Castrignano SB, et al. Virus Res. 2013 Dec 26;178(2):364-73. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.09.018. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 24055464
Cited by
- Viral pathogen discovery.
Chiu CY. Chiu CY. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013 Aug;16(4):468-78. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 May 29. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23725672 Free PMC article. Review. - Animal virus discovery: improving animal health, understanding zoonoses, and opportunities for vaccine development.
Delwart E. Delwart E. Curr Opin Virol. 2012 Jun;2(3):344-52. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.02.012. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Curr Opin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22463981 Free PMC article. Review. - A systematic approach to novel virus discovery in emerging infectious disease outbreaks.
Sridhar S, To KK, Chan JF, Lau SK, Woo PC, Yuen KY. Sridhar S, et al. J Mol Diagn. 2015 May;17(3):230-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2014.12.002. Epub 2015 Mar 4. J Mol Diagn. 2015. PMID: 25746799 Free PMC article. Review. - Development and evaluation of a non-ribosomal random PCR and next-generation sequencing based assay for detection and sequencing of hand, foot and mouth disease pathogens.
Nguyen AT, Tran TT, Hoang VM, Nghiem NM, Le NN, Le TT, Phan QT, Truong KH, Le NN, Ho VL, Do VC, Ha TM, Nguyen HT, Nguyen CV, Thwaites G, van Doorn HR, Le TV. Nguyen AT, et al. Virol J. 2016 Jul 7;13:125. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0580-9. Virol J. 2016. PMID: 27388326 Free PMC article. - Viral metagenomics.
Delwart EL. Delwart EL. Rev Med Virol. 2007 Mar-Apr;17(2):115-31. doi: 10.1002/rmv.532. Rev Med Virol. 2007. PMID: 17295196 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Choo Q L, Kuo G, Weiner A J, Overby L R, Bradley D W, Houghton M. Science. 1989;244:359–362. - PubMed
- Muerhoff A S, Leary T P, Desai S M, Mushahwar I K. J Med Virol. 1997;53:96–103. - PubMed
- Reyes G R, Kim J P. Mol Cell Probes. 1991;5:473–481. - PubMed
- Reyes G R, Purdy M A, Kim J P, Luk K C, Young L M, Fry K E, Bradley D W. Science. 1990;247:1335–1339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources