Posttranscription initiation control of tryptophan metabolism in Bacillus subtilis by the trp RNA-binding attenuation protein (TRAP), anti-TRAP, and RNA structure - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Posttranscription initiation control of tryptophan metabolism in Bacillus subtilis by the trp RNA-binding attenuation protein (TRAP), anti-TRAP, and RNA structure
P Babitzke et al. J Bacteriol. 2001 Oct.
No abstract available
Figures
FIG. 1
Folate, mtr, trp, yhaG, and yczA-ycbK operons. trpG is located within the folate operon, while the rest of the trp genes are clustered in the trpEDCFBA operon. yhaG encodes a putative tryptophan transport protein. mtrB encodes TRAP, while yczA encodes the AT protein (41). TRAP is responsible for regulating expression of the trp operon by transcription attenuation and a translational control mechanism. TRAP regulates translation of trpG, yhaG, and probably ycbK. P> marks the position of the promoters for each operon, while the black boxes show the positions of the TRAP binding sites. The positions of terminator hairpins (open circles) and antiterminator hairpins (filled circles) are shown.
FIG. 2
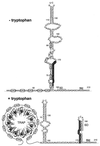
Transcription attenuation model of the trp operon. When tryptophan is limiting (−tryptophan) TRAP is not activated. During transcription, antiterminator formation (A and B) prevents formation of the terminator (C and D), which results in transcription of the trp operon structural genes. When tryptophan is in excess (+tryptophan) TRAP is activated. Tryptophan-activated TRAP can bind to the (G/U)AG repeats and promote termination by preventing antiterminator formation. The overlap between the antiterminator and terminator structures is shown. Numbering is from the start of transcription.
FIG. 3
trpE translational control model. Under tryptophan-limiting conditions, TRAP is not activated and is unable to bind to the trp leader transcript. In this case the trp leader RNA adopts a structure such that the trpE SD sequence is single stranded and available for translation. Under excess tryptophan conditions, TRAP is activated and binds to the (G/U)AG repeats. As a consequence, the trpE SD blocking hairpin forms, which prevents ribosome binding and translation. The overlap between the two alternative structures is shown. Numbering is from the start of transcription.
FIG. 4
Comparison of the TRAP binding sites. The (G/U)AG repeats are shown in bold type. The positions of the SD sequences and the start codons are shown for trpG, ycbK, and yhaG.
FIG. 5
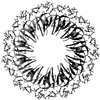
Ribbon diagram of TRAP complexed with an RNA containing 11 GAG repeats separated by AU spacers. TRAP binds to the linear transcript and wraps the RNA around the periphery of the TRAP complex. The TRAP subunits are shown in various shades of gray, and the RNA is shown in ball-and-stick models. The bound
l
-tryptophan molecules are shown as van der Waals spheres.
Similar articles
- trp RNA-binding attenuation protein (TRAP)-trp leader RNA interactions mediate translational as well as transcriptional regulation of the Bacillus subtilis trp operon.
Merino E, Babitzke P, Yanofsky C. Merino E, et al. J Bacteriol. 1995 Nov;177(22):6362-70. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.22.6362-6370.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7592410 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of the B. subtilis regulatory protein TRAP by the TRAP-inhibitory protein, AT.
Valbuzzi A, Yanofsky C. Valbuzzi A, et al. Science. 2001 Sep 14;293(5537):2057-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1062187. Science. 2001. PMID: 11557884 - Expression of the Bacillus subtilis trpEDCFBA operon is influenced by translational coupling and Rho termination factor.
Yakhnin H, Babiarz JE, Yakhnin AV, Babitzke P. Yakhnin H, et al. J Bacteriol. 2001 Oct;183(20):5918-26. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.20.5918-5926.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11566991 Free PMC article. - Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis trp operon by an RNA-binding protein.
Gollnick P. Gollnick P. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Mar;11(6):991-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00377.x. Mol Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 8022289 Review.
Cited by
- Phylogenetic conservation of RNA secondary and tertiary structure in the trpEDCFBA operon leader transcript in Bacillus.
Schaak JE, Babitzke P, Bevilacqua PC. Schaak JE, et al. RNA. 2003 Dec;9(12):1502-15. doi: 10.1261/rna.5149603. RNA. 2003. PMID: 14624006 Free PMC article. - Secondary structural entropy in RNA switch (Riboswitch) identification.
Manzourolajdad A, Arnold J. Manzourolajdad A, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Apr 28;16:133. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0523-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25928324 Free PMC article. - An RpoS-dependent sRNA regulates the expression of a chaperone involved in protein folding.
Silva IJ, Ortega AD, Viegas SC, García-Del Portillo F, Arraiano CM. Silva IJ, et al. RNA. 2013 Sep;19(9):1253-65. doi: 10.1261/rna.039537.113. Epub 2013 Jul 26. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23893734 Free PMC article. - Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
Mäder U, Homuth G, Scharf C, Büttner K, Bode R, Hecker M. Mäder U, et al. J Bacteriol. 2002 Aug;184(15):4288-95. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.15.4288-4295.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12107147 Free PMC article. - Cellular levels of trp RNA-binding attenuation protein in Bacillus subtilis.
McCabe BC, Gollnick P. McCabe BC, et al. J Bacteriol. 2004 Aug;186(15):5157-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.15.5157-5159.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15262953 Free PMC article.
References
- Antson A A, Dodson E J, Dodson G, Greaves R B, Chen X, Gollnick P. Structure of the trp RNA-binding attenuation protein, TRAP, bound to RNA. Nature. 1999;401:235–242. - PubMed
- Antson A A, Otridge J, Brzozowski A M, Dodson E J, Dodson G G, Wilson K S, Smith T M, Yang M, Kurecki T, Gollnick P. The structure of the trp RNA attenuation protein. Nature. 1995;374:693–700. - PubMed
- Babitzke P. Regulation of tryptophan biosynthesis: Trp-ing the TRAP or how Bacillus subtilis reinvented the wheel. Mol Microbiol. 1997;26:1–9. - PubMed
- Babitzke P, Yanofsky C. Structural features of L-tryptophan required for activation of TRAP, the trp RNA-binding attenuation protein of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:12452–12456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases