IGF status is altered by tamoxifen in patients with breast cancer - PubMed (original) (raw)
IGF status is altered by tamoxifen in patients with breast cancer
M J Campbell et al. Mol Pathol. 2001 Oct.
Abstract
Aims: An increased concentration of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is an independent risk factor for premenopausal breast cancer. Tamoxifen is thought initially to reduce concentrations of IGF-1 and increase concentrations of the IGF binding proteins. The aim of this study was to compare concentrations of IGF-1, IGF binding protein 1 (IGF-BP1), and IGF-BP3 in patients with breast cancer (n = 14) with those seen in control subjects (n = 23) and to assess the effect of tamoxifen on IGF status in these patients.
Methods: Non-fasting blood samples were collected from patients with breast cancer before surgery and after nine, 18, and 27 months of tamoxifen treatment. The baseline concentrations were compared with those of age and sex matched healthy control subjects.
Results: IGF-1, IGF-BP3, and IGF-BP1 concentrations were not significantly different in cases and controls. Tamoxifen treatment significantly increased IGF-BP1 after 18 and 27 months (baseline: mean, 21.6 ng/ml; SD, 16.6; 18 months: mean, 52.0 ng/ml; SD, 41.8; p = 0.019; 27 months: mean, 40.7 ng/ml; SD, 24.9; p = 0.043) and IGF-BP3 after nine, 18, and 27 months (baseline: mean, 3119 ng/ml; SD, 507; nine months: mean, 3673 ng/ml; SD, 476; p = 0.004; 18 months: mean, 3445 ng/ml; SD, 634; p = 0.034; 27 months: 3409 ng/ml; SD, 501; p = 0.043) when compared with baseline values. IGF-1 was not altered significantly from baseline at any time point. However, the IGF-1 to IGF-BP3 ratio was significantly decreased at both nine and 18 months (baseline: mean, 0.058; SD, 0.014; nine months: mean, 0.039; SD, 0.008; p = 0.033; 18 months: mean, 0.044; SD, 0.012; p = 0.01). This ratio was not significantly different from baseline at 27 months (mean, 0.054; SD, 0.01; p = 0.08).
Conclusions: Tamoxifen increases IGF-BP3 and IGF-BP1 concentrations. It also decreases the IGF-1 to IGF-BP3 ratio but this effect may be limited after long term use. Longer follow up, with larger numbers of patients, should determine when, and for how long, tamoxifen can reduce circulating IGF-1.
Figures
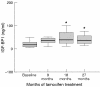
Figure 1
Effect of tamoxifen supplementation on insulin-like growth factor binding protein 1 (IGF-BP1). Values are median (black line) with interquartile ranges (boxed area) and minimum–maximum values (bars). *p < 0.05 for differences from baseline; Wilcoxon signed rank test.
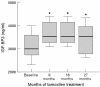
Figure 2
Effect of tamoxifen supplementation on insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGF-BP3). Values are median (black line) with interquartile ranges (boxed area) and minimum–maximum values (bars). * p <0.05 for differences from baseline; Wilcoxon signed rank test.
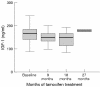
Figure 3
Effect of tamoxifen supplementation on insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). Values are median (black line) with interquartile ranges (boxed area) and minimum–maximum values (bars). *p < 0.05 for differences from baseline; Wilcoxon signed rank test.
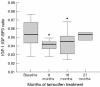
Figure 4
Effect of tamoxifen supplementation on the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) to IGF binding protein 3 (IGF-BP3) ratio. Values are median (black line) with interquartile ranges (boxed area) and minimum–maximum values (bars). *p < 0.05 for differences from baseline; Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Similar articles
- Effect of raloxifene on insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3, and leptin in premenopausal women at high risk for developing breast cancer.
Eng-Wong J, Hursting SD, Venzon D, Perkins SN, Zujewski JA. Eng-Wong J, et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2003 Dec;12(12):1468-73. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2003. PMID: 14693739 Clinical Trial. - Altered serum levels of insulin-like growth-factor binding proteins in breast cancer patients.
Ng EH, Ji CY, Tan PH, Lin V, Soo KC, Lee KO. Ng EH, et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 1998 Mar;5(2):194-201. doi: 10.1007/BF02303854. Ann Surg Oncol. 1998. PMID: 9527274 - Tamoxifen alters levels of serum insulin-like growth factors and binding proteins in postmenopausal breast cancer patients: a prospective paired cohort study.
Ho GH, Ji CY, Phang BH, Lee KO, Soo KC, Ng EH. Ho GH, et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 1998 Jun;5(4):361-7. doi: 10.1007/BF02303501. Ann Surg Oncol. 1998. PMID: 9641459 - The effect of tamoxifen on estradiol, SHBG, IGF-1, and CRP in women with breast cancer or at risk of developing breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Li X, Hou X, Hernández-Wolters B, Prabahar K, Kord-Varkaneh H, Mei B. Li X, et al. Exp Gerontol. 2024 Jun 15;191:112431. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112431. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Exp Gerontol. 2024. PMID: 38608792 Review. - The GH-IGF-I axis and breast cancer.
Laban C, Bustin SA, Jenkins PJ. Laban C, et al. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003 Jan;14(1):28-34. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(02)00003-6. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003. PMID: 12475609 Review.
Cited by
- Metformin may protect nondiabetic breast cancer women from metastasis.
El-Haggar SM, El-Shitany NA, Mostafa MF, El-Bassiouny NA. El-Haggar SM, et al. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016 Apr;33(4):339-57. doi: 10.1007/s10585-016-9782-1. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016. PMID: 26902691 - Evaluation of insulin-like growth factor-I in postmenopausal women with breast cancer treated with raloxifene.
da Silva BB, Moita DS, Pires CG, Sousa-Junior EC, dos Santos AR, Lopes-Costa PV. da Silva BB, et al. Int Semin Surg Oncol. 2007 Jul 23;4:18. doi: 10.1186/1477-7800-4-18. Int Semin Surg Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17645796 Free PMC article. - Cancer.
Grimberg A. Grimberg A. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2005;567:305-39. doi: 10.1007/0-387-26274-1_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2005. PMID: 16372400 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available. - Mechanisms by which IGF-I may promote cancer.
Grimberg A. Grimberg A. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003 Nov-Dec;2(6):630-5. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003. PMID: 14688466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bernstein L, Ross PK. Endogenous hormones and breast cancer risk. Epidemiol Rev 1993;15:48–65. - PubMed
- Karey KP, Sibarsu DA. Differential responsiveness of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 and T47D to growth factors and 17-beta estradiol. Cancer Res 1988;48:4083–92. - PubMed
- Bruning PF, van Doorn J, Bonfrer JMG, et al. Insulin-like growth-factor-binding protein 3 is decreased in early-stage operable pre-menopausal breast cancer. Int J Cancer 1995;62:266–70. - PubMed
- Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, et al. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-1 and risk of breast cancer. Lancet 1998;351:1393–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous