Irresistible IRES. Attracting the translation machinery to internal ribosome entry sites - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Irresistible IRES. Attracting the translation machinery to internal ribosome entry sites
S Vagner et al. EMBO Rep. 2001 Oct.
Abstract
Studies on the control of eukaryotic translation initiation by a cap-independent recruitment of the 40S ribosomal subunit to internal messenger RNA sequences called internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) have shown that these sequence elements are present in a growing list of viral and cellular RNAs. Here we discuss their prevalence, mechanisms whereby they may function and their uses in regulating gene expression.
Figures
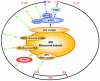
Fig. 1. Mechanisms of ribosome recruitment to mRNAs. In the cap- and poly(A) tail-mediated mechanism, the eIF4F complex (composed of eIF4E, eIF4G and eIF4A) targets the eIF3-associated 40S ribosomal subunit to the mRNA 5′ end. The cap and the poly(A) tail act synergistically through the interaction between eIF4G and PABP. In the IRES-mediated mechanism, the 40S ribosomal subunit can interact with mRNAs, even in the absence of canonical translation initiation factors. Green arrows indicate direct or indirect [through ITAFs(IRES _trans_-acting factors)] interactions between IRES elements and the translation initiation machinery identified thus far.
Similar articles
- Cryo-EM visualization of a viral internal ribosome entry site bound to human ribosomes: the IRES functions as an RNA-based translation factor.
Spahn CM, Jan E, Mulder A, Grassucci RA, Sarnow P, Frank J. Spahn CM, et al. Cell. 2004 Aug 20;118(4):465-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.08.001. Cell. 2004. PMID: 15315759 - Hepatitis-C-virus-like internal ribosome entry sites displace eIF3 to gain access to the 40S subunit.
Hashem Y, des Georges A, Dhote V, Langlois R, Liao HY, Grassucci RA, Pestova TV, Hellen CU, Frank J. Hashem Y, et al. Nature. 2013 Nov 28;503(7477):539-43. doi: 10.1038/nature12658. Epub 2013 Nov 3. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24185006 Free PMC article. - Tricks an IRES uses to enslave ribosomes.
Thompson SR. Thompson SR. Trends Microbiol. 2012 Nov;20(11):558-66. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2012.08.002. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Trends Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22944245 Free PMC article. Review. - Ribosomal Chamber Music: Toward an Understanding of IRES Mechanisms.
Yamamoto H, Unbehaun A, Spahn CMT. Yamamoto H, et al. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017 Aug;42(8):655-668. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28684008 Review. - Structural and mechanistic insights into hepatitis C viral translation initiation.
Fraser CS, Doudna JA. Fraser CS, et al. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007 Jan;5(1):29-38. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1558. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17128284 Review.
Cited by
- Mechanism of HIV-1 Tat RNA translation and its activation by the Tat protein.
Charnay N, Ivanyi-Nagy R, Soto-Rifo R, Ohlmann T, López-Lastra M, Darlix JL. Charnay N, et al. Retrovirology. 2009 Aug 11;6:74. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-6-74. Retrovirology. 2009. PMID: 19671151 Free PMC article. - La autoantigen is necessary for optimal function of the poliovirus and hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site in vivo and in vitro.
Costa-Mattioli M, Svitkin Y, Sonenberg N. Costa-Mattioli M, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Aug;24(15):6861-70. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.15.6861-6870.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15254251 Free PMC article. - Internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) activity generates endogenous carboxyl-terminal domains of Cx43 and is responsive to hypoxic conditions.
Ul-Hussain M, Olk S, Schoenebeck B, Wasielewski B, Meier C, Prochnow N, May C, Galozzi S, Marcus K, Zoidl G, Dermietzel R. Ul-Hussain M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 25;289(30):20979-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.540187. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24872408 Free PMC article. - Functional polymorphism in the 5'-UTR of CR2 is associated with susceptibility to nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Fan Q, He JF, Wang QR, Cai HB, Sun XG, Zhou XX, Qin HD, Shugart YY, Jia WH. Fan Q, et al. Oncol Rep. 2013 Jul;30(1):11-6. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2421. Epub 2013 Apr 23. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23612877 Free PMC article. - The initial enzyme for glycosylphosphatidylinositol biosynthesis requires PIG-Y, a seventh component.
Murakami Y, Siripanyaphinyo U, Hong Y, Tashima Y, Maeda Y, Kinoshita T. Murakami Y, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Nov;16(11):5236-46. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0743. Epub 2005 Sep 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16162815 Free PMC article.
References
- Bonneau A.M. and Sonenberg, N. (1987) Involvement of the 24-kDa cap-binding protein in regulation of protein synthesis in mitosis. J. Biol. Chem., 262, 11134–11139. - PubMed
- Chappell S.A., LeQuesne, J.P., Paulin, F.E., deSchoolmeester, M.L., Stoneley, M., Soutar, R.L., Ralston, S.H., Helfrich, M.H. and Willis, A.E. (2000b) A mutation in the c-myc-IRES leads to enhanced internal ribosome entry in multiple myeloma: a novel mechanism of oncogene de-regulation. Oncogene, 19, 4437–4440. - PubMed
- Coldwell M.J., Mitchell, S.A., Stoneley, M., MacFarlane, M. and Willis, A.E. (2000) Initiation of Apaf-1 translation by internal ribosome entry. Oncogene, 19, 899–905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous