Glucose and cAMP: adversaries in the regulation of hepatic gene expression - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Glucose and cAMP: adversaries in the regulation of hepatic gene expression
H C Towle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001.
No abstract available
Figures
Figure 1
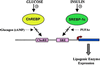
Schematic of the roles of ChREBP and SREBP in regulation of lipogenic enzyme gene transcription. Most lipogenic enzyme genes (e.g., fatty acid synthase) have response elements for binding ChREBP (ChoRE) and SREBP (SRE). These two factors work synergistically to induce transcription of the lipogenic enzyme genes in the presence of glucose and insulin. Glucagon, through its intracellular mediator cAMP, and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) act to inhibit the activity of ChREBP and SREBP, respectively. In this manner, the output of lipogenic enzyme gene production is integrated to multiple nutrient and hormonal signals.
Comment on
- Glucose and cAMP regulate the L-type pyruvate kinase gene by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of the carbohydrate response element binding protein.
Kawaguchi T, Takenoshita M, Kabashima T, Uyeda K. Kawaguchi T, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Nov 20;98(24):13710-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.231370798. Epub 2001 Nov 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11698644 Free PMC article.
References
- Hillgartner F B, Salati L M, Goodridge A G. Phys Rev. 1995;75:47–76. - PubMed
- Towle H C, Kaytor E N, Shih H-M. Annu Rev Nutr. 1997;17:405–433. - PubMed
- Girard J, Ferre P, Foufelle F. Annu Rev Nutr. 1997;17:325–352. - PubMed
- Vaulont S, Vasseur-Cognet M, Kahn A. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:31555–31558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources