Elevated expression of axin2 and hnkd mRNA provides evidence that Wnt/beta -catenin signaling is activated in human colon tumors - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2001 Dec 18;98(26):14973-8.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.261574498.
M Wiesmann, M Rohan, V Chan, A B Jefferson, L Guo, D Sakamoto, R H Caothien, J H Fuller, C Reinhard, P D Garcia, F M Randazzo, J Escobedo, W J Fantl, L T Williams
Affiliations
- PMID: 11752446
- PMCID: PMC64968
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.261574498
Elevated expression of axin2 and hnkd mRNA provides evidence that Wnt/beta -catenin signaling is activated in human colon tumors
D Yan et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001.
Abstract
Genetic studies have identified mutations in key regulators of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in a variety of cancers, most frequently in colon cancers. However, whether the pathway is activated in clinical cancer samples is not easily determined, and therefore it is useful to find markers that could be surrogates to show activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Gene expression profiles were analyzed in SW620, a colon cancer cell line in which beta-catenin levels are stabilized as a consequence of truncated adenomatous polyposis coli and were compared with profiles of the same cells transfected with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Treatment of cells with beta-catenin antisense oligodeoxynucleotides resulted in a decrease in the levels of axin2 and human naked cuticle (hnkd) mRNAs. Interestingly, the proteins encoded by both of these mRNAs are known inhibitors of the beta-catenin pathway. In 30 human cell lines derived from different origins, axin2 and hnkd were expressed only in human colon cancer cell lines that are known to have activating mutations in the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Further, levels of both axin2 and hnkd mRNA were also found to be elevated in about 65% of laser microdissected cells from human colon tumors compared with laser microdissected cells of normal morphology from the same patient samples. The increased expression of axin2 and hnkd correlated with truncations in adenomatous polyposis coli in the same patient samples. These results reveal that it is possible to detect activation of a carcinogenic pathway in human cancer samples with specific markers.
Figures
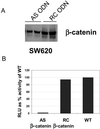
Figure 1
Reduction of cytosolic β-catenin levels and LEF-1 reporter activity in response to β-catenin antisense ODN transfection. (A) SW620 cell lysate was analyzed for cytosolic β-catenin levels by Western blotting 48 h posttransfection with β-catenin antisense and RC ODN in duplicated experiments. AS, antisense; RC, reverse control. (B) SW620 cells were transfected with β-catenin AS and RC ODN. After 24 h, the cells were transfected with reporter constructs as described in_Methods_. LEF-1 reporter activity was determined an additional 24 h later.
Figure 2
axin2 and hnkd mRNA levels are reduced in response to β-catenin antisense ODN transfection. SW620 cells were transfected with β-catenin antisense ODN. Total RNA from the cells was reverse transcribed 48 h posttransfection.axin2, hnkd, and β-catenin mRNA expression levels were determined by quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The graph represents the average of three experiments.
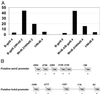
Figure 3
hNkd antagonizes Wnt signaling in mammalian cells and the putative promoters of axin2 and hnkd contain TCF-binding elements. (A) hNkd inhibits Wnt-1 signaling in a luciferase reporter assay in 293 cells. The data represent the average of two experiments. RLU, relative luciferase unit. (B) Schematic representation of the genomic sequence upstream of the axin2 and hnkd coding region identified as described in Methods. The putative TCF sites are shown as TBE boxes and nucleotide residues relative to the starting codon are indicated. A perfect match (CTTTGA/TA/T) is labeled with +, and an inverted perfect match is labeled as −.
Figure 4
axin2 and hnkd mRNA levels in human cell lines. Total RNA from a panel of 30 cell lines was reverse-transcribed, and axin2 and hnkd mRNA levels were determined by quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to actin.axin2 and hnkd mRNA levels are prominently elevated in human colon cancer cell lines.
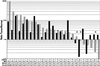
Figure 5
axin2 and hnkd mRNA levels in human colon tumors. Total RNA from laser microdissected tissues was amplified and reversed transcribed as described in Methods. axin2 and hnkd mRNA levels were determined by quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to β-glucuronidase. The mutational status of APC in the patients was determined as described (Methods) and is indicated. Three patients that are wild type for APC are marked with *. The ratios of mRNA expression in tumor versus normal tissues for both_axin2_ and hnkd mRNA levels are shown in the table.
Similar articles
- Novel colon cancer cell lines leading to better understanding of the diversity of respective primary cancers.
Vécsey-Semjén B, Becker KF, Sinski A, Blennow E, Vietor I, Zatloukal K, Beug H, Wagner E, Huber LA. Vécsey-Semjén B, et al. Oncogene. 2002 Jul 11;21(30):4646-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205577. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12096341 - beta-Catenin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in colon cancer.
Easwaran V, Lee SH, Inge L, Guo L, Goldbeck C, Garrett E, Wiesmann M, Garcia PD, Fuller JH, Chan V, Randazzo F, Gundel R, Warren RS, Escobedo J, Aukerman SL, Taylor RN, Fantl WJ. Easwaran V, et al. Cancer Res. 2003 Jun 15;63(12):3145-53. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12810642 - AXIN1 mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas, and growth suppression in cancer cells by virus-mediated transfer of AXIN1.
Satoh S, Daigo Y, Furukawa Y, Kato T, Miwa N, Nishiwaki T, Kawasoe T, Ishiguro H, Fujita M, Tokino T, Sasaki Y, Imaoka S, Murata M, Shimano T, Yamaoka Y, Nakamura Y. Satoh S, et al. Nat Genet. 2000 Mar;24(3):245-50. doi: 10.1038/73448. Nat Genet. 2000. PMID: 10700176 - Catenins, Wnt signaling and cancer.
Barker N, Clevers H. Barker N, et al. Bioessays. 2000 Nov;22(11):961-5. doi: 10.1002/1521-1878(200011)22:11<961::AID-BIES1>3.0.CO;2-T. Bioessays. 2000. PMID: 11056471 Review. - Regulation of beta-catenin signaling in the Wnt pathway.
Kikuchi A. Kikuchi A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Feb 16;268(2):243-8. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.1860. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 10679188 Review.
Cited by
- ABL1-dependent OTULIN phosphorylation promotes genotoxic Wnt/β-catenin activation to enhance drug resistance in breast cancers.
Wang W, Li M, Ponnusamy S, Chi Y, Xue J, Fahmy B, Fan M, Miranda-Carboni GA, Narayanan R, Wu J, Wu ZH. Wang W, et al. Nat Commun. 2020 Aug 7;11(1):3965. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17770-9. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32770022 Free PMC article. - Notch1 counteracts WNT/β-catenin signaling through chromatin modification in colorectal cancer.
Kim HA, Koo BK, Cho JH, Kim YY, Seong J, Chang HJ, Oh YM, Stange DE, Park JG, Hwang D, Kong YY. Kim HA, et al. J Clin Invest. 2012 Sep;122(9):3248-59. doi: 10.1172/JCI61216. Epub 2012 Aug 6. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 22863622 Free PMC article. - Wnt/β-Catenin-Responsive Cells in Prostatic Development and Regeneration.
Lee SH, Johnson DT, Luong R, Yu EJ, Cunha GR, Nusse R, Sun Z. Lee SH, et al. Stem Cells. 2015 Nov;33(11):3356-67. doi: 10.1002/stem.2096. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 26220362 Free PMC article. - β-Catenin gain of function in muscles impairs neuromuscular junction formation.
Wu H, Lu Y, Barik A, Joseph A, Taketo MM, Xiong WC, Mei L. Wu H, et al. Development. 2012 Jul;139(13):2392-404. doi: 10.1242/dev.080705. Epub 2012 May 23. Development. 2012. PMID: 22627288 Free PMC article. - H. pylori virulence factor CagA increases intestinal cell proliferation by Wnt pathway activation in a transgenic zebrafish model.
Neal JT, Peterson TS, Kent ML, Guillemin K. Neal JT, et al. Dis Model Mech. 2013 May;6(3):802-10. doi: 10.1242/dmm.011163. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Dis Model Mech. 2013. PMID: 23471915 Free PMC article.
References
- Polakis P. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:15–21. - PubMed
- Groden J, Thliveris A, Samowitz W, Carlson M, Gelbert L, Albertsen H, Joslyn G, Stevens J, Spirio L, Robertson M, et al. Cell. 1991;66:589–600. - PubMed
- Kinzler K W, Nilbert M C, Su L K, Vogelstein B, Bryan T M, Levy D B, Smith K J, Preisinger A C, Hedge P, McKechnie D, et al. Science. 1991;253:661–665. - PubMed
- Satoh S, Daigo Y, Furukawa Y, Kato T, Miwa N, Nishiwaki T, Kawasoe T, Ishiguro H, Fujita M, Tokino T, et al. Nat Genet. 2000;24:245–250. - PubMed
- Liu W, Dong X, Mai M, Seelan R S, Taniguchi K, Krishnadath K K, Halling K C, Cunningham J M, Boardman L A, Qian C, et al. Nat Genet. 2000;26:146–147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous