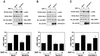Stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha activates LIM kinase 1 and induces cofilin phosphorylation for T-cell chemotaxis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha activates LIM kinase 1 and induces cofilin phosphorylation for T-cell chemotaxis
Michiru Nishita et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Feb.
Abstract
Stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha (SDF-1alpha), the ligand for G-protein-coupled receptor CXCR4, is a chemotactic factor for T lymphocytes. LIM kinase 1 (LIMK1) phosphorylates cofilin, an actin-depolymerizing and -severing protein, at Ser-3 and regulates actin reorganization. We investigated the role of cofilin phosphorylation by LIMK1 in SDF-1alpha-induced chemotaxis of T lymphocytes. SDF-1alpha significantly induced the activation of LIMK1 in Jurkat human leukemic T cells and peripheral blood lymphocytes. SDF-1alpha also induced cofilin phosphorylation, actin reorganization, and activation of small GTPases, Rho, Rac, and Cdc42, in Jurkat cells. Pretreatment with pertussis toxin inhibited SDF-1alpha-induced LIMK1 activation, thus indicating that Gi protein is involved in LIMK1 activation. Expression of dominant negative Rac (DN-Rac), but not DN-Rho or DN-Cdc42, blocked SDF-1alpha-induced activation of LIMK1, which means that SDF-1alpha-induced LIMK1 activation is mediated by Rac but not by Rho or Cdc42. We used a cell-permeable peptide (S3 peptide) that contains the phosphorylation site (Ser-3) of cofilin to inhibit the cellular function of LIMK1. S3 peptide inhibited the kinase activity of LIMK1 in vitro. Treatment of Jurkat cells with S3 peptide inhibited the SDF-1alpha-induced cofilin phosphorylation, actin reorganization, and chemotactic response of Jurkat cells. These results suggest that the phosphorylation of cofilin by LIMK1 plays a critical role in the SDF-1alpha-induced chemotactic response of T lymphocytes.
Figures
FIG. 1.
SDF-1α activates LIMK1 in Jurkat cells and PBL. (A) Jurkat cells were stimulated with 5 nM SDF-1α. At the indicted times, cells were lysed and endogenous LIMK1 was immunoprecipitated and subjected to an in vitro kinase reaction, using His6-cofilin as a substrate. Reaction mixtures were subjected to SDS-PAGE and analyzed using autoradiography and amido black staining for cofilin. Arrows indicate the position of cofilin. Relative kinase activities of LIMK1 after SDF-1α stimulation are shown as means and standard deviations of three independent experiments, with the value at zero time taken as 1.0. (B) PBL were stimulated with 5 nM SDF-1α, and the kinase activity of endogenous LIMK1 at the indicated times after SDF-1α stimulation was analyzed as in panel A.
FIG. 2.
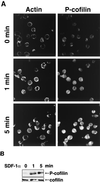
SDF-1α induces actin reorganization and cofilin phosphorylation in Jurkat cells. (A) Jurkat cells stuck to coverslips were stimulated with 5 nM SDF-1α. At the indicated times, the cells were fixed and stained with anti-β-actin (left) and anti-P-cofilin antibodies (right). (B) Jurkat cells were stimulated with 5 nM SDF-1α. At the indicated times, the cells were lysed and aliquots of total lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the antibody against P-cofilin (top) or cofilin (bottom).
FIG. 3.
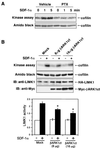
Effects of PTX and βARK1ct on SDF-1α-induced LIMK1 activation. (A) Jurkat cells were incubated in the presence or absence of PTX (100 ng/ml) for 16 h and then stimulated with 5 nM SDF-1α. At the indicated times after SDF-1α stimulation, the cells were lysed and endogenous LIMK1 was immunoprecipitated and subjected to an in vitro kinase reaction, using His6-cofilin as a substrate. Reaction mixtures were subjected to SDS-PAGE and analyzed using autoradiography and amido black staining for cofilin. (B) Jurkat cells were cotransfected with expression plasmids coding for HA-LIMK1 and plasmids for Myc-βARK1ct or vector (Mock). The cells were stimulated with 5 nM SDF-1α for 1 min and lysed. HI-LIMK1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay, as in panel A. Expression of HA-LIMK1 and Myc-βARK1ct was analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-LIMK1 and anti-Myc antibodies. The bottom panel indicates the relative LIMK1 kinase activity, with the value of unstimulated Mock cells taken as 1.0. Results are shown as the means and standard deviations of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.005 compared with SDF-1α-stimulated mock-transfected cells.
FIG. 4.
Activation of Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 by SDF-1α and effects of PTX on their activation. (A) Activation of Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 by SDF-1α. Jurkat cells were stimulated with 5 nM SDF-1α. At the indicated times, the cells were lysed and the lysates were subjected to the affinity precipitation assay for determining Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 activities in the presence of GST-RBD (top) or GST-PBD (middle and bottom). Proteins bound to GST-RBD or GST-PBD and aliquots of total lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the antibody against RhoA, Rac, or Cdc42. (B) PTX treatment inhibits SDF-1α-induced activation of Rac and Cdc42 but not Rho. Jurkat cells were pretreated with PTX (100 ng/ml) for 16 h or not pretreated and were then incubated with or without 5 nM SDF-1α for 1 min. Cells were then lysed and subjected to the affinity precipitation assay, as in panel A.
FIG. 5.
SDF-1α-induced LIMK1 activation is inhibited by the dominant negative form of Rac but not of either Cdc42 or Rho. Jurkat cells were cotransfected with expression plasmids encoding Myc-LIMK1 and plasmids for RhoN19 (A), RacN17 (B), or Cdc42N17 (C). The cells were stimulated for 1 min with 5 nM SDF-1α and lysed. Myc-LIMK1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay, using His6-cofilin as a substrate. Expression of Myc-LIMK1 and HA-tagged RhoN19, RacN17, and Cdc42N17 was analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-LIMK1 and anti-HA antibodies. Results are shown as the means and standard deviations of three independent experiments.
FIG. 6.
Phosphorylation of Thr-508 is involved in SDF-1α-induced activation of LIMK1. Jurkat cells were transfected with expression plasmids encoding Myc-LIMK1 or its T508V mutant. The cells were incubated for 1 min with or without 5 nM SDF-1α and lysed. Myc-LIMK1 and its mutant were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay, using His6-cofilin as a substrate. Expression of Myc-LIMK1 and its mutant was analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-LIMK1 antibody. WT, wild type.
FIG. 7.
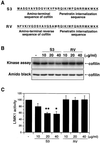
A cell-permeable S3-peptide, but not RV-peptide, inhibits the kinase activity of LIMK1 in vitro. (A) Structures of S3 and RV peptides. (B) In vitro kinase assay. Jurkat cells were stimulated with 5 nM SDF-1α for 1 min and lysed. LIMK1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-LIMK1 antibody and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay, using His6-cofilin as a substrate, in the presence or absence of the indicated amounts of S3 or RV peptide. (C) The bands on the autoradiographs were quantified by densitometry. Results are shown as the means and standard deviation of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 compared with control. **, P < 0.005 compared with control.
FIG. 8.
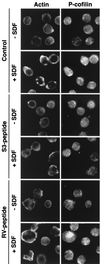
Effects of S3 and RV peptide on SDF-1α-induced cofilin phosphorylation and actin reorganization in Jurkat cells. Jurkat cells attached to coverslips were preincubated with or without 40 μg of S3 or RV peptide per ml for 30 min and then further incubated with or without 5 nM SDF-1α for 1 min. The cells were fixed and stained with anti-β-actin and anti-P-cofilin antibodies.
FIG. 9.
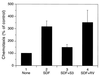
Effects of S3 and RV peptide on SDF-1α-induced chemotaxis in Jurkat cells. Jurkat cells were preincubated with chemotaxis medium in the presence or absence of 40 μg of S3 or RV peptide per ml for 30 min, and the chemotactic response of Jurkat cells towards 5 nM SDF-1α was determined in a 96-well chemotaxis chamber at 37°C for 3 h, as described in Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as percentages of the control and are shown as the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments.
Similar articles
- The CXC chemokine stromal cell-derived factor activates a Gi-coupled phosphoinositide 3-kinase in T lymphocytes.
Sotsios Y, Whittaker GC, Westwick J, Ward SG. Sotsios Y, et al. J Immunol. 1999 Dec 1;163(11):5954-63. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10570282 - Cofilin phosphorylation and actin cytoskeletal dynamics regulated by rho- and Cdc42-activated LIM-kinase 2.
Sumi T, Matsumoto K, Takai Y, Nakamura T. Sumi T, et al. J Cell Biol. 1999 Dec 27;147(7):1519-32. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.7.1519. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10613909 Free PMC article. - Specific activation of LIM kinase 2 via phosphorylation of threonine 505 by ROCK, a Rho-dependent protein kinase.
Sumi T, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T. Sumi T, et al. J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 5;276(1):670-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007074200. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11018042 - Lim kinases, regulators of actin dynamics.
Bernard O. Bernard O. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(6):1071-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.11.011. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17188549 Review. - Ras initiates phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/PKB mediated signalling pathways in untransformed human peripheral blood T lymphocytes.
Samstag Y, Nebl G. Samstag Y, et al. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2005;45:52-62. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2005.02.005. Epub 2005 Aug 9. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2005. PMID: 16083947 Review.
Cited by
- Slit-2/Robo-1 modulates the CXCL12/CXCR4-induced chemotaxis of T cells.
Prasad A, Qamri Z, Wu J, Ganju RK. Prasad A, et al. J Leukoc Biol. 2007 Sep;82(3):465-76. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1106678. Epub 2007 Jun 12. J Leukoc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17565045 Free PMC article. - Involvement of p114-RhoGEF and Lfc in Wnt-3a- and dishevelled-induced RhoA activation and neurite retraction in N1E-115 mouse neuroblastoma cells.
Tsuji T, Ohta Y, Kanno Y, Hirose K, Ohashi K, Mizuno K. Tsuji T, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Oct 15;21(20):3590-600. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-02-0095. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20810787 Free PMC article. - Solo regulates the localization and activity of PDZ-RhoGEF for actin cytoskeletal remodeling in response to substrate stiffness.
Kunitomi A, Chiba S, Higashitani N, Higashitani A, Sato S, Mizuno K, Ohashi K. Kunitomi A, et al. Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Jun 1;35(6):ar87. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-11-0421. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38656797 Free PMC article. - Discovery of Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitors of LIM Domain Kinase for Inhibiting HIV-1.
Yi F, Guo J, Dabbagh D, Spear M, He S, Kehn-Hall K, Fontenot J, Yin Y, Bibian M, Park CM, Zheng K, Park HJ, Soloveva V, Gharaibeh D, Retterer C, Zamani R, Pitt ML, Naughton J, Jiang Y, Shang H, Hakami RM, Ling B, Young JAT, Bavari S, Xu X, Feng Y, Wu Y. Yi F, et al. J Virol. 2017 Jun 9;91(13):e02418-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02418-16. Print 2017 Jul 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28381571 Free PMC article. - Actin cytoskeletal reorganizations and coreceptor-mediated activation of rac during human immunodeficiency virus-induced cell fusion.
Pontow SE, Heyden NV, Wei S, Ratner L. Pontow SE, et al. J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(13):7138-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.13.7138-7147.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15194790 Free PMC article.
References
- Abe, H., S. Ohshima, and T. Obinata. 1989. A cofilin-like protein is involved in the regulation of actin assembly in developing skeletal muscle. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 106:696–702. - PubMed
- Aiuti, A., I. J. Webb, C. Bleul, T. Springer, and R. J. Gutierrez. 1997. The chemokine SDF-1 is a chemoattractant for human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells and provides a new mechanism to explain the mobilization of CD34+ progenitors to peripheral blood. J. Exp. Med. 185:111–120. - PMC - PubMed
- Aizawa, H., S. Wakatsuki, A. Ishii, K. Moriyama, Y. Sasaki, K. Ohashi, Y. Aizawa-Sekine, A. Fujisawa-Sehara, K. Mizuno, Y. Goshima, and I. Yahara. 2001. Phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase is necessary for semaphorin 3A-induced growth cone collapse. Nat. Neurosci. 4:367–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous