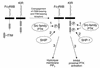ITAMs versus ITIMs: striking a balance during cell regulation - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
ITAMs versus ITIMs: striking a balance during cell regulation
Daniel D Billadeau et al. J Clin Invest. 2002 Jan.
No abstract available
Figures
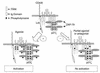
Figure 1
A model depicting TCR-mediated ζ chain phosphorylation. The figure depicts the TCR (α and β) along with the associated CD3 chains and the p21 form of the ζ homodimer. In the resting state, some TCRs are associated with p21ζ, which bears phosphorylated tyrosines in ITAM B (3, 4) and C (5, 6) that can potentially be bound by up to four inactive ZAP-70 molecules (depicted in upper TCR complex). The Src family PTK Lck is shown myristoylated and associated with CD4 or CD8. The Src family PTK Fyn is not shown but is known to associate with the CD3ε subunit. Upon agonist binding there is receptor clustering (not shown), and CD4/8-associated Lck (and CD3ε-associated Fyn, not shown) can then phosphorylate the four tyrosines within the membrane-proximal ITAM (ITAM-A, tyrosines 1 and 2) to produce p23ζ. In addition, active Lck phosphorylates and activates bound ZAP-70, and tyrosines within the ITAMs of other CD3 subunits, resulting in the recruitment and activation of more ZAP-70 molecules (depicted in lower left). In contrast, upon binding to a partial agonist or an antagonist there is potentially less activation of Lck, which results in neither the full phosphorylation of the p21ζ into the p23ζ form (bottom right) nor the activation and recruitment of ZAP-70 (bottom right). Because of the blunted response through the TCR, signals that would normally result in T cell activation do not occur. Whether or not monophosphorylated ITAMs are formed and whether they serve to recruit negative regulators following partial agonist- or antagonist-TCR interaction will require further experimentation.
Figure 2
A model of ITIM-related cellular regulation. Co-ligation of ITAM-containing activating receptors with ITIM-bearing inhibitory receptors facilitates the Src family PTK-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of the ITIMs. For FcγRIIB, this creates high-affinity epitopes for SH2-containing SHIP and the subsequent hydrolysis of the membrane inositol phosphate PIP3. For killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIRs), the tyrosine-phosphorylated ITIMs recruit SH2-containing SHP-1 (and SHP-2), leading to a block in early PTK activation.
Similar articles
- Co-receptor and accessory regulation of B-cell antigen receptor signal transduction.
Buhl AM, Cambier JC. Buhl AM, et al. Immunol Rev. 1997 Dec;160:127-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1997.tb01033.x. Immunol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9476671 Review. - [MHC-restricted antigen recognition by T cells].
Yagita H. Yagita H. Nihon Rinsho. 1990 Sep;48(9):1921-8. Nihon Rinsho. 1990. PMID: 2232193 Japanese. No abstract available. - B lymphocyte signaling pathways in systemic autoimmunity: implications for pathogenesis and treatment.
Zouali M, Sarmay G. Zouali M, et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Sep;50(9):2730-41. doi: 10.1002/art.20487. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15457440 Review. No abstract available. - Blockade of T cell activation using a surface-linked single-chain antibody to CTLA-4 (CD152).
Griffin MD, Hong DK, Holman PO, Lee KM, Whitters MJ, O'Herrin SM, Fallarino F, Collins M, Segal DM, Gajewski TF, Kranz DM, Bluestone JA. Griffin MD, et al. J Immunol. 2000 May 1;164(9):4433-42. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.9.4433. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10779742 - B cell inhibitory receptors and autoimmunity.
Pritchard NR, Smith KG. Pritchard NR, et al. Immunology. 2003 Mar;108(3):263-73. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01592.x. Immunology. 2003. PMID: 12603592 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Combined Analysis of DNA Methylome and Transcriptome Reveal Novel Candidate Genes Related to Porcine Escherichia coli F4ab/ac-Induced Diarrhea.
Wang W, Zhou C, Tang H, Yu Y, Zhang Q. Wang W, et al. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 May 29;10:250. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00250. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32547963 Free PMC article. - Different partners, opposite outcomes: a new perspective of the immunobiology of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.
Orabona C, Pallotta MT, Grohmann U. Orabona C, et al. Mol Med. 2012 Jul 18;18(1):834-42. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2012.00029. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22481272 Free PMC article. Review. - Unveiling the significance of TREM1/2 in hemorrhagic stroke: structure, function, and therapeutic implications.
Kong Y, Wang D, Jin X, Liu Y, Xu H. Kong Y, et al. Front Neurol. 2024 Feb 7;15:1334786. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1334786. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38385036 Free PMC article. Review. - Modulators of endothelial cell filopodia: PECAM-1 joins the club.
DeLisser HM. DeLisser HM. Cell Adh Migr. 2011 Jan-Feb;5(1):37-41. doi: 10.4161/cam.5.1.13575. Epub 2011 Jan 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2011. PMID: 20935458 Free PMC article. - Defining the TLT-1 interactome from resting and activated human platelets.
Schmoker AM, Perez Pearson LM, Cruz C, Colon Flores LG, Branfeild S, Pagán Torres FD, Fonseca K, Cantres YM, Salgado Ramirez CA, Melendez LM, Ballif BA, Washington AV. Schmoker AM, et al. J Proteomics. 2020 Mar 20;215:103638. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103638. Epub 2020 Jan 8. J Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31923473 Free PMC article.
References
- Reth M. Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature. 1989;338:383–384. - PubMed
- Cambier JC. New nomenclature for the Reth motif (or ARH1/TAM/ARAM/YXXL) Immunol Today. 1995;16:110. - PubMed
- Amigorena S, et al. Cytoplasmic domain heterogeneity and functions of IgG Fc receptors in B lymphocytes. Science. 1992;256:1808–1812. - PubMed
- Ravetch JV, Lanier LL. Immune inhibitory receptors. Science. 2000;290:84–89. - PubMed
- Weiss A. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction: a tale of tails and cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1993;73:209–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources