Glucocorticoids reverse IL-1beta-induced impairment of beta-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation and up-regulation of G-protein-coupled receptor kinases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Glucocorticoids reverse IL-1beta-induced impairment of beta-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation and up-regulation of G-protein-coupled receptor kinases
Judith C W Mak et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Feb.
Abstract
1. The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of glucocorticoid dexamethasone on airway responsiveness to albuterol after intratracheal instillation of saline or IL-1beta in Brown-Norway rats in vivo and to elucidate the molecular mechanism of this effect. 2. IL-1beta caused a significant reduction in albuterol-mediated relaxation to protect against MCh-induced bronchoconstriction. Dexamethasone attenuated the IL-1beta-induced impaired relaxation while alone had no effect when compared to rats treated identically with saline. 3. The density of beta(2)-adrenoceptors was significantly reduced in lung membranes harvested from IL-1beta-treated rats, which was associated with impaired isoproterenol- and forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation and adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity ex vivo. Dexamethasone did not prevent IL-1beta-induced down-regulation of beta(2)-adrenoceptors but completely blocked IL-1beta-induced impairment of cyclic AMP accumulation and AC activity stimulated by isoproterenol and forskolin. 4. The inhibitory G-protein subtypes, G(ialpha1), G(ialpha2) and G(ialpha3), were detected in lung membranes prepared from all groups of rats but the intensity of G(ialpha1) and G(ialpha2) was markedly increased in IL-1beta-treated rats, which were not prevented by dexamethasone. 5. The activity of cytosolic GRK and the expression of GRK2 and GRK5 were elevated in the lung of IL-1beta-treated rats, which were completely abolished by dexamethasone. 6. These results indicate that treatment of rats with IL-1beta results in desensitization of pulmonary beta(2)-adrenoceptors. In light of data obtained in this study, we propose that both the decrease in AC activity and the increase in GRK activity, which are reversed by dexamethasone, may underlie beta(2)-adrenoceptor desensitization.
Figures
Figure 1
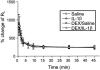
Time-course of per cent change in RL after inhalation of 4 mg ml−1 methacholine (MCh). The bronchoconstrictor response to the inhalation of MCh was rapid and was maximal by 5 min. The bronchoconstrictor response was stable for 45 min. All groups of animals showed a similar time-course and there were no significant differences between the groups. _n_=3 in each group.
Figure 2
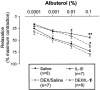
Effect of IL-1β instillation (500 U), dexamethasone (DEX; 3 mg kg−1, i.p.) and/or combined treatments on the protective actions of albuterol against methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction. IL-1β attenuated the relaxant effect of albuterol. DEX alone did not have any effects while DEX reversed the IL-1β-induced attenuation of albuterol effect. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 in comparison to saline-treated group.
Figure 3
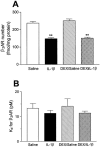
Effect of IL-1β and/or dexamethasone (DEX) on the density (as measured by the maximal binding, Bmax) and the affinity (as measured by the dissociation constant, K d) of β2-adrenoceptors (β2ARs). Total [125I]-iodocyanopindolol ([125I]-ICYP) was displaced by the specific β1-receptor antagonist, CGP-20712A (100 n
M
), or isoproterenol (200 μ
M
, to give nonspecific binding). The affinity of β2-adrenoceptors was not altered by either IL-1β or by dexamethasone. However, IL-1β caused a significant reduction in the density of receptors, an effect that was not prevented by dexamethasone. Data are means±s.e.mean of four animals in each group. **P<0.01.
Figure 4
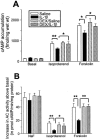
Effect of IL-1β and/or dexamethasone (DEX) on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP) accumulation stimulated by isoproterenol (10 μ
M
) and forskolin (10 μ
M
) (A), and on adenylyl cyclase activity stimulated by sodium fluoride (10 m
M
), isoproterenol and forskolin (B). Intratracheal instillation of IL-1β caused significant attenuation in isoproterenol- and forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation and adenylyl cyclase activity, which was reversed by DEX. Data are means±s.e.means of 4 – 6 animals in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
Figure 5
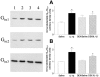
Comparison of Western blots for the expression of Giα isoforms in lung membranes prepared from each group of animals. The left-hand panel shows a representative example of Western blot analysis from a rat from each experimental group. Note enhanced expression of Giα1 and Giα2 in IL-1β-treated (lane 2), and dexamethasone (DEX) plus IL-1β-treated (lane 4) compared with saline (lane 1), and DEX plus saline (lane 3) groups. Right-hand panels (A,B) Densitometric measurements of Giα1 and Giα2 immunoreactivity were normalized to Giα3. There was a significant increase in Giα1 and Giα2 induced by IL-1β, but dexamethasone had no significant effect. Data are means±s.e.mean of 4 – 6 animals in each group. *P<0.05.
Figure 6
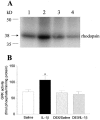
Assessment of GRK activity in lung cytosolic fractions from different treatment groups. (A) Autoradiograph depicting light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin (∼38 kD). Rat lungs from saline (lane 1), IL-1β-treated (lane 2), DEX plus saline (lane 3), and DEX plus IL-1β-treated (lane 4) were shown. (B) Quantification of GRK activity measurements in each group of animals. Data are means±s.e.mean of four animals in each group. *P<0.05.
Figure 7
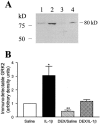
(A) Representative autoradiograph of Western blot depicting immuno-detectable GRK2 (∼80 kD) in lung cytosolic fractions from different treatment groups. Rat lungs from saline (lane 1), IL-1β-treated (lane 2), DEX plus saline (lane 3), and DEX plus IL-1β-treated (lane 4) were shown. (B) Densitometric measurements of GRK2 immunoreactivity. Data are means±s.e.mean of 4 – 6 animals in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
Figure 8
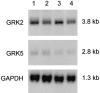
Representative autoradiographs of Northern blot for steady-state level of GRK2, GRK5 and house-keeping gene glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) mRNA expression in lung from different treatment groups. Rat lungs from saline (lane 1), IL-1β-treated (lane 2), DEX plus saline (lane 3), and DEX plus IL-1β-treated (lane 4) were shown.
Similar articles
- Chronic systemic administration of salmeterol to rats promotes pulmonary beta(2)-adrenoceptor desensitization and down-regulation of G(s alpha).
Finney PA, Donnelly LE, Belvisi MG, Chuang TT, Birrell M, Harris A, Mak JC, Scorer C, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM, Giembycz MA. Finney PA, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Mar;132(6):1261-70. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703946. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11250877 Free PMC article. - Mechanisms of impaired beta-adrenoceptor-induced airway relaxation by interleukin-1beta in vivo in the rat.
Koto H, Mak JC, Haddad EB, Xu WB, Salmon M, Barnes PJ, Chung KF. Koto H, et al. J Clin Invest. 1996 Oct 15;98(8):1780-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI118977. J Clin Invest. 1996. PMID: 8878428 Free PMC article. - Albuterol-induced downregulation of Gsalpha accounts for pulmonary beta(2)-adrenoceptor desensitization in vivo.
Finney PA, Belvisi MG, Donnelly LE, Chuang TT, Mak JC, Scorer C, Barnes PJ, Adcock IM, Giembycz MA. Finney PA, et al. J Clin Invest. 2000 Jul;106(1):125-35. doi: 10.1172/JCI8374. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10880056 Free PMC article. - G-protein-coupled receptors: regulatory role of receptor kinases and arrestin proteins.
Lefkowitz RJ, Inglese J, Koch WJ, Pitcher J, Attramadal H, Caron MG. Lefkowitz RJ, et al. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1992;57:127-33. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1992.057.01.016. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1992. PMID: 1339651 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Dual-specificity phosphatase 1 as a pharmacogenetic modifier of inhaled steroid response among asthmatic patients.
Jin Y, Hu D, Peterson EL, Eng C, Levin AM, Wells K, Beckman K, Kumar R, Seibold MA, Karungi G, Zoratti A, Gaggin J, Campbell J, Galanter J, Chapela R, Rodríguez-Santana JR, Watson HG, Meade K, Lenoir M, Rodríguez-Cintrón W, Avila PC, Lanfear DE, Burchard EG, Williams LK. Jin Y, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Sep;126(3):618-25.e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.06.007. Epub 2010 Jul 31. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20673984 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - A cross-tissue transcriptome-wide association study reveals GRK4 as a novel susceptibility gene for COPD.
Chen G, Jin Y, Chu C, Zheng Y, Yang C, Chen Y, Zhu X. Chen G, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 18;14(1):28438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80122-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39558015 Free PMC article. - Mechanism of glucocorticoid protection of airway smooth muscle from proasthmatic effects of long-acting beta2-adrenoceptor agonist exposure.
Nino G, Hu A, Grunstein JS, Grunstein MM. Nino G, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 May;125(5):1020-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.02.007. Epub 2010 Apr 14. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20392484 Free PMC article. - Inhibition of p38 MAPK-dependent bronchial contraction after ozone by corticosteroids.
Li F, Zhang M, Hussain F, Triantaphyllopoulos K, Clark AR, Bhavsar PK, Zhou X, Chung KF. Li F, et al. Eur Respir J. 2011 Apr;37(4):933-42. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00021110. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Eur Respir J. 2011. PMID: 20693246 Free PMC article. - Beta-agonists and asthma: too much of a good thing?
Shore SA, Drazen JM. Shore SA, et al. J Clin Invest. 2003 Aug;112(4):495-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI19642. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12925688 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- BENOVIC J.L., MAYOR F., STANISZEWSKI C., LEFKOWITZ R.J., CARON M.G. Purification and characterization of the β-adrenergic receptor kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1987;262:9026–9032. - PubMed
- BILLINGTON C.K., PASCUAL R.M., HAWKINS M.L., PENN R.B., HALL I.P. Interleukin-1β and rhinovirus sensitize adenylyl cyclase in human airway smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001;24:633–639. - PubMed
- BIN W., AKSOY M.O., YANG Y., KELSEN S.G. IL-1β enhances β2-adrenergic receptor expression in human airway epithelial cells by activating PKC. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2001;280:L675–L679. - PubMed
- BOUVIER M., LEEB-LUNDBERG L.M., BENOVIC J.L., CARON M.G., LEFKOWITZ R.J. Regulation of adrenergic receptor function by phosphorylation. II. Effects of agonist occupancy on phosphorylation of α1- and β2-adrenergic receptors by protein kinase C and the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1987;262:3106–3113. - PubMed
- CHOMCZYNSKI P., SACCHI N. Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987;162:156–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical