Quantitative-trait homozygosity and association mapping and empirical genomewide significance in large, complex pedigrees: fasting serum-insulin level in the Hutterites - PubMed (original) (raw)
Quantitative-trait homozygosity and association mapping and empirical genomewide significance in large, complex pedigrees: fasting serum-insulin level in the Hutterites
Mark Abney et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Apr.
Abstract
We present methods for linkage and association mapping of quantitative traits for a founder population with a large, known genealogy. We detect linkage to quantitative-trait loci (QTLs) through a multipoint homozygosity-mapping method. We propose two association methods, one of which is single point and uses a general two-allele model and the other of which is multipoint and uses homozygosity by descent for a particular allele. In all three methods, we make extensive use of the pedigree and genotype information, while keeping the computations simple and efficient. To assess significance, we have developed a permutation-based test that takes into account the covariance structure due to relatedness of individuals and can be used to determine empirical genomewide and locus-specific P values. In the case of multivariate-normally distributed trait data, the permutation-based test is asymptotically exact. The test is broadly applicable to a variety of mapping methods that fall within the class of linear statistical models (e.g., variance-component methods), under the assumption of random ascertainment with respect to the phenotype. For obtaining genomewide P values, our proposed method is appropriate when positions of markers are independent of the observed linkage signal, under the null hypothesis. We apply our methods to a genome screen for fasting insulin level in the Hutterites. We detect significant genomewide linkage on chromosome 19 and suggestive evidence of QTLs on chromosomes 1 and 16.
Figures
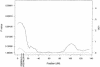
Figure 1
Results of multipoint HBD analysis. P values and equivalent LOD scores with 1 df are plotted with respect to chromosomal position for the genome. The solid line plots the locus-specific value, and the dotted line plots the genomewide value.
Figure 1
Results of multipoint HBD analysis. P values and equivalent LOD scores with 1 df are plotted with respect to chromosomal position for the genome. The solid line plots the locus-specific value, and the dotted line plots the genomewide value.
Figure 2
Results of the multipoint HBD analysis for chromosome 19. The solid line plots the locus-specific value, and the dotted line plots the genomewide value. The position of D19S591, which showed suggestive evidence of association under the ASHBD and GTAM analyses, is indicated on the _X-_axis.
Figure 3
Results of the multipoint HBD analysis for chromosome 16. The solid line plots the locus-specific value, and the dotted line plots the genomewide value. The positions of D16S2622 and ATA41E04, which showed suggestive evidence of association under the ASHBD analysis, are indicated on the _X-_axis.
Similar articles
- The genetic dissection of complex traits in a founder population.
Ober C, Abney M, McPeek MS. Ober C, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Nov;69(5):1068-79. doi: 10.1086/324025. Epub 2001 Oct 3. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11590547 Free PMC article. - A genomewide scan identifies two novel loci involved in specific language impairment.
SLI Consortium. SLI Consortium. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Feb;70(2):384-98. doi: 10.1086/338649. Epub 2002 Jan 4. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 11791209 Free PMC article. - A genome-wide scan using tree-based association analysis for candidate loci related to fasting plasma glucose levels.
Chen CH, Chang CJ, Yang WS, Chen CL, Fann CS. Chen CH, et al. BMC Genet. 2003 Dec 31;4 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S65. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-4-S1-S65. BMC Genet. 2003. PMID: 14975133 Free PMC article. - Joint multipoint linkage analysis of multivariate qualitative and quantitative traits. I. Likelihood formulation and simulation results.
Williams JT, Van Eerdewegh P, Almasy L, Blangero J. Williams JT, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 1999 Oct;65(4):1134-47. doi: 10.1086/302570. Am J Hum Genet. 1999. PMID: 10486333 Free PMC article. - Gene finding strategies.
Vink JM, Boomsma DI. Vink JM, et al. Biol Psychol. 2002 Oct;61(1-2):53-71. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0511(02)00052-2. Biol Psychol. 2002. PMID: 12385669 Review.
Cited by
- PRIMAL: Fast and accurate pedigree-based imputation from sequence data in a founder population.
Livne OE, Han L, Alkorta-Aranburu G, Wentworth-Sheilds W, Abney M, Ober C, Nicolae DL. Livne OE, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Mar 3;11(3):e1004139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004139. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 25735005 Free PMC article. - Genome-wide association study of plasma lipoprotein(a) levels identifies multiple genes on chromosome 6q.
Ober C, Nord AS, Thompson EE, Pan L, Tan Z, Cusanovich D, Sun Y, Nicolae R, Edelstein C, Schneider DH, Billstrand C, Pfaffinger D, Phillips N, Anderson RL, Philips B, Rajagopalan R, Hatsukami TS, Rieder MJ, Heagerty PJ, Nickerson DA, Abney M, Marcovina S, Jarvik GP, Scanu AM, Nicolae DL. Ober C, et al. J Lipid Res. 2009 May;50(5):798-806. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800515-JLR200. Epub 2009 Jan 5. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19124843 Free PMC article. - A second-generation genomewide screen for asthma-susceptibility alleles in a founder population.
Ober C, Tsalenko A, Parry R, Cox NJ. Ober C, et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Nov;67(5):1154-62. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9297(07)62946-2. Epub 2000 Oct 5. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 11022011 Free PMC article. - An Unbiased Estimator of Gene Diversity with Improved Variance for Samples Containing Related and Inbred Individuals of any Ploidy.
Harris AM, DeGiorgio M. Harris AM, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Feb 9;7(2):671-691. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.037168. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28040781 Free PMC article. - Comparing population structure as inferred from genealogical versus genetic information.
Colonna V, Nutile T, Ferrucci RR, Fardella G, Aversano M, Barbujani G, Ciullo M. Colonna V, et al. Eur J Hum Genet. 2009 Dec;17(12):1635-41. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2009.97. Epub 2009 Jun 24. Eur J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19550436 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for microsatellite map)
References
- Anderson MJ, Robinson J (2001) Permutation tests for linear models. Aust NZ J Stat 43:75–88
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL 49596/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 56399/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK55889/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055889/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG001645/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG 01645/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL049596/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R29 HG001645/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL056399/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases