Is ageing associated with a shift in the balance between Type 1 and Type 2 cytokines in humans? - PubMed (original) (raw)
Is ageing associated with a shift in the balance between Type 1 and Type 2 cytokines in humans?
M Sandmand et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002 Jan.
Abstract
The balance between Type 1 and Type 2 cytokines is important for the outcome of several infectious diseases. As elderly humans show increased morbidity and mortality from infectious diseases, this study tests if ageing is associated with a change towards Type 2 dominance in T cells. Expression of IFN-gamma, and IL-4 was measured in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells by flow cytometry in three groups: young controls (n=28), 81-year-olds (n=22), and centenarians (n=25). The major findings were that the percentage of IFN-gamma+ as well as IL-4+ T cells was increased in aged subjects. Furthermore, after adjusting for decreased lymphocyte counts in the elderly, the concentration in the blood of IFN-gamma+ and IL-4+ CD8+ T cells was still increased in the 81-year-olds. In centenarians, a shift towards a relative dominance of Type 2 cytokine expression was found within CD8+ T cells. Furthermore, the percentage of T cells with cytokine expression was closely correlated to the in vivo expression of CD95 and CD45RO. In conclusion, we found some evidence for an age-related shift towards a Type 2 cytokine profile.
Figures
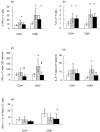
Fig. 1
Cytokine expression in T lymphocytes. Cytokine expression among CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was detected by flow cytometry after 4 h of stimulation with PMA and ionomycin. Young n = 24, 81-year-old n = 14, 100-year-old n = 25. (a) The percentage of IFN-γ+ cells among CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes. (b) The percentage of IL-4+ cells among CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes. (c) The number of IFN-γ producing cells/ml blood. (d) The number of IL-4 producing cells/ml blood. (e) IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio within CD4+ and CD8+ cells. Geometric means and 95% confidence intervals are shown. * denotes a significant difference (P < 0·05) from the young group; # denotes a significant difference (P < 0·05) from the 81-year-old group; □ 21–30 years;  81 years; ▪ 100 years.
81 years; ▪ 100 years.
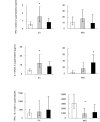
Fig. 2
Cytokine production in BMNC supernatants following PMA + ionomycin stimulation. Cytokine production was detected by ELISA after stimulation for 5 and 48 h. IFN-γ; Young, n = 23; 81-year-old, n = 10; 100-year-old, n = 18. IL-4; Young, n = 17; 81-year-old, n = 8; 100-year-old, n = 18. Geometric means and 95% confidence intervals are shown. * denotes a significant difference (P < 0·05) from the young group; □ 21–30 years;  81 years; ▪ 100 years.
81 years; ▪ 100 years.
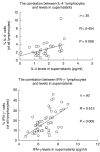
Fig. 3
Correlation between the percentage of cytokine-expressing lymphocytes and cytokine levels in culture supernatants. BMNC for intracellular cytokine detection and BMNC for supernatants were stimulated by using exactly the same amounts of PMA + ionomycin. The percentage of all lymphocytes expressing intracellular cytokines was correlated with cytokine levels in supernatants after 5 h. The supernatants after 5 h were ln transformed. Each independent variable was tested for an interaction with age groups. No interactions were found, and accordingly age groups were pooled. Geometric means and 95% confidence intervals are shown.
Similar articles
- T helper 1/T helper 2 cytokine imbalance in respiratory syncytial virus infection is associated with increased endogenous plasma cortisol.
Pinto RA, Arredondo SM, Bono MR, Gaggero AA, Díaz PV. Pinto RA, et al. Pediatrics. 2006 May;117(5):e878-86. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-2119. Epub 2006 Apr 17. Pediatrics. 2006. PMID: 16618789 - Age-related changes in intracellular TH1/TH2 cytokine production, immunoproliferative T lymphocyte response and natural killer cell activity in newborns, children and adults.
Gasparoni A, Ciardelli L, Avanzini A, Castellazzi AM, Carini R, Rondini G, Chirico G. Gasparoni A, et al. Biol Neonate. 2003;84(4):297-303. doi: 10.1159/000073638. Biol Neonate. 2003. PMID: 14593240 - Analysis of Th1 and Th2 cytokines expressing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis by flow cytometry.
Berner B, Akça D, Jung T, Muller GA, Reuss-Borst MA. Berner B, et al. J Rheumatol. 2000 May;27(5):1128-35. J Rheumatol. 2000. PMID: 10813277 - [A role for T-helper type 1 and type 2 cytokines in the pathogenesis of various human diseases].
Kasakura S. Kasakura S. Rinsho Byori. 1998 Sep;46(9):915-21. Rinsho Byori. 1998. PMID: 9800477 Review. Japanese. - Age-related changes in Type 1 and Type 2 cytokine production in humans.
Gardner EM, Murasko DM. Gardner EM, et al. Biogerontology. 2002;3(5):271-90. doi: 10.1023/a:1020151401826. Biogerontology. 2002. PMID: 12237564 Review.
Cited by
- Allergy and asthma in the elderly.
Mathur SK. Mathur SK. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Oct;31(5):587-95. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1265899. Epub 2010 Oct 12. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20941659 Free PMC article. Review. - Age-related changes in ocular mucosal tolerance: Lessons learned from gut and respiratory tract immunity.
Galletti JG, de Paiva CS. Galletti JG, et al. Immunology. 2021 Sep;164(1):43-56. doi: 10.1111/imm.13338. Epub 2021 May 2. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 33837534 Free PMC article. Review. - Depressive symptoms post hip fracture in older adults are associated with phenotypic and functional alterations in T cells.
Duggal NA, Upton J, Phillips AC, Hampson P, Lord JM. Duggal NA, et al. Immun Ageing. 2014 Dec 16;11(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12979-014-0025-5. eCollection 2014. Immun Ageing. 2014. PMID: 25628751 Free PMC article. - Relationship between inflammatory mediators, Aβ levels and ApoE genotype in Alzheimer disease.
Reale M, Kamal MA, Velluto L, Gambi D, Di Nicola M, Greig NH. Reale M, et al. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012 May;9(4):447-57. doi: 10.2174/156720512800492549. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2012. PMID: 22272623 Free PMC article. - IL-2 and IL-10 gene polymorphisms are associated with respiratory tract infection and may modulate the effect of vitamin E on lower respiratory tract infections in elderly nursing home residents.
Belisle SE, Hamer DH, Leka LS, Dallal GE, Delgado-Lista J, Fine BC, Jacques PF, Ordovas JM, Meydani SN. Belisle SE, et al. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010 Jul;92(1):106-14. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2010.29207. Epub 2010 May 19. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20484443 Free PMC article.
References
- Mosmann TR, Sad S. The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunol Today. 1996;17:138–46. - PubMed
- Crossley KB, Peterson PK. Infections in the elderly. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:209–15. - PubMed
- Yoshikawa TT. Perspective aging and infectious diseases: past, present, and future. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:1053–7. - PubMed
- LeMaoult J, Szabo P, Weksler ME. Effect of age on humoral immunity, selection of the B-cell repertoire and B-cell development. Immunol Rev. 1997;160:115–26. - PubMed
- Shearer GM. Th1/Th2 changes in aging. Mech Ageing Dev. 1997;94:1–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials