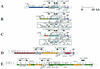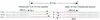Novel type of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec identified in community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains - PubMed (original) (raw)
Novel type of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec identified in community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains
Xiao Xue Ma et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Apr.
Abstract
We identified a new type of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) from two community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains. The novel element, designated type IV SCCmec, had a unique combination of the class B mec gene complex and the type 2 ccr gene complex and was much smaller in size (21 to 24 kb) than previously identified SCCmec elements of hospital-acquired MRSA. Consistent with the strains' susceptibilities to various non-beta-lactam antibiotics, the type IV SCCmec was devoid of any antibiotic resistance genes other than the mecA gene.
Figures
FIG. 1.
Structure of the SCC_mec_ elements identified from C-MRSA strains in comparison with the three types of SCC_mec_ elements. (A) Type I SCC_me_c carried by NCTC 10442. (B) Type IV SCC_mec_ carried by strain CA05 (subtype a). (C) Type IV SCC_mec_ carried by strain 8/6-3P (subtype b). (D) Type II SCC_mec_ carried by N315. (E) Type III SCC_mec_ carried by 85/2082. The ORFs of greater than 200 nucleotides in six possible reading frames of type IV SCC_mec_ elements are illustrated in the squares under the bars that represent essential genes and restriction sites for Hin_dIII and Xba_I. Differences in coloration correspond to differences in the nucleotide sequences. Color codes are as follows: white, ORFs or the parts of ORFs that are conserved in all four types of SCC_mec elements with greater than 99% amino acid identities; gray, ORFs or the parts of ORFs that are conserved in four types of SCC_mec with amino acid identities of 46 to 98%; magenta, ORFs or the parts of ORFs that are common to type I and type II SCC_mec_ elements; yellow, ORFs or the parts of ORFs that are common to type II and type III SCC_mec_ elements; blue, ORFs or the parts of ORFs that are unique to type I SCC_mec_; red, ORFs or the parts of ORFs that are unique to type II SCC_mec_; green, ORFs or the parts of ORFs that are unique to type III SCC_mec_, light green, ORFs or the parts of ORFs that are unique to type IVa SCC_mec_; and orange, ORFs or the parts of ORFs that are unique to type IVb SCC_mec_. The locations of primers used for amplification of the type IV SCC_mec_ are indicated by arrows: they are primers α5 (5′-TGTTAAGTATATTGCACTTTATGATTCAATGCCT-3′), cLs1 (5′-TGCCAATCACAGTTCAATCAATT-3′), α6 (5′-ATTAGCCGATTTGGTAATTGAA-3′), mCR8 (5′-ATATTCCCGTATGAAAAACAGGACTTGAACTTGCA-3′), and CL2b (ATATTCCCGATAGAAAAACAGGACTTGAACTTGCA) and previously described primers is4, mA2, mA3, and cR1 (11, 12, 14). The entire nucleotide sequences of the type IV SCC_mec_ elements are available in the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases under accession no. AB063172 (subtype a) and AB063173 (subtype b). H, _Hin_dIII, X, _Xba_I; E, _Eco_RI; P, Pst1.
FIG. 2.
Chromosome-SCC_mec_ junction sequences of type IV SCC_mec_. The nucleotide sequences around the left and right boundaries of the SCC_mec_ elements of CA05 and 8/6-3P are aligned with those of type II SCC_mec_. Thin arrows indicate inverted repeats IR-L and IR-R at both extremities of SCC_mec_ elements. Thick arrows indicate direct repeats DRscc-L and DRscc-R.
Similar articles
- Analysis of Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec in Staphylococcus haemolyticus and Staphylococcus sciuri: identification of a novel ccr gene complex with a newly identified ccrA allotype (ccrA7).
Urushibara N, Paul SK, Hossain MA, Kawaguchiya M, Kobayashi N. Urushibara N, et al. Microb Drug Resist. 2011 Jun;17(2):291-7. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2010.0144. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Microb Drug Resist. 2011. PMID: 21388304 - [Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the community].
Vonk AG, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM. Vonk AG, et al. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2007 Feb 17;151(7):401-7. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2007. PMID: 17343138 Review. Dutch. - The evolution of Staphylococcus aureus.
Deurenberg RH, Stobberingh EE. Deurenberg RH, et al. Infect Genet Evol. 2008 Dec;8(6):747-63. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2008.07.007. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Infect Genet Evol. 2008. PMID: 18718557 Review.
Cited by
- Epidemiological and molecular characterization of community and hospital acquired Staphylococcus aureus strains prevailing in Shenyang, Northeastern China.
Sun DD, Ma XX, Hu J, Tian Y, Pang L, Shang H, Cui LZ. Sun DD, et al. Braz J Infect Dis. 2013 Nov-Dec;17(6):682-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2013.02.007. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Braz J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23916451 Free PMC article. - Severe community-acquired pneumonia due to Staphylococcus aureus, 2003-04 influenza season.
Hageman JC, Uyeki TM, Francis JS, Jernigan DB, Wheeler JG, Bridges CB, Barenkamp SJ, Sievert DM, Srinivasan A, Doherty MC, McDougal LK, Killgore GE, Lopatin UA, Coffman R, MacDonald JK, McAllister SK, Fosheim GE, Patel JB, McDonald LC. Hageman JC, et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006 Jun;12(6):894-9. doi: 10.3201/eid1206.051141. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16707043 Free PMC article. - Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in horses and horse personnel, 2000-2002.
Weese JS, Archambault M, Willey BM, Hearn P, Kreiswirth BN, Said-Salim B, McGeer A, Likhoshvay Y, Prescott JF, Low DE. Weese JS, et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Mar;11(3):430-5. doi: 10.3201/eid1103.040481. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15757559 Free PMC article. - Combination of multiplex PCRs for staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type assignment: rapid identification system for mec, ccr, and major differences in junkyard regions.
Kondo Y, Ito T, Ma XX, Watanabe S, Kreiswirth BN, Etienne J, Hiramatsu K. Kondo Y, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Jan;51(1):264-74. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00165-06. Epub 2006 Oct 16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17043114 Free PMC article. - Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology and clinical consequences of an emerging epidemic.
David MZ, Daum RS. David MZ, et al. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010 Jul;23(3):616-87. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00081-09. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20610826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
- Brown, D. F., and P. E. Reynolds. 1980. Intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 122:275-278. - PubMed
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1999. Four pediatric deaths from community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus—Minnesota and North Dakota, 1997-1999. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 48:707-710. - PubMed
- Embil, J., K. Ramotar, L. Tomance, M. Alfa, J. Conly, S. Cronk, G. Taylor, B. Sutherland, T. Louie, E. Henderson, et al. 1994. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in tertiary care institutions on the Canadian prairies 1990-1992. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 15:646-651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases