Annotated expressed sequence tags and cDNA microarrays for studies of brain and behavior in the honey bee - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Annotated expressed sequence tags and cDNA microarrays for studies of brain and behavior in the honey bee
Charles W Whitfield et al. Genome Res. 2002 Apr.
Abstract
To accelerate the molecular analysis of behavior in the honey bee (Apis mellifera), we created expressed sequence tag (EST) and cDNA microarray resources for the bee brain. Over 20,000 cDNA clones were partially sequenced from a normalized (and subsequently subtracted) library generated from adult A. mellifera brains. These sequences were processed to identify 15,311 high-quality ESTs representing 8912 putative transcripts. Putative transcripts were functionally annotated (using the Gene Ontology classification system) based on matching gene sequences in Drosophila melanogaster. The brain ESTs represent a broad range of molecular functions and biological processes, with neurobiological classifications particularly well represented. Roughly half of Drosophila genes currently implicated in synaptic transmission and/or behavior are represented in the Apis EST set. Of Apis sequences with open reading frames of at least 450 bp, 24% are highly diverged with no matches to known protein sequences. Additionally, over 100 Apis transcript sequences conserved with other organisms appear to have been lost from the Drosophila genome. DNA microarrays were fabricated with over 7000 EST cDNA clones putatively representing different transcripts. Using probe derived from single bee brain mRNA, microarrays detected gene expression for 90% of Apis cDNAs two standard deviations greater than exogenous control cDNAs. [The sequence data described in this paper have been submitted to Genbank data library under accession nos. BI502708-BI517278. The sequences are also available at http://titan.biotec.uiuc.edu/bee/honeybee\_project.htm.\]
Figures
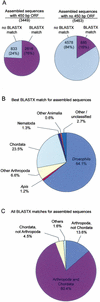
Figure 1
Open reading frame (ORF) and
BLASTX
results. (A) The proportion of assembled sequences with and without
BLASTX
matches in the Non-Redundant Protein (nr) database (E ≤10−5) is indicated for assembled sequences with and without an identified 450 bp ORF. Relative area of pie charts indicates number of sequences. (B) Apis sequences with matches in the nr database (3501 total) were classified by the organism of the “best hit” protein sequence. (C) Apis sequences with matches in the nr database (3501 total) were separately analyzed for matches in Arthropoda and Chordata protein databases (see Table 8 for sub-database creation).
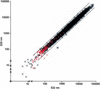
Figure 2
Signal intensities from an example microarray. Values plotted are feature minus background intensity at 635 and 532 nm wavelengths for each cDNA spot (see Methods). Values were normalized such that the median ratio (635:532 nm) equals 1.0. Apis cDNAs are shown as black x's, exogenous negative control cDNAs are shown as red x's. Cy3-labeled probe (532 nm) and Cy5-labeled probe (635 nm) were independently derived from the same starting sample (using in vitro transcription to amplify starting mRNA; see Methods). The starting sample consisted of a mixture of two dissected adult bee brains (one bee observed foraging and one bee observed caring for brood). The coefficient of correlation (r) between 635 and 532 nm values was 0.9926 (based on log-transformed values). Divergence of values from the diagonal (ratio = 1) reflects technical variation introduced during RNA isolation, mRNA amplification by in vitro transcription, and fluorescent labeling of probe. The two diagonal bars indicate ratios (635:532 nm) equal to 0.5 and 2.0.
Similar articles
- The use of Open Reading frame ESTs (ORESTES) for analysis of the honey bee transcriptome.
Nunes FM, Valente V, Sousa JF, Cunha MA, Pinheiro DG, Maia RM, Araujo DD, Costa MC, Martins WK, Carvalho AF, Monesi N, Nascimento AM, Peixoto PM, Silva MF, Ramos RG, Reis LF, Dias-Neto E, Souza SJ, Simpson AJ, Zago MA, Soares AE, Bitondi MM, Espreafico EM, Espindola FS, Paco-Larson ML, Simoes ZL, Hartfelder K, Silva WA Jr. Nunes FM, et al. BMC Genomics. 2004 Nov 3;5:84. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-5-84. BMC Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15527499 Free PMC article. - A comparative analysis of highly conserved sex-determining genes between Apis mellifera and Drosophila melanogaster.
Cristino AS, Nascimento AM, Costa Lda F, Simões ZL. Cristino AS, et al. Genet Mol Res. 2006 Mar 31;5(1):154-68. Genet Mol Res. 2006. PMID: 16755507 - ESTIMA, a tool for EST management in a multi-project environment.
Kumar CG, LeDuc R, Gong G, Roinishivili L, Lewin HA, Liu L. Kumar CG, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004 Nov 4;5:176. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-176. BMC Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15527510 Free PMC article. - Drosophila microarray platforms.
Gupta V, Oliver B. Gupta V, et al. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003 Jul;2(2):97-105. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/2.2.97. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003. PMID: 15239930 Review. - Large-scale analysis of gene expression: methods and application to the kidney.
Cheval L, Virlon B, Billon E, Aude JC, Elalouf JM, Doucet A. Cheval L, et al. J Nephrol. 2002 Mar-Apr;15 Suppl 5:S170-83. J Nephrol. 2002. PMID: 12027216 Review.
Cited by
- Genetics of reproduction and regulation of honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) social behavior.
Page RE Jr, Rueppell O, Amdam GV. Page RE Jr, et al. Annu Rev Genet. 2012;46:97-119. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155610. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Annu Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22934646 Free PMC article. - Differential gene expression in abdomens of the malaria vector mosquito, Anopheles gambiae, after sugar feeding, blood feeding and Plasmodium berghei infection.
Dana AN, Hillenmeyer ME, Lobo NF, Kern MK, Romans PA, Collins FH. Dana AN, et al. BMC Genomics. 2006 May 19;7:119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-119. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16712725 Free PMC article. - Isolation, annotation and applications of expressed sequence tags from the olive fly, Bactrocera oleae.
Tsoumani KT, Augustinos AA, Kakani EG, Drosopoulou E, Mavragani-Tsipidou P, Mathiopoulos KD. Tsoumani KT, et al. Mol Genet Genomics. 2011 Jan;285(1):33-45. doi: 10.1007/s00438-010-0583-y. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Mol Genet Genomics. 2011. PMID: 20978910 - Biologically meaningful expression profiling across species using heterologous hybridization to a cDNA microarray.
Renn SC, Aubin-Horth N, Hofmann HA. Renn SC, et al. BMC Genomics. 2004 Jul 6;5(1):42. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-5-42. BMC Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15238158 Free PMC article. - Evolution of the Yellow/Major Royal Jelly Protein family and the emergence of social behavior in honey bees.
Drapeau MD, Albert S, Kucharski R, Prusko C, Maleszka R. Drapeau MD, et al. Genome Res. 2006 Nov;16(11):1385-94. doi: 10.1101/gr.5012006. Epub 2006 Oct 25. Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 17065613 Free PMC article.
References
- Adams MD, Celniker SE, Holt RA, Evans CA, Gocayne JD, Amanatides PG, Scherer SE, Li PW, Hoskins RA, Galle RF, et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–2195. - PubMed
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB. Normalization and subtraction: Two approaches to facilitate gene discovery. Genome Res. 1996;6:791–806. - PubMed
- Brillet, C., Robinson, G.E., Bues, R., and Le Conte, Y. 2001. Racial differences in division of labor in colonies of the honey bee, Apis Mellifera. Ethology 2002. In press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials