A quantitative trait locus influencing anxiety in the laboratory rat - PubMed (original) (raw)
Rosa M Escorihuela, Jeffrey A Gray, Raúl Aguilar, Luis Gil, Lydia Giménez-Llort, Adolf Tobeña, Amarjit Bhomra, Alison Nicod, Richard Mott, Peter Driscoll, Gerard R Dawson, Jonathan Flint
Affiliations
- PMID: 11932246
- PMCID: PMC187519
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.203402
A quantitative trait locus influencing anxiety in the laboratory rat
Alberto Fernández-Teruel et al. Genome Res. 2002 Apr.
Abstract
A critical test for a gene that influences susceptibility to fear in animals is that it should have a consistent pattern of effects across a broad range of conditioned and unconditioned models of anxiety. Despite many years of research, definitive evidence that genetic effects operate in this way is lacking. The limited behavioral test regimes so far used in genetic mapping experiments and the lack of suitable multivariate methodologies have made it impossible to determine whether the quantitative trait loci (QTL) detected to date specifically influence fear-related traits. Here we report the first multivariate analysis to explore the genetic architecture of rodent behavior in a battery of animal models of anxiety. We have mapped QTLs in an F2 intercross of two rat strains, the Roman high and low avoidance rats, that have been selectively bred for differential response to fear. Multivariate analyses show that one locus, on rat chromosome 5, influences behavior in different models of anxiety. The QTL influences two-way active avoidance, conditioned fear, elevated plus maze, and open field activity but not acoustic startle response or defecation in a novel environment. The direction of effects of the QTL alleles and a coincidence between the behavioral profiles of anxiolytic drug and genetic action are consistent with the QTL containing at least one gene with a pleiotropic action on fear responses. As the neural basis of fear is conserved across species, we suggest that the QTL may have relevance to trait anxiety in humans.
Figures
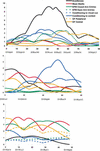
Figure 1
LOD plots for single measures on chromosomes 5, 10, and 15. The horizontal distance shows the distance along the chromosome in centimorgans (cM) and the markers used in the study are shown.
Similar articles
- Genetic evidence for chromosome 4 loci influencing learning and memory.
Anselmi M, Correa FJ, Santos JR, Silva AF, Cunha JA, Leão AH, Campêlo CL, Ribeiro AM, Silva RH, Izídio GS. Anselmi M, et al. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016 May;131:182-91. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.03.024. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27044679 - Selection for contextual fear conditioning affects anxiety-like behaviors and gene expression.
Ponder CA, Kliethermes CL, Drew MR, Muller J, Das K, Risbrough VB, Crabbe JC, Gilliam TC, Palmer AA. Ponder CA, et al. Genes Brain Behav. 2007 Nov;6(8):736-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2007.00306.x. Epub 2007 Feb 16. Genes Brain Behav. 2007. PMID: 17309658 - Learned fear, emotional reactivity and fear of heights: a factor analytic map from a large F(2) intercross of Roman rat strains.
Aguilar R, Gil L, Flint J, Gray JA, Dawson GR, Driscoll P, Giménez-Llort L, Escorihuela RM, Fernández-Teruel A, Tobeña A. Aguilar R, et al. Brain Res Bull. 2002 Jan 1;57(1):17-26. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(01)00632-3. Brain Res Bull. 2002. PMID: 11827733 - Analysis of quantitative trait loci that influence animal behavior.
Flint J. Flint J. J Neurobiol. 2003 Jan;54(1):46-77. doi: 10.1002/neu.10161. J Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 12486698 Review. - Quantitative trait locus analysis.
Grisel JE. Grisel JE. Alcohol Res Health. 2000;24(3):169-74. Alcohol Res Health. 2000. PMID: 11199287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Genetic polymorphisms in the serotonin, dopamine and opioid pathways influence social attention in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta).
Howarth ERI, Szott ID, Witham CL, Wilding CS, Bethell EJ. Howarth ERI, et al. PLoS One. 2023 Aug 2;18(8):e0288108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288108. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37531334 Free PMC article. - From Phenomes to Genes: Phenotype-based Strategies in Rodents for Research on the Neurobiological and Genetic Bases of Psychiatric-relevant Traits.
Fernández-Teruel A. Fernández-Teruel A. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(9):1836-1839. doi: 10.2174/1570159X2109230518164435. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37439333 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Effects of Tail Pinch on BDNF and trkB Expression in the Hippocampus of Roman Low- (RLA) and High-Avoidance (RHA) Rats.
Serra MP, Sanna F, Boi M, Trucas M, Fernández-Teruel A, Corda MG, Giorgi O, Quartu M. Serra MP, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 30;24(11):9498. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119498. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298449 Free PMC article. - Acute Stress Induces Different Changes on the Expression of BDNF and trkB in the Mesocorticolimbic System of Two Lines of Rats Differing in Their Response to Stressors.
Serra MP, Sanna F, Boi M, Poddighe L, Secci L, Trucas M, Fernández-Teruel A, Corda MG, Giorgi O, Quartu M. Serra MP, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 30;23(23):14995. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314995. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499323 Free PMC article. - Hunting for Genes Underlying Emotionality in the Laboratory Rat: Maps, Tools and Traps.
Ramos A, Granzotto N, Kremer R, Boeder AM, de Araújo JFP, Pereira AG, Izídio GS. Ramos A, et al. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(9):1840-1863. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220901154034. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36056863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bignami G. Selection for high rates and low rates of avoidance conditioning in the rat. Anim Behav. 1965;13:221–227. - PubMed
- Broadhurst PL, Bignami G. Correlative effect of psychogenetic selection: A study of the Roman high and low avoidance strains of rats. Behav Res Ther. 1965;2:273–280. - PubMed
- Caldarone B, Saavedra C, Tartaglia K, Wehner JM, Dudek BC, Flaherty L. Quantitative trait loci analysis affecting contextual conditioning in mice. Nat Genet. 1997;17:335–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous