Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium DT 104 antibiotic resistance genomic island I in serotype paratyphi B - PubMed (original) (raw)
Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium DT 104 antibiotic resistance genomic island I in serotype paratyphi B
Danièle Meunier et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002 Apr.
Abstract
We have identified Salmonella genomic island I (SGI1) in an isolate of Salmonella enterica serotype Paratyphi B. This antibiotic-resistance gene cluster, which confers multidrug resistance, has been previously identified in S. enterica serotype Typhimurium phage types DT 104 and DT 120 and in S. enterica serotype Agona.
Figures
Figure 1
Genetic organization of the antibiotic-resistance gene cluster of SGI1 of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium DT 104. DR-L and DR-R are the left and right direct repeats, respectively, bracketing SGI1. Polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) used to assess the genetic organization of the antibiotic-resistance genes (PCRs floR, A, B, C, D, and E) and the SGI1 junctions to the chromosome (PCRs LJ and RJ for left and right junctions, respectively) are indicated. Abbreviations for restriction sites: X, _Xba_I; H, _Hin_dIII; Xh, _Xho_I.
Figure 2
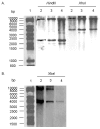
A. Southern blot hybridization with the _Xba_I probe (Figure 1) containing all antibiotic-resistance genes of _Hin_dIII- and _Xho_I-digested genomic DNAs of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium DT 104 strain BN9181 (lanes 2), serotype Agona strain 959SA97 (lanes 3), and serotype Paratyphi B strain (lanes 4). Lane 1: DNA ladder. B. Southern blot hybridization with the p1-9 probe of _Xba_I-digested genomic DNAs of S. enterica serotype Typhimurium DT 104 strain BN9181 (lanes 2), serotype Agona strain 959SA97 (lanes 3), and serotype Paratyphi B strain (lanes 4). Lane 1: DNA ladder.
Figure 3
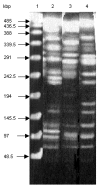
Macrorestriction analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of genomic DNAs cut by _Xba_I of S. enterica serotype Typhimurium DT 104 strain BN9181 (lane 2), serotype Agona strain 959SA97 (lane 3), and the serotype Paratyphi B strain (lane 4). Lane 1: DNA ladder.
Similar articles
- An additional novel antimicrobial resistance gene cluster in Salmonella genomic island 1 of a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 human isolate.
Kim S, Kim SH, Chun SG, Park MS, Lim HM, Lee BK. Kim S, et al. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009 May;6(4):471-9. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2008.0199. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009. PMID: 19292580 - Characterization of resistance genes in multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium isolated from diseased cattle in France (2002 to 2007).
Targant H, Ponsin C, Brunet C, Doublet B, Cloeckaert A, Madec JY, Meunier D. Targant H, et al. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010 Apr;7(4):419-25. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2009.0414. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2010. PMID: 20092404 - Variant Salmonella genomic island 1 antibiotic resistance gene cluster containing a novel 3'-N-aminoglycoside acetyltransferase gene cassette, aac(3)-Id, in Salmonella enterica serovar newport.
Doublet B, Weill FX, Fabre L, Chaslus-Dancla E, Cloeckaert A. Doublet B, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Oct;48(10):3806-12. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.10.3806-3812.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15388438 Free PMC article. - Multi-drug resistance in Salmonella enterica: efflux mechanisms and their relationships with the development of chromosomal resistance gene clusters.
Quinn T, O'Mahony R, Baird AW, Drudy D, Whyte P, Fanning S. Quinn T, et al. Curr Drug Targets. 2006 Jul;7(7):849-60. doi: 10.2174/138945006777709548. Curr Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16842216 Review. - Genetic map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VIII.
Sanderson KE, Hessel A, Rudd KE. Sanderson KE, et al. Microbiol Rev. 1995 Jun;59(2):241-303. doi: 10.1128/mr.59.2.241-303.1995. Microbiol Rev. 1995. PMID: 7603411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Variant Salmonella genomic island 1 antibiotic resistance gene cluster in Salmonella enterica serovar Albany.
Doublet B, Lailler R, Meunier D, Brisabois A, Boyd D, Mulvey MR, Chaslus-Dancla E, Cloeckaert A. Doublet B, et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003 May;9(5):585-91. doi: 10.3201/eid0905.020609. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12737743 Free PMC article. - Antimicrobial resistance, class 1 integrons, and genomic island 1 in Salmonella isolates from Vietnam.
Vo AT, van Duijkeren E, Gaastra W, Fluit AC. Vo AT, et al. PLoS One. 2010 Feb 26;5(2):e9440. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009440. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20195474 Free PMC article. - Florfenicol resistance gene floR is part of a novel transposon.
Doublet B, Schwarz S, Kehrenberg C, Cloeckaert A. Doublet B, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 May;49(5):2106-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.5.2106-2108.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15855539 Free PMC article. - Multiple-antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica serotype Paratyphi B isolates collected in France between 2000 and 2003 is due mainly to strains harboring Salmonella genomic islands 1, 1-B, and 1-C.
Weill FX, Fabre L, Grandry B, Grimont PA, Casin I. Weill FX, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Jul;49(7):2793-801. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.7.2793-2801.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15980351 Free PMC article.
References
- Hancock D, Besser T, Gay J, Rice D, Davis M, Gay C. The global epidemiology of multiresistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104. In: Brown C, Bolin C, editors. Emerging diseases of animals. Washington: ASM Press; 2000. p. 217-43.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources