The hypocretin/orexin system - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The hypocretin/orexin system
I O Ebrahim et al. J R Soc Med. 2002 May.
No abstract available
Figures
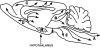
Figure 1
Projections of the hypocretin (orexin) system (A), to cholinergic neurons, reticular formation and spinal cord; (B), to thalamus and basal ganglia; (C), to basal forebrain; (D), to amygdala and dopaminergic neurons including suprachiasmatic nucleus; (E), to locus coeruleus.
Similar articles
- Sleep, feeding, and neuropeptides: roles of orexins and orexin receptors.
Mieda M, Yanagisawa M. Mieda M, et al. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002 Jun;12(3):339-45. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(02)00331-8. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 12049942 Review. - [Involvement of orexins/hypocretins in multiple physiological functions].
Ueta Y. Ueta Y. J UOEH. 2001 Jun 1;23(2):147-59. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.23.147. J UOEH. 2001. PMID: 11431960 Review. Japanese. - [Orexins and orexin receptors].
Kotaska K, Průsa R. Kotaska K, et al. Cesk Fysiol. 1999 Aug;48(3):119-21. Cesk Fysiol. 1999. PMID: 10568074 Review. Czech. - Hypocretin/orexin: maintenance of wakefulness and a multiplicity of other roles.
Kilduff TS. Kilduff TS. Sleep Med Rev. 2005 Aug;9(4):227-30. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2005.04.002. Sleep Med Rev. 2005. PMID: 15998593 No abstract available. - Narcolepsy: a key role for hypocretins (orexins).
Siegel JM. Siegel JM. Cell. 1999 Aug 20;98(4):409-12. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81969-8. Cell. 1999. PMID: 10481905 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Tau Pathology of Alzheimer Disease: Possible Role of Sleep Deprivation.
Ahmadian N, Hejazi S, Mahmoudi J, Talebi M. Ahmadian N, et al. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2018 Sep-Oct;9(5):307-316. doi: 10.32598/bcn.9.5.307. Epub 2018 Sep 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30719245 Free PMC article. Review. - New medications development for smoking cessation.
Lengel D, Kenny PJ. Lengel D, et al. Addict Neurosci. 2023 Sep;7:100103. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2023.100103. Epub 2023 May 18. Addict Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37519910 Free PMC article. - Genetic determinants of metabolic biomarkers and their associations with cardiometabolic traits in Hispanic/Latino adolescents.
Kim D, Justice AE, Chittoor G, Blanco E, Burrows R, Graff M, Howard AG, Wang Y, Rohde R, Buchanan VL, Voruganti VS, Almeida M, Peralta J, Lehman DM, Curran JE, Comuzzie AG, Duggirala R, Blangero J, Albala C, Santos JL, Angel B, Lozoff B, Gahagan S, North KE. Kim D, et al. Pediatr Res. 2022 Aug;92(2):563-571. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01729-7. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Pediatr Res. 2022. PMID: 34645953 Free PMC article. - The Crosstalk Between Amyloid-β, Retina, and Sleep for the Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease: A Narrative Review.
De Guia IL, Eslick S, Naismith SL, Kanduri S, Shah TM, Martins RN. De Guia IL, et al. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2024 Jun 25;8(1):1009-1021. doi: 10.3233/ADR-230150. eCollection 2024. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2024. PMID: 39114553 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Sutcliffe JG, de Lecea L. The hypocretins: excitatory neuromodulatory peptides for multiple homeostatic systems, including sleep and feeding. J Neurosci Res 2000;62: 161-8 - PubMed
- Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G-protein coupled receptors that regulate feeding behaviour. Cell 1998;92: 573-5 - PubMed
- Peyron C. Distribution of immunoreactive neurons and fibers for a hypothalamic neuropeptide precursor related to secretin. Soc Neurosci Abstr 1997;23: 2032
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical