The role of alpha(v)beta(3) in prostate cancer progression - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
The role of alpha(v)beta(3) in prostate cancer progression
Carlton R Cooper et al. Neoplasia. 2002 May-Jun.
Abstract
Integrin alpha(v)beta(3) is involved in varied cell biological activities, including angiogenesis, cell adhesion, and migration on several extracellular matrix components. Although alpha(v)beta(3) is not typically expressed in epithelial cells, it is expressed in macrophages, activated leukocytes, cytokine-stimulated endothelial cells, osteoclasts, and certain invasive tumors. Interestingly, the adhesion and migration of breast cancer cells on bone matrix are mediated, in part, by alpha(v)beta(3). Similar to breast cancer cells, prostate cancer cells preferentially metastasize to the bone. The biological events that mediate this metastatic pattern of prostate cancer are not well defined. This review discusses the role alpha(v)beta(3) plays in prostate cancer progression, with specific emphasis on bone metastasis and on alpha(v)beta(3) signaling in prostate cancer cells. The data suggest that alpha(v)beta(3), in part, facilitates prostate cancer metastasis to bone by mediating prostate cancer cell adhesion to and migration on osteopontin and vitronectin, which are common proteins in the bone microenvironment. These biological events require the activation of focal adhesion kinase and the subsequent activation of PI-3 kinase/Akt signaling pathway.
Figures
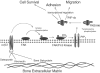
Figure 1
αvβ3 signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells. Ligation of αvβ3 with multiple ligands (i.e., osteopontin, BSP, or vitronectin) activates FAK, which interacts and activates PI-3 kinase [23]. The products of PI-3 kinase activity recruit PKB/Akt to the cell membrane where it is activated by phosphorylation and it phosphorylates several substrates to elicit a variety of biological responses, including cell survival, adhesion, and migration. Although NF-κB is potentially involved in the αvβ3 signal transduction pathway [8], its role in this signaling pathway is not known for prostate cancer cells.
Similar articles
- Substrate specificity of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin-mediated cell migration and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway activation.
Zheng DQ, Woodard AS, Tallini G, Languino LR. Zheng DQ, et al. J Biol Chem. 2000 Aug 11;275(32):24565-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002646200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10835423 - The CK2 phosphorylation of vitronectin. Promotion of cell adhesion via the alpha(v)beta 3-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway.
Seger D, Seger R, Shaltiel S. Seger D, et al. J Biol Chem. 2001 May 18;276(20):16998-7006. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003766200. Epub 2001 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278271 - Prostatic carcinoma cell migration via alpha(v)beta3 integrin is modulated by a focal adhesion kinase pathway.
Zheng DQ, Woodard AS, Fornaro M, Tallini G, Languino LR. Zheng DQ, et al. Cancer Res. 1999 Apr 1;59(7):1655-64. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10197643 - Matrix remodeling after stroke. De novo expression of matrix proteins and integrin receptors.
Ellison JA, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ. Ellison JA, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;890:204-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07996.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10668427 Review. - Integrin-mediated signaling in the regulation of osteoclast adhesion and activation.
Duong LT, Rodan GA. Duong LT, et al. Front Biosci. 1998 Aug 1;3:d757-68. doi: 10.2741/A319. Front Biosci. 1998. PMID: 9682033 Review.
Cited by
- Radiolabeled Cyclic RGD Peptide Bioconjugates as Radiotracers Targeting Multiple Integrins.
Liu S. Liu S. Bioconjug Chem. 2015 Aug 19;26(8):1413-38. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00327. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Bioconjug Chem. 2015. PMID: 26193072 Free PMC article. Review. - α(V)β(3) integrin-targeted PLGA-PEG nanoparticles for enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of a Pt(IV) prodrug.
Graf N, Bielenberg DR, Kolishetti N, Muus C, Banyard J, Farokhzad OC, Lippard SJ. Graf N, et al. ACS Nano. 2012 May 22;6(5):4530-9. doi: 10.1021/nn301148e. Epub 2012 May 14. ACS Nano. 2012. PMID: 22584163 Free PMC article. - BKCa promotes growth and metastasis of prostate cancer through facilitating the coupling between αvβ3 integrin and FAK.
Du C, Zheng Z, Li D, Chen L, Li N, Yi X, Yang Y, Guo F, Liu W, Xie X, Xie M. Du C, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):40174-40188. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9559. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27233075 Free PMC article. - Small extracellular vesicles modulated by αVβ3 integrin induce neuroendocrine differentiation in recipient cancer cells.
Quaglia F, Krishn SR, Daaboul GG, Sarker S, Pippa R, Domingo-Domenech J, Kumar G, Fortina P, McCue P, Kelly WK, Beltran H, Liu Q, Languino LR. Quaglia F, et al. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 May 24;9(1):1761072. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1761072. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 32922691 Free PMC article. - Proteins involved in regulating bone invasion in skull base meningiomas.
Salehi F, Jalali S, Alkins R, Lee JI, Lwu S, Burrell K, Gentili F, Croul S, Zadeh G. Salehi F, et al. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013 Mar;155(3):421-7. doi: 10.1007/s00701-012-1577-9. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013. PMID: 23238945 Free PMC article.
References
- Varner JA, Cheresh DA. Tumor Angiogenesis and the Role of Vascular Cell Integrin αvβ3. In: DeVita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Important advances In Oncology. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven Publishers; 1996. pp. 69–87. - PubMed
- Teitelbaum SL, Ross FP. Mechanisms of tumor-induced osteolysis. Lab Invest. 1994;71:453–455. - PubMed
- Ross FP, et al. Interactions between the bone matrix proteins osteopontin and bone sialoprotein and the osteoclast integrin alphaVbeta3 potentiate bone resorption. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:9901–9907. - PubMed
- Cheng S-L, et al. Regulation of alphaVbeta3 and alphaVbeta5 integrins by dexamethasone in normal human osteoblastic cells. J Cell Biochem. 2000;77:265–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous