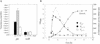Regulation of the overlapping pic/set locus in Shigella flexneri and enteroaggregative Escherichia coli - PubMed (original) (raw)
Regulation of the overlapping pic/set locus in Shigella flexneri and enteroaggregative Escherichia coli
Martin Behrens et al. Infect Immun. 2002 Jun.
Abstract
Most strains of Shigella flexneri 2a and enteroaggregative Escherichia coli carry a highly conserved chromosomal locus which encodes a 109-kDa secreted mucinase (called Pic) and, on the opposite strand in overlapping fashion, an oligomeric enterotoxin called ShET1, encoded by the setA and setB genes. Here, we characterize the genetic regulation of these overlapping genes. Our data suggest that pic and the setBA loci are transcribed as complementary 4-kb mRNA species. The major pic promoter is maximally activated at 37 degrees C in exponential growth phase. Our data suggest that the setB gene is transcribed from a promoter which lies more than 1.5 kb upstream of the setB structural gene; setA may be transcribed via readthrough of the setB transcript and possibly by its own promoter. The long leader of the setB gene provides a strong silencing effect on setB transcription. The signals which provide relief from setB silencing are not clear, but significant induction is observed in a continuous anaerobic culture of human fecal bacteria, suggesting that some complex characteristics of the human intestine act to lift repression of setB expression. Our studies provide the first insights into the mechanisms affecting expression of this unusual virulence locus.
Figures
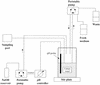
FIG. 1.
Diagram of the apparatus used for continuous culture of human fecal bacteria. See Materials and Methods for a detailed description.
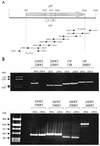
FIG. 2.
Organization of the pic/set locus. (A) Map of the chromosomal DNA fragment encoding pic and setBA and results of RT-PCR experiments to determine the initiation and termination sites of set transcription. Locations of nested set primers are indicated, along with presence (solid line) or absence (dotted line) of product generated by that primer pair. (B) Agarose gel electrophoresis demonstrating products of RT-PCR from the pic/set locus, using the primers illustrated in panel A. RNA was extracted from EAEC strain 042 and subjected to RT synthesis and cDNA amplification by standard PCR (cDNA lanes). A direct PCR step was carried out in parallel on 042 DNA to demonstrate the specificity of the PCR (DNA lanes). The primer pairs used are shown above the lanes. Molecular size markers are shown in the first lane of each gel; the sizes of some markers are indicated.
FIG. 3.
β-Galactosidase activity derived from pic and set promoter fusions either in vector pRS551 transformed into EAEC 042 or as single-copy chromosomal integrations in E. coli K-12 strain TE2680. Values are the results of triplicate determination + standard deviation. The plasmids are described in Table 2. The numbers above the inserts refer to nucleotide positions with respect to Fig. 2. pic fusions are expressed from left to right and set fusions from right to left with respect to the lacZ gene. ND, not determined.
FIG. 4.
DNA strand-specific regulation of the pic and set genes by the set DRE silencer region. Results represent β-galactosidase measurements of at least triplicate determinations from L-broth cultures grown to late logarithmic phase; error bars represent 1 standard deviation. Test strains were EAEC strain 042 transformed with pic or set promoter DNA cloned upstream of the lacZ reporter in plasmid pRS551. Constructs used in these experiments were pS37/19 (setB promoter with the silencer in the native orientation); pS37/19-inverted (setB promoter with the silencer in the inverted orientation), pP37/19 (P_pic_2,3 promoter region with the silencer in the native orientation), and pP37/19-inverted (P_pic_2,3 promoters with the silencer in the inverted orientation).
FIG. 5.
(A) Effect of growth phase on pic and set expression as determined by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. RNA was extracted from E. coli 042 grown in L-broth for various times (0.5, 1.5, and 6.5 h) after 1:20 dilution of an overnight culture with fresh medium. cDNA was synthesized and subjected to quantitative RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. (B) β-Galactosidase activity of E. coli 042 harboring plasmid pP15/2 (P_pic_1,2,3), pP16/2 (P_pic_2,3), or pP3/2 (P_pic_3) grown in L-broth and assayed at various times after dilution of overnight cultures with fresh medium.
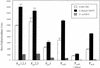
FIG. 6.
Transcriptional regulation of pic and set in EAEC strain 042, E. coli K-12, and S. flexneri 2457T. Plasmids containing all three pic promoter regions (P_pic_1,2,3), two pic promoter regions (P_pic_2,3), the most downstream pic promoter region (P_pic_3), the setB promoter (P_setB_), the setB promoter with the DRE silencer region, or the setA promoter (P_setA_) constructed in pRS551 were transformed into EAEC 042, S. flexneri 2457T, or E. coli K-12 and tested for β-galactosidase activity. Bacterial strains were grown to exponential phase in L-broth medium at 37°C to the late logarithmic phase. Bars represent results of at least three determinations; error bars represent 1 standard deviation.
Similar articles
- The Pic protease of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli promotes intestinal colonization and growth in the presence of mucin.
Harrington SM, Sheikh J, Henderson IR, Ruiz-Perez F, Cohen PS, Nataro JP. Harrington SM, et al. Infect Immun. 2009 Jun;77(6):2465-73. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01494-08. Epub 2009 Apr 6. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19349428 Free PMC article. - Enteroaggregative escherichia coli virulence factors in traveler's diarrhea strains.
Vila J, Vargas M, Henderson IR, Gascón J, Nataro JP. Vila J, et al. J Infect Dis. 2000 Dec;182(6):1780-3. doi: 10.1086/317617. Epub 2000 Oct 17. J Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 11069254 - Oxygen and contact with human intestinal epithelium independently stimulate virulence gene expression in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli.
Ellis SJ, Yasir M, Browning DF, Busby SJW, Schüller S. Ellis SJ, et al. Cell Microbiol. 2019 Jun;21(6):e13012. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13012. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Cell Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30673154 Free PMC article. - Prevalence of the genes for shigella enterotoxins 1 and 2 among clinical isolates of shigella in Israel.
Yavzori M, Cohen D, Orr N. Yavzori M, et al. Epidemiol Infect. 2002 Jun;128(3):533-5. doi: 10.1017/s0950268802006866. Epidemiol Infect. 2002. PMID: 12113500 Free PMC article. - Genetic determinants of virulence in Shigella and dysenteric strains of Escherichia coli: their involvement in the pathogenesis of dysentery.
Kopecko DJ, Baron LS, Buysse J. Kopecko DJ, et al. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:71-95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985. PMID: 2414072 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Intracellular expression of the plasmid-encoded toxin from enteroaggregative Escherichia coli.
Sui BQ, Dutta PR, Nataro JP. Sui BQ, et al. Infect Immun. 2003 Sep;71(9):5364-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5364-5370.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12933885 Free PMC article. - Colocation of genes encoding a tRNA-mRNA hybrid and a putative signaling peptide on complementary strands in the genome of the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima.
Montero CI, Lewis DL, Johnson MR, Conners SB, Nance EA, Nichols JD, Kelly RM. Montero CI, et al. J Bacteriol. 2006 Oct;188(19):6802-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.00470-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16980482 Free PMC article. - A novel gene, ardD, determines antirestriction activity of the non-conjugative transposon Tn5053 and is located antisense within the tniA gene.
Balabanov VP, Kotova VY, Kholodii GY, Mindlin SZ, Zavilgelsky GB. Balabanov VP, et al. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012 Dec;337(1):55-60. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12005. Epub 2012 Oct 3. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22967207 Free PMC article. - A Novel pH-Regulated, Unusual 603 bp Overlapping Protein Coding Gene pop Is Encoded Antisense to ompA in Escherichia coli O157:H7 (EHEC).
Zehentner B, Ardern Z, Kreitmeier M, Scherer S, Neuhaus K. Zehentner B, et al. Front Microbiol. 2020 Mar 20;11:377. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00377. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32265854 Free PMC article. - The Genome Reverse Compiler: an explorative annotation tool.
Warren AS, Setubal JC. Warren AS, et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Jan 27;10:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-35. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19173744 Free PMC article.
References
- Al-Hasani, K., K. Rajakumar, D. Bulach, R. Robins-Browne, B. Adler, and H. Sakellaris. 2001. Genetic organization of the she pathogenicity island in S. flexneri 2a. Microb. Pathog. 30:1-8. - PubMed
- Caramel, A., and K. Schnetz. 2000. Antagonistic control of the Escherichia coli bgl promoter by FIS and CAP in vitro. Mol. Microbiol. 36:85-92. - PubMed
- Claret, L., and J. Rouviere-Yaniv. 1996. Regulation of HU alpha and HU beta by CRP and FIS in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 263:126-139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI43615/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI33096/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI043615/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033096/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI043615/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources