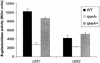Quorum-sensing Escherichia coli regulator A: a regulator of the LysR family involved in the regulation of the locus of enterocyte effacement pathogenicity island in enterohemorrhagic E. coli - PubMed (original) (raw)
Quorum-sensing Escherichia coli regulator A: a regulator of the LysR family involved in the regulation of the locus of enterocyte effacement pathogenicity island in enterohemorrhagic E. coli
Vanessa Sperandio et al. Infect Immun. 2002 Jun.
Abstract
The locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) is a chromosomal pathogenicity island that encodes the proteins involved in the formation of the attaching and effacing lesions by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) and enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC). The LEE comprises 41 open reading frames organized in five major operons, LEE1, LEE2, LEE3, tir (LEE5), and LEE4, which encode a type III secretion system, the intimin adhesin, the translocated intimin receptor (Tir), and other effector proteins. The first gene of LEE1 encodes the Ler regulator, which activates all the other genes within the LEE. We previously reported that the LEE genes were activated by quorum sensing through Ler (V. Sperandio, J. L. Mellies, W. Nguyen, S. Shin, and J. B. Kaper, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:15196-15201, 1999). In this study we report that a putative regulator in the E. coli genome is itself activated by quorum sensing. This regulator is encoded by open reading frame b3243; belongs to the LysR family of regulators; is present in EHEC, EPEC, and E. coli K-12; and shares homology with the AphB and PtxR regulators of Vibrio cholerae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, respectively. We confirmed the activation of b3243 by quorum sensing by using transcriptional fusions and renamed this regulator quorum-sensing E. coli regulator A (QseA). We observed that QseA activated transcription of ler and therefore of the other LEE genes. An EHEC qseA mutant had a striking reduction of type III secretion activity, which was complemented when qseA was provided in trans. Similar results were also observed with a qseA mutant of EPEC. The QseA regulator is part of the regulatory cascade that regulates EHEC and EPEC virulence genes by quorum sensing.
Figures
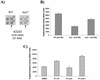
FIG. 1.
Activation of b3243 transcription by quorum sensing. (A) Portion of E. coli K-12 gene array (Sigma-Genosys) containing the b3243 open reading frame hybridized with cDNA synthesized from RNAs extracted from strains 86-24 (wild-type) and VS94 (luxS mutant). (B) β-Galactosidase activities of a qseA::lacZ fusion (pVS160) in 86-24 (wild type [WT]), VS94 (luxS mutant), and VS95 (luxS complemented) strain backgrounds in DMEM at an OD600 of 1.0. (C) β-Galactosidase activity of a qseA::lacZ fusion (pVS160) in VS94 (luxS mutant) in fresh DMEM, DMEM preconditioned by growth of wild-type strain 86-24 (PC-WT), DMEM preconditioned by growth of strain VS94 (PC-luxS −), and DMEM preconditioned by growth of strain VS95 (PC-luxS +). Error bars indicate standard deviations.
FIG. 2.
Alignments of EHEC and K-12 QseA with AphB from V. cholerae and PtxR from P. aeruginosa. Underlined amino acid residues comprise the predicted helix-turn-helix of QseA.
FIG. 3.
(A) Western blots of secreted proteins from strains 86-24 (wild type [WT]), VS145 (qseA mutant), and VS151 (complemented mutant) probed with anti-Tir, anti-EspA, and anti-EspB polyclonal antisera. (B) Western blot of whole-cell lysates from strains 86-24, VS145, and VS151 with anti-H7 flagellin antiserum. (C) Western blot of whole-cell lysates from strains 86-24, VS145, and VS151 with anti-Stx2A antiserum.
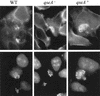
FIG. 4.
FAS test with HeLa cells infected for 6 h at 37°C and 5% CO2 with strains 86-24, VS145, and VS151. The upper panels are the cells stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate-phalloidin, and the lower panels are the bacteria stained with propidium iodide. WT, wild type.
FIG. 5.
β-Galactosidase activities of _ler-1_[_LEE1_] and _sepZ1_[_LEE2_]::lacZ single-copy chromosomal fusions in E2348/69 (wild-type [WT] EPEC), VS193 (EPEC qseA mutant), and VS193 complemented with pVS208 (qseA+). Error bars indicate standard deviations.
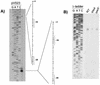
FIG. 6.
(A) Primer extension analysis of the LEE1 promoter region using primer K983 (bp 40912 to 40928 of the EHEC LEE sequence, GenBank accession number AE005593) and RNA from strain 86-24 grown in DMEM to an OD600 of 1.0. The primer extension was run in parallel to a sequencing reaction of plasmid pVS23 (regulatory region of LEE1 in pBluescript). (B) Primer extension analysis of LEE1 using primer K983 and RNAs from strains 86-24, VS145, and VS151 grown in DMEM to an OD600 of 1.0. The primer extensions were run in parallel to a sequencing reaction of a λ ladder control. WT, wild type.
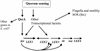
FIG. 7.
Model of quorum-sensing regulation in EHEC. Quorum sensing activates transcription of qseA, which in turn activates transcription of the LEE genes by quorum sensing. Whether QseA directly binds to the ler promoter is not yet established. There are also additional transcriptional factors, not yet described, involved in the activation of the LEE genes by quorum sensing. For clarity, additional factors that regulate expression of LEE genes by non-quorum-sensing mechanisms, such as integration host factor, H-NS, and Per, are not depicted.
Similar articles
- QseA directly activates transcription of LEE1 in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.
Sharp FC, Sperandio V. Sharp FC, et al. Infect Immun. 2007 May;75(5):2432-40. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02003-06. Epub 2007 Mar 5. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17339361 Free PMC article. - The LysR-type regulator QseA regulates both characterized and putative virulence genes in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7.
Kendall MM, Rasko DA, Sperandio V. Kendall MM, et al. Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jun 1;76(5):1306-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07174.x. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20444105 Free PMC article. - Interkingdom Chemical Signaling in Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7.
Kendall MM. Kendall MM. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;874:201-13. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-20215-0_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26589220 Review.
Cited by
- Autoinducer 2 is required for biofilm growth of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans.
Shao H, Lamont RJ, Demuth DR. Shao H, et al. Infect Immun. 2007 Sep;75(9):4211-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00402-07. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17591788 Free PMC article. - Differential effects of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and indole on Escherichia coli O157:H7 chemotaxis, colonization, and gene expression.
Bansal T, Englert D, Lee J, Hegde M, Wood TK, Jayaraman A. Bansal T, et al. Infect Immun. 2007 Sep;75(9):4597-607. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00630-07. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17591798 Free PMC article. - Global transcriptional response of Escherichia coli O157:H7 to growth transitions in glucose minimal medium.
Bergholz TM, Wick LM, Qi W, Riordan JT, Ouellette LM, Whittam TS. Bergholz TM, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2007 Oct 29;7:97. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-97. BMC Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17967175 Free PMC article. - Autoinducer-2 Quorum Sensing Contributes to Regulation of Microcin PDI in Escherichia coli.
Lu SY, Zhao Z, Avillan JJ, Liu J, Call DR. Lu SY, et al. Front Microbiol. 2017 Dec 22;8:2570. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02570. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29312248 Free PMC article. - EutR is a direct regulator of genes that contribute to metabolism and virulence in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7.
Luzader DH, Clark DE, Gonyar LA, Kendall MM. Luzader DH, et al. J Bacteriol. 2013 Nov;195(21):4947-53. doi: 10.1128/JB.00937-13. Epub 2013 Aug 30. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23995630 Free PMC article.
References
- Bassler, B. L. 1999. How bacteria talk to each other: regulation of gene expression by quorum sensing. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2:582-587. - PubMed
- Bustamante, V., F. Santana, E. Calva, and J. L. Puente. 2001. Transcriptional regulation of type III secretion genes in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: Ler antagonizes H-NS-dependent repression. Mol. Microbiol. 39:664-678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK058957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI021657/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI021657/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI41325/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK58957/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI21657/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases