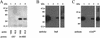The human papillomavirus type 31 late 3' untranslated region contains a complex bipartite negative regulatory element - PubMed (original) (raw)
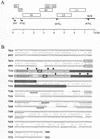
FIG. 1.
Diagram of the HPV-31 genome, and alignment of HPV-31 (nt 6931 to 7393) and HPV-16 (nt 7014 to 7499) sequences. (A) Linearized genomic structure of HPV-31, showing early (E) and late (L) gene coding regions (boxes). P97 is a constitutively active promoter; P742 is a promoter activated in differentiated cells. p(A)E and p(A)L, positions of the early and late poly(A) sites, respectively; heavy line, noncoding region (NCR) of the virus. (B) HPV-31 L1/late gene 3′ UTR sequences contain an NLE. Shown is an alignment of HPV-16 L1/late gene 3′ UTR sequences (upper sequences) and HPV-31 L1/late gene 3′ UTR sequences (lower sequences). Boxed regions, positions of the HPV-16 NRE and the HPV-31 NLE; light grey boxes, loops of predicted stem-loop structures; boldface boxes, L1 stop codons (TAA); dark grey boxes, GU-rich 3′ portions of the NRE and NLE; inverted triangles, intron-exon boundaries of weak consensus 5′ splice sites; double-underlined sequences; poly(A) hexanucleotides (AAUAAA); single-underlined sequences, GU/U-rich CstF-binding sites.
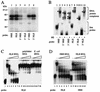
FIG. 2.
Functional assays with HeLa cells to map inhibitory sequences in the HPV-31 late gene 3′ UTR. (A) Diagram of the plasmid constructs used in transfection experiments. Box with diamonds, HSV-2 IE gene promoter; open box, CAT reporter gene; stippled box, HPV-31 L1/late gene 3′ UTR sequences; arrowhead, late poly(A) site; P, _Pst_I restriction site; H, _Hin_dIII restriction site; hatched box, NLE; grey box, late poly(A) signal and CstF-64 binding site. (B) Bar chart of CAT activity in HeLa cells for HPV-31 constructs containing 5′ or 3′ deletions assayed in the presence of [3H]chloramphenicol. Values are means plus standard deviations of duplicate transfections from three separate experiments.
FIG. 3.
Functional assays with HeLa cells to confirm mapping of inhibitory sequences in the HPV-31 late gene 3′ UTR. (A) Diagram of the plasmid constructs used in transfection experiments. Boxes with diamonds, HSV-2 IE gene promoter; open boxes, CAT reporter gene; black boxes, HSV-2 IE gene poly(A) sequences; stippled box; HPV-31 L1/late gene 3′ UTR sequences; arrowheads, poly(A) sites; P, _Pst_I restriction site; H, _Hin_dIII restriction site; hatched boxes; NLEs; grey boxes, late poly(A) signals and CstF-64 binding sites. (B) Bar chart of CAT activity in HeLa cells for HPV-31 constructs containing internal deletions assayed in the presence of [3H]chloramphenicol. Values are means plus standard deviations of duplicate transfections from three separate experiments. (C) Bar chart of CAT activity in HeLa cells for constructs containing the HSV-2 IE gene 5 poly(A) sequences. Values are means plus standard deviations of duplicate transfections from three separate experiments.
FIG. 4.
HPV-31 L1/late gene 3′ UTR sequences (nt 6931 to 7393), showing the position of inhibitory elements and polyadenylation signals. Open boxes, MIE (nt 7081 to 7210); underlined region, poly(A) hexanucleotide; arrow, CstF binding site (GU/U); Grey box, SIE (nt 7284 to 7393).
FIG. 5.
UV cross-linking and EMSA experiments to compare protein binding to the HPV-16 NRE and HPV-31 NLE. (A) UV cross-linking of 32P-labeled NRE and NLE probes to HeLa cell nuclear extracts. Lane 1, full-length (HPV-16) NRE; lane 2, full-length (HPV-31) NLE; lane 3, 5′ NRE (49 nt); lane 4, 5′ NLE (46 nt); lane 5, 3′ NRE (30 nt); lane 6, 3′ NLE (56 nt). (B) EMSA using 32P-labeled RNA probes and HeLa cell nuclear extracts very similar to those used for panel A run on a nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel. RNA-protein complexes and free probes are bracketed. Arrows, RNA-protein complexes. NE, HeLa cell nuclear extracts. (C) EMSA competition assay using a 32P-labeled NLE probe (1.5 pmol) and HeLa nuclear extracts. Lane 1, no extracts; lane 2, no competitor RNA; lanes 3 to 7, 1- to 16-fold molar excess of specific competitor, i.e., 1.5 to 24 pmol of in vitro-transcribed, unlabeled NLE RNA; lane 8, no competitor RNA; lanes 9 to 13, 1- to 16-fold molar excess of nonspecific competitor, i.e., 1.5 to 24 pmol of in vitro-transcribed pBluescript KS(+) polylinker RNA; lane 14, no competitor RNA; lanes 15 to 18, nonspecific competitor, i.e., 500 ng to 4 μg of E. coli tRNA. (D) EMSA competition assay using 32P-labeled NLE and NRE probes and HeLa nuclear extracts. Lanes 1 to 7, NLE probe (1.5 pmol); lane 1, no extracts; lane 2, no competitor; lanes 3 to 7, 1- to 16-fold molar excess, i.e., 1.5 to 24 pmol of in vitro-transcribed, unlabeled NRE RNA; lanes 8 to 14, NRE probe (1.5 pmol); lane 8, no extracts; lane 9, no competitor; lanes 10 to 14, 1- to 16-fold molar excess, i.e., 1.5 to 24 pmol of in vitro-transcribed, unlabeled NLE RNA.
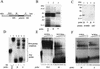
FIG. 6.
UV cross-linking and Western blotting to identify specific RNA-processing factors that bind to the NLE. (A) UV cross-linking of 32P-labeled NRE and NLE probes to bacterially expressed GST-tagged CstF-64 RBD protein. Lane 1, GST protein and NRE probe; lane 2, GST protein and NLE probe; lane 3, GST-tagged CstF-64 RBD and NRE probe; lane 4, GST-tagged CstF-64 RBD and NLE probe. (B) Western blot with the 19F12 anti-HuR monoclonal antibody. Lane 1, 20 μg of HeLa nuclear extracts; lane 2, 20 μl of proteins purified with beads alone; lane 3, 20 μl of proteins purified with NLE RNA; lane 4, 20 μl of proteins purified with poly(U) RNA. (C) Western blot with the MC3 anti-U2AF65 monoclonal antibody. Lane 1, 20 μg of HeLa nuclear extracts; lane 2, 20 μl of proteins purified with beads alone; lane 3, 20 μl of proteins purified using NLE RNA; lane 4, 20 μl of proteins purified with poly(U) RNA.
FIG. 7.
UV cross-linking and EMSA of protein binding to sequences surrounding the late poly(A) signal. (A) Diagram of the HPV-31 late gene 3′ UTR sequences showing the positions of the probes used for protein binding studies. Hatched box, MIE; grey box, poly(A) and CstF binding sites; stippled box, SIE; lines, positions of NLE probe (nt 7041 to 7141), M probe (nt 7161 to 7211), and S probe (nt 7284 to 7343). (B) UV cross-linking of 32P-labeled NLE, M, and S probes to HeLa nuclear extracts. Lane 1, NLE (101 nt); lane 2, M (50 nt); lane 3, S (60 nt). Asterisks, minor proteins of similar sizes that bind both NLE and M probes. (C) UV cross-linking of 32P-labeled M and S probes to bacterially expressed CstF-64 RBD. Lane 1, GST-tagged CstF-64 RBD protein with an M probe; lane 2, GST-tagged CstF-64 RBD protein with an S probe; lane 3, GST protein with an M probe; lane 4, GST protein with an S probe. 64 RBD, GST-tagged CstF-64 RBD. (D) EMSA of 32P-labeled NLE, M, and S probes using HeLa cell nuclear extracts. RNA-protein complexes and free probes are bracketed. Arrows, RNA-protein complexes; NE, HeLa nuclear extracts. (E) EMSA competition assay. Lanes 1 to 8, 32P-labeled NLE probe (1.5 pmol); lane 1, no extracts; lane 2, no competitor RNA; lanes 3 to 8, 1- to 32-fold molar excess, i.e., 1.5 to 48 pmol of in vitro-transcribed unlabeled M RNA; lanes 9 to 16, 32P-labeled M probe (1.5 pmol); lane 9, no extracts; lane 10, no competitor RNA; lanes 11 to 16, 1- to 32-fold molar excess, i.e., 1.5 to 48 pmol of in vitro-transcribed unlabeled NLE RNA. (F) EMSA competition assay. Lanes 1 to 8, 32P-labeled M probe (1.5 pmol); lane 1, no extracts; lane 2, no competitor RNA; lanes 3 to 6, 1- to 32-fold molar excess, i.e., 1.5 to 48 pmol of in vitro-transcribed unlabeled S RNA; lanes 9 to 16, 32P-labeled S probe (1.5 pmol); lane 9, no extracts; lane 10, no competitor RNA; lanes 11 to 16, 1- to 32-fold molar excess, i.e., 1.5 to 48 pmol of in vitro-transcribed, unlabeled M RNA.