Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Finland - PubMed (original) (raw)
Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Finland
Saara Salmenlinna et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002 Jun.
Abstract
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is no longer only hospital acquired. MRSA is defined as community acquired if the MRSA-positive specimen was obtained outside hospital settings or within 2 days of hospital admission, and if it was from a person who had not been hospitalized within 2 years before the date of MRSA isolation. To estimate the proportion of community-acquired MRSA, we analyzed previous hospitalizations for all MRSA-positive persons in Finland from 1997 to 1999 by using data from the National Hospital Discharge Register. Of 526 MRSA-positive persons, 21% had community-acquired MRSA. Three MRSA strains identified by phage typing, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and ribotyping were associated with community acquisition. None of the strains were multiresistant, and all showed an mec hypervariable region hybridization pattern A (HVR type A). None of the epidemic multiresistant hospital strains were prevalent in nonhospitalized persons. Our population-based data suggest that community-acquired MRSA may also arise de novo, through horizontal acquisition of the mecA gene.
Figures
Figure
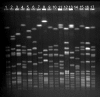
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) profiles of the 14 most common methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strain types identified, Finland, 1997–1999. Lanes 1, 9, 17: S. aureus NCTC 8325 (molecular weight marker); lanes 2–4: strain types associated with community acquisition (Mikkeli clone, E22, E31); lane 5: E1; lane 6: E24; lane 7: E5; lane 8: Kemi clone; lane 10: E27; lane 11: UK EMRSA-15; lane 12: E19; lane 13: Pori clone; lane 14: E20; lane 15: Iberian clone; and lane 16: O25.
Similar articles
- Emergence of community-associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Hawaii, 2001-2003.
Estivariz CF, Park SY, Hageman JC, Dvorin J, Melish MM, Arpon R, Coon P, Slavish S, Kim M, McDougal LK, Jensen B, McAllister S, Lonsway D, Killgore G, Effler PE, Jernigan DB. Estivariz CF, et al. J Infect. 2007 Apr;54(4):349-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2006.08.002. Epub 2006 Sep 20. J Infect. 2007. PMID: 16989904 - Epidemiology and molecular characteristics of community-associated methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus from skin/soft tissue infections in a children's hospital in Beijing, China.
Wu D, Wang Q, Yang Y, Geng W, Wang Q, Yu S, Yao K, Yuan L, Shen X. Wu D, et al. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010 May;67(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.12.006. Epub 2010 Mar 12. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20227225 - Epidemiological typing of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from children in Taiwan.
Wang CC, Lo WT, Chu ML, Siu LK. Wang CC, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2004 Aug 15;39(4):481-7. doi: 10.1086/422642. Epub 2004 Jul 28. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15356810 - The evolution of Staphylococcus aureus.
Deurenberg RH, Stobberingh EE. Deurenberg RH, et al. Infect Genet Evol. 2008 Dec;8(6):747-63. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2008.07.007. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Infect Genet Evol. 2008. PMID: 18718557 Review. - Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: current perspectives.
Kluytmans-Vandenbergh MF, Kluytmans JA. Kluytmans-Vandenbergh MF, et al. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006 Mar;12 Suppl 1:9-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01341.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006. PMID: 16445719 Review.
Cited by
- Update on bacterial pathogens: virulence and resistance.
Cercenado E, Garau J, Almirante B, Ramón Azanza J, Cantón R, Cisterna R, María Eiros J, Fariñas C, Fortún J, Gudiol F, Mensa J, Pachón J, Pascual Á, Luis Pérez J, Rodríguez A, Sánchez M, Vila J. Cercenado E, et al. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008 Apr;26:3-21. doi: 10.1016/S0213-005X(08)76378-X. Epub 2009 May 13. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008. PMID: 38620184 Free PMC article. - Whole genome sequencing reveals new links between spa t172/CC59 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus cases in low-endemicity region of Southwest Finland, 2007‒2016.
Silvola J, Gröndahl-Yli-Hannuksela K, Hirvioja T, Rantakokko-Jalava K, Rintala E, Auranen K, Junnila J, Marttila H, Lindholm L, Vuopio J. Silvola J, et al. Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 9;12(1):21326. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-25556-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36494398 Free PMC article. - Changing epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a low endemicity area-new challenges for MRSA control.
Junnila J, Hirvioja T, Rintala E, Auranen K, Rantakokko-Jalava K, Silvola J, Lindholm L, Gröndahl-Yli-Hannuksela K, Marttila H, Vuopio J. Junnila J, et al. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Dec;39(12):2299-2307. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-03824-9. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31989375 Free PMC article. - Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Colonization in Chinese Children: A Prevalence Meta-Analysis and Review of Influencing Factors.
Lin J, Peng Y, Xu P, Zhang T, Bai C, Lin D, Ou Q, Yao Z. Lin J, et al. PLoS One. 2016 Jul 21;11(7):e0159728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159728. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27442424 Free PMC article. Review. - Nasal colonization in children with community acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Davoodabadi F, Mobasherizadeh S, Mostafavizadeh K, Shojaei H, Havaei SA, Koushki AM, Moghadasizadeh Z, Meidani M, Shirani K. Davoodabadi F, et al. Adv Biomed Res. 2016 May 11;5:86. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.182217. eCollection 2016. Adv Biomed Res. 2016. PMID: 27274501 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical