Mouse horizontal cells do not express connexin26 or connexin36 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Mouse horizontal cells do not express connexin26 or connexin36
M R Deans et al. Cell Commun Adhes. 2001.
Abstract
Gap junctions between neurons function as electrical synapses, and are present in all layers of mammalian and teleost retina. These synapses are largest and most prominent between horizontal cells where they function to increase the receptive field of a single neuron beyond the width of its dendrites. Receptive field size and the extent of gap junctional coupling between horizontal cells is regulated by ambient light levels and may mediate light/dark adaptation. Furthermore, teleost horizontal cell gap junction hemichannels may facilitate a mechanism of feedback inhibition between horizontal cells and cone photoreceptors. As a prelude to using mouse genetic models to study horizontal cell gap junctions and hemichannels, we sought to determine the connexin complement of mouse horizontal cells. Cx36, Cx37, Cx43, Cx45 and Cx57 mRNA could be detected in mouse retina by RT-PCR. Microscopy was used to further examine the distribution of Cx26 and Cx36. Cx26 immunofluorescence and a beta-gal reporter under regulatory control of the Cx36 promoter did not colocalize with a horizontal cell marker, indicating that these genes are not expressed by horizontal cells. The identity of the connexin(s) forming electrical synapses between mouse horizontal cells and the connexin that may form hemichannels in the horizontal cell telodendria remains unknown.
Figures
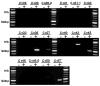
Figure 1
Mouse retina RNA was screened by RT-PCR for the presence of each of the 16 cloned connexin genes. mRNA was detected for 5 connexins; Cx36, Cx37, Cx43, Cx45 and Cx57. To control against amplification of genomic DNA, cRNA was generated in two reactions, one containing (+) and the other lacking (−) the reverse transcriptase enzyme. Results were identical between oligo-dT and random hexamer primed cRNA.
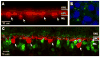
Figure 2
Cx26 immunopositive puncta (green) could not be detected on calbindin positive processes(red) in the OPL(A), but could be easily located in control sections from mouse liver (B) counterstained with the nuclear label DAPI (blue). In retina from mice in which one copy of Cx36 was replaced with β-gal, immunofluorescence for this reporter (green) does not colocalize with calbindin (red) positive horizontal cells (C). ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer. Arrows indicate horizontal cell bodies.
Similar articles
- Connexin45-containing neuronal gap junctions in rodent retina also contain connexin36 in both apposing hemiplaques, forming bihomotypic gap junctions, with scaffolding contributed by zonula occludens-1.
Li X, Kamasawa N, Ciolofan C, Olson CO, Lu S, Davidson KG, Yasumura T, Shigemoto R, Rash JE, Nagy JI. Li X, et al. J Neurosci. 2008 Sep 24;28(39):9769-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2137-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18815262 Free PMC article. - Expression patterns of connexin genes in mouse retina.
Güldenagel M, Söhl G, Plum A, Traub O, Teubner B, Weiler R, Willecke K. Güldenagel M, et al. J Comp Neurol. 2000 Sep 18;425(2):193-201. J Comp Neurol. 2000. PMID: 10954839 - Prolonged dark adaptation changes connexin expression in the mouse retina.
Kihara AH, de Castro LM, Moriscot AS, Hamassaki DE. Kihara AH, et al. J Neurosci Res. 2006 May 15;83(7):1331-41. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20815. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16496335 - Electrical synapses--gap junctions in the brain.
Meier C, Dermietzel R. Meier C, et al. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;43:99-128. doi: 10.1007/400_013. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006. PMID: 17068969 Review. - Connexin expression in the retina.
Söhl G, Güldenagel M, Traub O, Willecke K. Söhl G, et al. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000 Apr;32(1):138-45. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(99)00074-0. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000. PMID: 10751663 Review.
Cited by
- Connexin36 is essential for transmission of rod-mediated visual signals in the mammalian retina.
Deans MR, Volgyi B, Goodenough DA, Bloomfield SA, Paul DL. Deans MR, et al. Neuron. 2002 Nov 14;36(4):703-12. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)01046-2. Neuron. 2002. PMID: 12441058 Free PMC article. - Expression of connexin36 in cone pedicles and OFF-cone bipolar cells of the mouse retina.
Feigenspan A, Janssen-Bienhold U, Hormuzdi S, Monyer H, Degen J, Söhl G, Willecke K, Ammermüller J, Weiler R. Feigenspan A, et al. J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 31;24(13):3325-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5598-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15056712 Free PMC article. - Lateral interactions in the outer retina.
Thoreson WB, Mangel SC. Thoreson WB, et al. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012 Sep;31(5):407-41. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2012.04.003. Epub 2012 May 3. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 22580106 Free PMC article. Review. - New roles for astrocytes: gap junction hemichannels have something to communicate.
Bennett MV, Contreras JE, Bukauskas FF, Sáez JC. Bennett MV, et al. Trends Neurosci. 2003 Nov;26(11):610-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2003.09.008. Trends Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14585601 Free PMC article. Review. - Gating, permselectivity and pH-dependent modulation of channels formed by connexin57, a major connexin of horizontal cells in the mouse retina.
Palacios-Prado N, Sonntag S, Skeberdis VA, Willecke K, Bukauskas FF. Palacios-Prado N, et al. J Physiol. 2009 Jul 1;587(Pt 13):3251-69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.171496. Epub 2009 May 11. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19433576 Free PMC article.
References
- Bloomfield SA, et al. A comparison of receptive field and tracer coupling size of horizontal cells in the rabbit retina. Vis Neurosci. 1995;12:985–999. - PubMed
- Condorelli DF, et al. Cloning of a new gap junction gene (Cx36) highly expressed in mammalian brain neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:1202–1208. - PubMed
- Deans MR, et al. Synchronous activity of inhibitory networks in neocortex requires electrical synapses containing connexin36. Neuron. 2001;31:477–485. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous