Exceptional haplotype variation in maize - PubMed (original) (raw)
Exceptional haplotype variation in maize
Jeffrey L Bennetzen et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002.
No abstract available
Figures
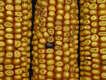
Figure 1
A rare purple kernel resulting from intragenic recombination within the bz1 locus. The linked_shrunken1_ (sh1) trait is also segregating on these ears, and its recessive homozygosity explains the kernels that appear somewhat shrunken. Photo courtesy of H. Dooner.
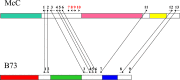
Figure 2
A simplified schematic of the bz1 regions in maize inbreds B73 and McC. Arrows with numbers indicate the location, size, and transcriptional orientations of predicted genes in the region. The_bz1_ locus is gene 2 in the sequentially numbered series, and allelic loci are connected by lines. The filled regions represent LTR–retrotransposon blocks. The different colors of the fills indicate that each of these blocks is unique in its LTR–retrotransposon composition.
Comment on
- Intraspecific violation of genetic colinearity and its implications in maize.
Fu H, Dooner HK. Fu H, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jul 9;99(14):9573-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.132259199. Epub 2002 Jun 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12060715 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- Plant transposable elements generate the DNA sequence diversity needed in evolution.
Schwarz-Sommer Z, Gierl A, Cuypers H, Peterson PA, Saedler H. Schwarz-Sommer Z, et al. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):591-7. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03671.x. EMBO J. 1985. PMID: 15926219 Free PMC article. - Helitrons contribute to the lack of gene colinearity observed in modern maize inbreds.
Lal SK, Hannah LC. Lal SK, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jul 19;102(29):9993-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504713102. Epub 2005 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16009929 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Gene expression of a gene family in maize based on noncollinear haplotypes.
Song R, Messing J. Song R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Jul 22;100(15):9055-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1032999100. Epub 2003 Jul 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12853580 Free PMC article. - Paramutation in maize and related allelic interactions.
Patterson GI, Chandler VL. Patterson GI, et al. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;197:121-41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79145-1_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7493488 Review. No abstract available. - DNA methylation and activity of the maize Spm transposable element.
Fedoroff NV. Fedoroff NV. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;197:143-64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79145-1_10. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7493489 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- A novel class of Helitron-related transposable elements in maize contain portions of multiple pseudogenes.
Gupta S, Gallavotti A, Stryker GA, Schmidt RJ, Lal SK. Gupta S, et al. Plant Mol Biol. 2005 Jan;57(1):115-27. doi: 10.1007/s11103-004-6636-z. Plant Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15821872 - Transposable elements in phytopathogenic Verticillium spp.: insights into genome evolution and inter- and intra-specific diversification.
Amyotte SG, Tan X, Pennerman K, Jimenez-Gasco Mdel M, Klosterman SJ, Ma LJ, Dobinson KF, Veronese P. Amyotte SG, et al. BMC Genomics. 2012 Jul 16;13:314. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-314. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22800085 Free PMC article. - Control of flowering time and spike development in cereals: the earliness per se Eps-1 region in wheat, rice, and Brachypodium.
Faricelli ME, Valárik M, Dubcovsky J. Faricelli ME, et al. Funct Integr Genomics. 2010 May;10(2):293-306. doi: 10.1007/s10142-009-0146-7. Epub 2009 Oct 23. Funct Integr Genomics. 2010. PMID: 19851796 Free PMC article. - Structural variation and evolution of a defense-gene cluster in natural populations of Aegilops tauschii.
Brooks SA, Huang L, Herbel MN, Gill BS, Brown-Guedira G, Fellers JP. Brooks SA, et al. Theor Appl Genet. 2006 Feb;112(4):618-26. doi: 10.1007/s00122-005-0160-7. Epub 2006 Jan 10. Theor Appl Genet. 2006. PMID: 16402192 - Analysis of retrotransposon structural diversity uncovers properties and propensities in angiosperm genome evolution.
Vitte C, Bennetzen JL. Vitte C, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 21;103(47):17638-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605618103. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17101966 Free PMC article.
References
- Gale M D, Devos K M. Science. 1998;282:656–659. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources