Determination of PCR efficiency in chelex-100 purified clinical samples and comparison of real-time quantitative PCR and conventional PCR for detection of Chlamydia pneumoniae - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Determination of PCR efficiency in chelex-100 purified clinical samples and comparison of real-time quantitative PCR and conventional PCR for detection of Chlamydia pneumoniae
Tina Mygind et al. BMC Microbiol. 2002.
Abstract
Background: Chlamydia pneumoniae infection has been detected by serological methods, but PCR is gaining more interest. A number of different PCR assays have been developed and some are used in combination with serology for diagnosis. Real-time PCR could be an attractive new PCR method; therefore it must be evaluated and compared to conventional PCR methods.
Results: We compared the performance of a newly developed real-time PCR with a conventional PCR method for detection of C. pneumoniae. The PCR methods were tested on reference samples containing C. pneumoniae DNA and on 136 nasopharyngeal samples from patients with chronic cough. We found the same detection limit for the two methods and clinical performance was equal for the real-time PCR and for the conventional PCR method, although only three samples tested positive. To investigate whether the low prevalence of C. pneumoniae among patients with chronic cough was caused by suboptimal PCR efficiency in the samples, PCR efficiency was determined based on the real-time PCR. Seventeen of twenty randomly selected clinical samples had similar PCR efficiency to samples containing pure genomic C. pneumoniae DNA.
Conclusion: These results indicate that the performance of real-time PCR is comparable to that of conventional PCR, but this needs to be confirmed further. Real-time PCR can be used to investigate the PCR efficiency which gives a rough estimate of how well the real-time PCR assay work in a specific sample type. Suboptimal PCR efficiency of PCR is not a likely explanation for the low positivity rate of C. pneumoniae in patients with chronic cough.
Figures
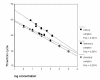
Figure 1
Determination of the efficiency for the standard, reference and clinical samples. The threshold cycle is the cycle number at which the fluorescence curve for a given sample crosses the user-defined noise band. Log to the concentration for the reference samples is set as log to arbitrary numbers with four-fold difference as the reference samples are four-fold serial dilutions. The actual concentration is not needed when determining the efficiency as it depends on the slope of the line only.
Figure 2
Effect of difference in efficiency between standard samples and samples. This figure illustrates the error in determination of concentration by real-time PCR at cycle no. 30 when the efficiencies differ between standard samples and samples. Number of cycles: n, Efficiency standard samples: Estd, efficiency reference samples: Ers, Number of amplicons at cycle n: Nn, Number of amplicons at cycle zero: N0. When the two equations are divided by eachother it is seen that there is an 23-fold underestimation of the concentration when Estd = 2.0 and Ers = 1.8. From this calculation it is also evident that at higher cycle number the error in concentration determination is larger.
Similar articles
- Comparison of a new quantitative ompA-based real-Time PCR TaqMan assay for detection of Chlamydia pneumoniae DNA in respiratory specimens with four conventional PCR assays.
Apfalter P, Barousch W, Nehr M, Makristathis A, Willinger B, Rotter M, Hirschl AM. Apfalter P, et al. J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Feb;41(2):592-600. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.2.592-600.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12574252 Free PMC article. - Construction of an internal control for the detection of Chlamydia pneumoniae by PCR.
Ursi D, Ieven M, Van Bever HP, Goossens H. Ursi D, et al. Mol Cell Probes. 1998 Aug;12(4):235-8. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.1998.0180. Mol Cell Probes. 1998. PMID: 9727200 - Failure to detect Chlamydia pneumoniae DNA in cerebral aneurysmal sac tissue with two different polymerase chain reaction methods.
Cagli S, Oktar N, Dalbasti T, Erensoy S, Ozdamar N, Göksel S, Sayiner A, Bilgiç A. Cagli S, et al. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003 Jun;74(6):756-9. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.74.6.756. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12754346 Free PMC article. Review. - Polymerase chain reaction detection of Chlamydia pneumoniae in circulating white blood cells.
Boman J, Gaydos CA. Boman J, et al. J Infect Dis. 2000 Jun;181 Suppl 3:S452-4. doi: 10.1086/315609. J Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10839737 Review.
Cited by
- Use of pJANUS-02-001 as a calibrator plasmid for Roundup Ready soybean event GTS-40-3-2 detection: an interlaboratory trial assessment.
Lievens A, Bellocchi G, De Bernardi D, Moens W, Savini C, Mazzara M, Van den Eede G, Van den Bulcke M. Lievens A, et al. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Mar;396(6):2165-73. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-3346-z. Epub 2009 Dec 17. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20016879 Free PMC article. - Real-Time PCR Protocol for Detection and Quantification of Three Pathogenic Members of the Vibrionaceae Family.
Costa C, Ferreira GD, Simões M, Silva JL, Campos MJ. Costa C, et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Oct 18;10(10):2060. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10102060. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296336 Free PMC article. - The mRNA and protein expression of A-kinase anchor proteins 13 in human colorectal cancer.
Hu JK, Wang L, Li Y, Yang K, Zhang P, Chen XZ, Wang R, Zhou ZG. Hu JK, et al. Clin Exp Med. 2010 Mar;10(1):41-9. doi: 10.1007/s10238-009-0065-x. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Clin Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 19779964 - Isolation of Chlamydia pneumoniae from serum samples of the patients with acute coronary syndrome.
Petyaev IM, Zigangirova NA, Petyaev AM, Pashko UP, Didenko LV, Morgunova EU, Bashmakov YK. Petyaev IM, et al. Int J Med Sci. 2010 Jun 10;7(4):181-90. doi: 10.7150/ijms.7.181. Int J Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 20596362 Free PMC article. - Standardisation of data from real-time quantitative PCR methods - evaluation of outliers and comparison of calibration curves.
Burns MJ, Nixon GJ, Foy CA, Harris N. Burns MJ, et al. BMC Biotechnol. 2005 Dec 7;5:31. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-5-31. BMC Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16336641 Free PMC article.
References
- Grayston JT. Infections caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae strain TWAR. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;15:757–761. - PubMed
- Dowell SF, Peeling RW, Boman J, Carlone GM, Fields BS, Guarner J, Hammerschlag MR, Jackson LA, Kuo CC, Maass M, Messmer TO, Talkington DF, Tondella ML, Zaki SR. C. pneumoniae Workshop Participants. Standardizing Chlamydia pneumoniae assays: recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (USA) and the Laboratory Centre for Disease Control (Canada). Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:492–503. doi: 10.1086/322632. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources