Characterization of a Bacillus subtilis thermosensitive teichoic acid-deficient mutant: gene mnaA (yvyH) encodes the UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Characterization of a Bacillus subtilis thermosensitive teichoic acid-deficient mutant: gene mnaA (yvyH) encodes the UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase
Blazenka Soldo et al. J Bacteriol. 2002 Aug.
Abstract
The Bacillus subtilis thermosensitive mutant ts-21 bears two C-G-->T-A transitions in the mnaA gene. At the nonpermissive temperature it is characterized by coccoid cell morphology and reduced cell wall phosphate content. MnaA converts UDP-N-acetylglucosamine into UDP-N-acetylmannosamine, a precursor of the teichoic acid linkage unit.
Figures
FIG. 1.
Correction of the strain ts-21 mutations by subclones of the mnaA-gtaB region. Plasmids correcting or not correcting the thermosensitive phenotype are indicated by + or −, respectively. The map corresponds to the region previously designated orfX-gtaB (27). Plasmids p6309, p6311, p6312, p6328, and p6344 were previously described (27). pBS635 was obtained by cloning into pBAD-TOPO vector (Invitrogen) the PCR product extending from nucleotide 639 of lytR to nucleotide 43 of gtaB and generated on strain 168 (5) DNA.
FIG. 2.
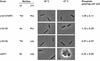
Cell morphology and cell wall phosphate content of mutant L6571 (ts-21) and its thermoresistant derivatives. Cells were grown for 20 h on LB agar plates at 30 and 47°C. Cell wall phosphate was determined for cells grown at 47°C. Residues at positions 69 and 374 in MnaA of each investigated strain are indicated. WT, wild type.
FIG. 3.
Alignment of the B. subtilis MnaA domains comprising Thr-69 and Pro-374 with their counterparts from different bacteria. All listed proteins are 43 to 64% identical to B. subtilis MnaA. The B. subtilis MnaA Thr-69 and Pro-374, as well as their equivalents in MnaA homologs, are boxed. Conserved residues are in boldface.
FIG. 4.
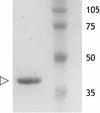
Coomassie blue-stained gel of the MnaA-His6 fusion protein obtained following overexpression in E. coli TOP10(pBS629). Cells were induced with 0.2% _l_-arabinose and grown for 5 h. Purified protein is indicated by the arrowhead. At a higher protein loading, a few minor bands could be detected. Molecular weight markers are in thousands.
FIG. 5.
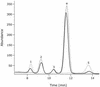
MnaA-His6 assay. High-pressure liquid chromatography analysis was performed on trifluoroacetic acid hydrolysis products of ManNAc (dotted line), purified recombinant MnaA-His6 protein with UDP-GlcNAc without incubation (dashed line), and purified recombinant MnaA-His6 protein with UDP-GlcNAc incubated for 2 h (solid line). Under experimental conditions used, the equilibrium of interconversion between UDP-GlcNAc and UDP-ManNAc is reached in less than 10 min (data not presented). Peaks 1 to 5 are indicated.
Similar articles
- Identification of an essential gene of Listeria monocytogenes involved in teichoic acid biogenesis.
Dubail I, Bigot A, Lazarevic V, Soldo B, Euphrasie D, Dupuis M, Charbit A. Dubail I, et al. J Bacteriol. 2006 Sep;188(18):6580-91. doi: 10.1128/JB.00771-06. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16952950 Free PMC article. - The tagGH operon of Bacillus subtilis 168 encodes a two-component ABC transporter involved in the metabolism of two wall teichoic acids.
Lazarevic V, Karamata D. Lazarevic V, et al. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Apr;16(2):345-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02306.x. Mol Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 7565096 - Biosynthesis of wall polymers in Bacillus subtilis.
Wyke AW, Ward JB. Wyke AW, et al. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1055-63. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1055-1063.1977. J Bacteriol. 1977. PMID: 405370 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- A structural basis for the allosteric regulation of non-hydrolysing UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerases.
Velloso LM, Bhaskaran SS, Schuch R, Fischetti VA, Stebbins CE. Velloso LM, et al. EMBO Rep. 2008 Feb;9(2):199-205. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401154. Epub 2008 Jan 11. EMBO Rep. 2008. PMID: 18188181 Free PMC article. - Chemical Genetic Analysis and Functional Characterization of Staphylococcal Wall Teichoic Acid 2-Epimerases Reveals Unconventional Antibiotic Drug Targets.
Mann PA, Müller A, Wolff KA, Fischmann T, Wang H, Reed P, Hou Y, Li W, Müller CE, Xiao J, Murgolo N, Sher X, Mayhood T, Sheth PR, Mirza A, Labroli M, Xiao L, McCoy M, Gill CJ, Pinho MG, Schneider T, Roemer T. Mann PA, et al. PLoS Pathog. 2016 May 4;12(5):e1005585. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005585. eCollection 2016 May. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27144276 Free PMC article. - Use of a bacteriophage lysin to identify a novel target for antimicrobial development.
Schuch R, Pelzek AJ, Raz A, Euler CW, Ryan PA, Winer BY, Farnsworth A, Bhaskaran SS, Stebbins CE, Xu Y, Clifford A, Bearss DJ, Vankayalapati H, Goldberg AR, Fischetti VA. Schuch R, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 10;8(4):e60754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060754. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593301 Free PMC article. - Wall teichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria.
Brown S, Santa Maria JP Jr, Walker S. Brown S, et al. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013;67:313-36. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155620. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24024634 Free PMC article. Review. - Suppressor Mutations Linking gpsB with the First Committed Step of Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis in Listeria monocytogenes.
Rismondo J, Bender JK, Halbedel S. Rismondo J, et al. J Bacteriol. 2016 Dec 13;199(1):e00393-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00393-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27795316 Free PMC article.
References
- Ames, B. N. 1966. Assay of inorganic phosphate, total phosphate and phosphatases. Methods Enzymol. 8:115-118.
- Araki, Y., and E. Ito. 1989. Linkage units in cell walls of gram-positive bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 17:121-135. - PubMed
- Archibald, A. R., I. C. Hancock, and C. R. Harwood. 1993. Cell wall structure, synthesis and turnover, p. 381-410. In A. L. Sonenshein, J. A. Hoch, and R. Losick (ed.), Bacillus subtilis and other gram-positive bacteria: biochemistry, physiology, and molecular genetics. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
- Briehl, M., H. M. Pooley, and D. Karamata. 1989. Mutants of Bacillus subtilis 168 thermosensitive for growth and wall teichoic acid synthesis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 135:1325-1334. - PubMed
- Burkholder, P. R., and N. H. Giles. 1947. Induced biochemical mutations in Bacillus subtilis. Am. J. Bot. 33:345-348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases